Unveiling the Protein Powerhouse: Greek Yogurt and Cottage Cheese
The quest to determine which food source has a higher protein content is a common concern for health-conscious individuals. Among the many options available, Greek yogurt and cottage cheese have emerged as popular choices, offering impressive nutritional profiles and versatility in various diets. This article delves into the comparison of Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, focusing on their protein content and other essential nutrients, to help you make an informed decision about which one suits your needs best.
Nutritional Profiles: Greek Yogurt and Cottage Cheese Compared
To effectively compare Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, it’s essential to examine their nutritional profiles side by side. Both food options are renowned for their protein content, but they also offer a wealth of other essential nutrients. Here’s a brief overview:
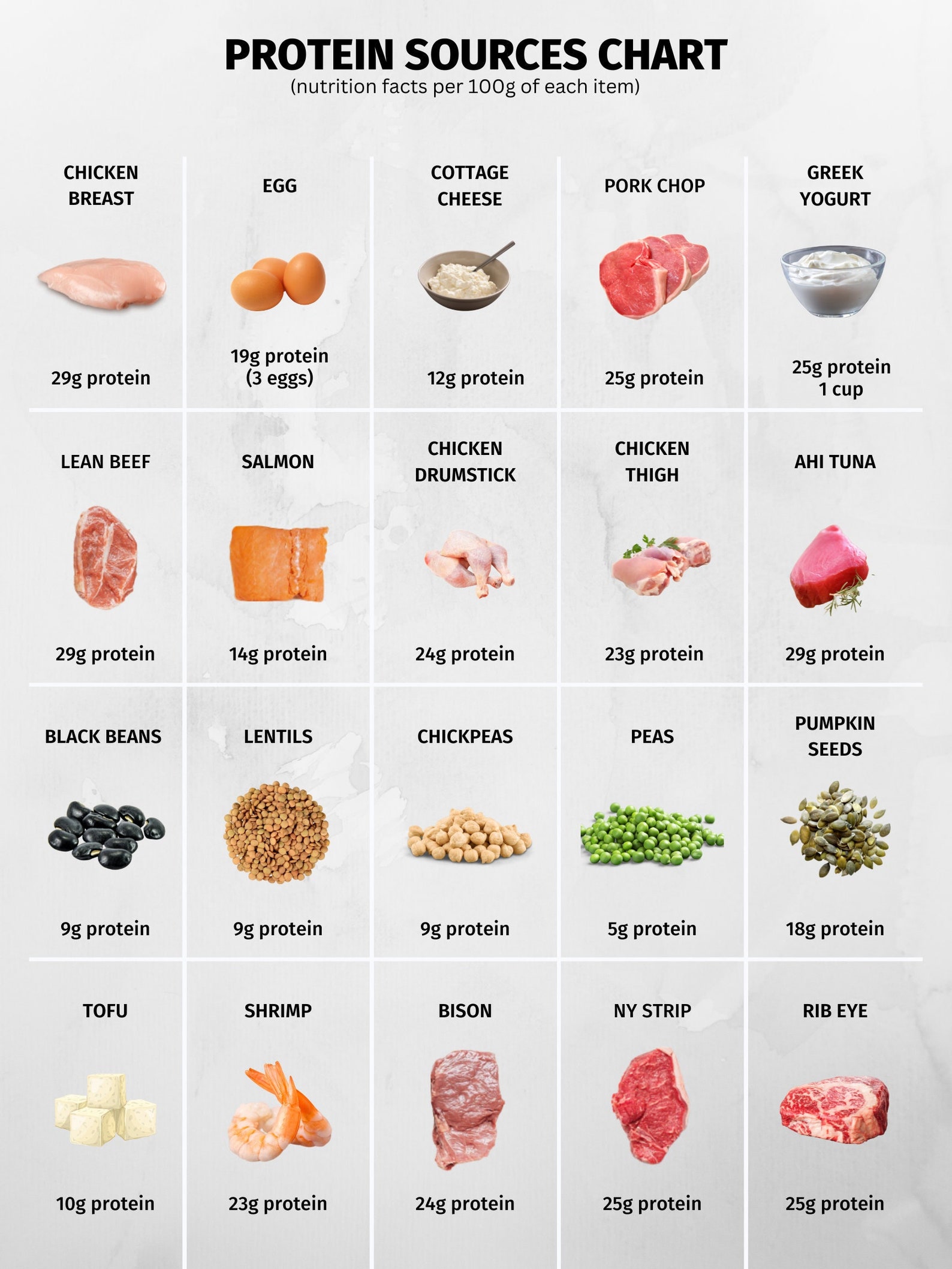
- Protein: Greek yogurt contains approximately 15-20 grams of protein per 170 grams (6 ounces), while cottage cheese offers around 18-25 grams per 225 grams (8 ounces).
