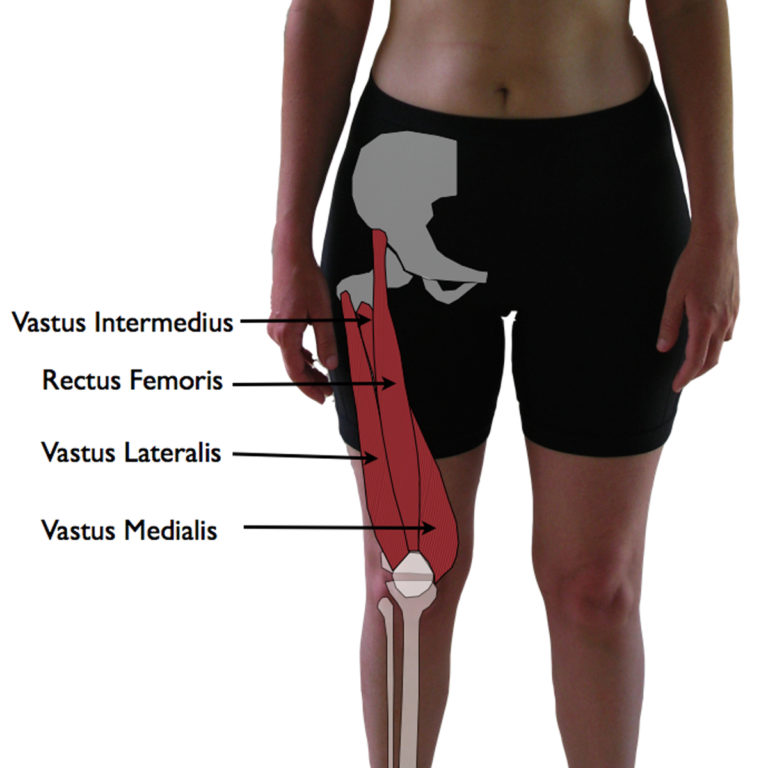
Identifying Quad Strain: Understanding the Symptoms
Quad strain is a common injury that affects the quadriceps muscle, a large muscle group located at the front of the thigh. This injury often occurs due to sudden acceleration, jumping, or changing direction, especially in sports activities. To effectively manage quad strain, it is crucial to understand its symptoms and differentiate it from other leg injuries.
The most common symptoms of quad strain include pain, swelling, and muscle stiffness. The pain may be sharp or dull and can worsen with movement or pressure. Swelling usually occurs around the affected area, while muscle stiffness can make it difficult to move the leg or maintain a normal range of motion. In some cases, bruising may also be present