- Calcium: Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are excellent sources of calcium, with Greek yogurt providing about 15-20% of the daily recommended intake (DRI) and cottage cheese offering approximately 20-30% per serving.
- Probiotics: Greek yogurt, especially those labeled as containing “live and active cultures,” can provide beneficial probiotics that support gut health.
- Fat: Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are available in various fat percentages, including regular, low-fat, and non-fat options. Choosing low-fat or non-fat versions can help reduce overall calorie and fat intake.
When comparing Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, it’s clear that both are protein-rich options with additional nutritional benefits. However, the protein content may vary depending on the specific product and type. In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into the protein content of each food source.
The Protein Punch: Understanding Protein Quality and Quantity
When discussing protein content in Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, it’s crucial to consider both the quantity and quality of protein. Protein quality refers to the protein’s ability to provide essential amino acids and its digestibility. Here’s what you need to know:
- Complete vs. Incomplete Proteins: Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are considered complete proteins, meaning they provide all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. This is in contrast to incomplete proteins, which lack one or more essential amino acids.
- Digestibility: The digestibility of a protein source is an indicator of how well the body can absorb and utilize the protein’s amino acids. Greek yogurt and cottage cheese have high digestibility rates, ensuring that the body can efficiently use the protein for various functions, such as muscle growth and repair.
- Amino Acid Composition: The specific amino acid composition of a protein source can influence its overall quality. Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese contain branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are particularly beneficial for muscle recovery and growth.
When comparing the protein quality of Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, both options offer complete proteins with high digestibility and beneficial amino acid compositions. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the protein content of each food source, focusing on the impact of different types and added ingredients.
Greek Yogurt: A Deep Dive into Its Protein Content
Greek yogurt is a popular choice for those seeking a protein-rich food option, and for a good reason. With its thick and creamy texture, Greek yogurt offers a higher protein content than traditional yogurt. Here’s a closer look at the protein content of Greek yogurt and the factors that can influence it:
- Types of Greek Yogurt: Greek yogurt is available in various types, including regular, low-fat, and non-fat options. Regular Greek yogurt typically contains the highest fat content, which can range from 5-10%, while low-fat and non-fat versions have reduced fat percentages. However, the protein content remains relatively consistent across these types, with regular Greek yogurt containing approximately 15-20 grams of protein per 170 grams (6 ounces), and low-fat and non-fat versions offering around 17-20 grams per serving.
- Added Ingredients: Greek yogurt can be found in various flavors, with added ingredients such as fruits, nuts, and granola. While these additions can enhance the taste and nutritional profile, they may also contribute to additional calories and sugar. When selecting Greek yogurt with added ingredients, opt for options with minimal added sugars and prioritize whole food additions, like fresh fruit or nuts.
In summary, Greek yogurt is a protein powerhouse, offering a consistent protein content across its different types. When incorporating Greek yogurt into your diet, be mindful of added ingredients to ensure you’re making the most nutritious choice. In the following section, we’ll explore cottage cheese’s protein advantages and the role of casein as a slow-digesting protein source.
Cottage Cheese: Dissecting Its Protein Advantages
Cottage cheese is another protein-rich food option that has gained popularity among health-conscious individuals. With its mild flavor and versatile texture, cottage cheese can be incorporated into various dishes. Here’s a closer look at cottage cheese’s protein advantages:
- Fat Percentages: Similar to Greek yogurt, cottage cheese is available in different fat percentages, including regular, reduced-fat, and non-fat versions. Regular cottage cheese typically contains around 4% fat, while reduced-fat and non-fat options have lower fat percentages. The protein content remains relatively consistent across these types, with regular cottage cheese offering approximately 18-25 grams of protein per 225 grams (8 ounces), and reduced-fat and non-fat versions containing around 20-25 grams per serving.
- Casein as a Slow-Digesting Protein Source: Cottage cheese is primarily composed of casein, a slow-digesting protein that provides a sustained release of amino acids into the bloodstream. This slow digestion can help promote muscle recovery and growth over an extended period, making cottage cheese an excellent choice for post-workout meals or snacks.
In summary, cottage cheese is a protein-rich food option, with various fat percentages available to suit different dietary needs. Its primary protein source, casein, offers a slow-digesting and sustained release of amino acids, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. In the following section, we’ll provide practical tips on incorporating Greek yogurt and cottage cheese into your diet.
How to Incorporate Greek Yogurt and Cottage Cheese into Your Diet
Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese can be easily incorporated into a balanced diet to help increase protein intake. Here are some practical tips, serving suggestions, and recipe ideas:
- Breakfast Boost: Incorporate Greek yogurt or cottage cheese into your morning routine by adding them to smoothies, oatmeal, or chia seed pudding. You can also enjoy them as a standalone breakfast option, topped with fresh fruit, nuts, or a drizzle of honey.
- Snack Time: Greek yogurt and cottage cheese make for satisfying and protein-rich snacks. Pair them with whole grain crackers, veggie sticks, or a handful of berries for a balanced and energy-sustaining option.
- Savory Dishes: Greek yogurt and cottage cheese can be used as a base for dips, such as tzatziki or ranch, or as a healthier substitute for sour cream in various recipes. They can also be incorporated into pasta dishes, casseroles, or stuffed vegetables for an extra protein boost.
- Meal Prep: Prepare Greek yogurt or cottage cheese-based salads, parfaits, or overnight oats in advance for a quick and convenient protein-packed meal or snack throughout the week.
By incorporating Greek yogurt and cottage cheese into your diet, you can enjoy the benefits of increased protein intake while also diversifying your nutritional profile. In the following section, we’ll summarize our findings and declare the protein champion, while emphasizing the importance of personal preferences and dietary needs in food choices.
The Verdict: Greek Yogurt vs. Cottage Cheese
After examining the nutritional profiles, protein content, and additional benefits of Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, it’s clear that both are excellent protein-rich food options. The protein champion will ultimately depend on individual dietary needs, preferences, and goals:
- Protein Quantity: When comparing protein content alone, Greek yogurt typically has a slight edge, offering around 15-20 grams per 170 grams (6 ounces) compared to cottage cheese’s 18-25 grams per 225 grams (8 ounces). However, the difference is minimal, and both options provide a substantial protein boost.
- Protein Quality: Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are complete proteins, offering all nine essential amino acids. Greek yogurt contains faster-digesting whey protein, while cottage cheese primarily consists of slow-digesting casein. Depending on your specific needs, one may be more suitable than the other.
- Nutritional Profile: Both options provide essential nutrients like calcium and probiotics (in Greek yogurt). However, cottage cheese tends to have a higher sodium content, while Greek yogurt may contain more sugar (especially in flavored varieties). Consider your overall dietary needs and preferences when choosing between the two.
- Dietary Needs and Preferences: Personal preferences, dietary restrictions, and goals should guide your decision. For example, those following a low-sodium diet may prefer Greek yogurt, while those seeking a slow-digesting protein source may opt for cottage cheese. Additionally, consider the taste, texture, and versatility of each option when incorporating them into your diet.
In conclusion, Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are both protein powerhouses, offering unique advantages and nutritional profiles. By understanding their differences and similarities, you can make an informed decision about which one best suits your dietary needs and preferences. Remember, personal preferences and dietary requirements should always be the primary factors in choosing the right protein-rich food option for you.
Maximizing Protein Intake: Additional Tips and Strategies
Now that you have a better understanding of the protein content and advantages of Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, consider incorporating these additional tips and strategies to maximize your protein intake:
- Variety: Consuming a variety of protein sources ensures that you receive a well-rounded mix of essential amino acids and other nutrients. In addition to Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, explore other protein-rich options like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Timing: To optimize muscle recovery and growth, aim to consume protein-rich foods or supplements within 30-60 minutes after exercise. This timeframe is often referred to as the “anabolic window” and can help enhance the body’s ability to repair and build muscle tissue.
- Combining Protein Sources: When consuming incomplete protein sources, pair them with complementary proteins to ensure you receive all nine essential amino acids. For example, combine rice with beans or peanut butter with whole-grain bread to create complete protein combinations.
- Protein Supplements: For those struggling to meet their daily protein needs through whole foods alone, consider incorporating protein supplements like whey or casein protein powder. These supplements can help increase protein intake, especially after workouts or when access to whole food sources is limited.
By incorporating these tips and strategies into your diet, you can maximize your protein intake and support your overall health and well-being. Remember, the choice between Greek yogurt and cottage cheese ultimately depends on your personal preferences and dietary needs. Both options offer unique advantages and nutritional profiles, making them valuable additions to a balanced and protein-rich diet.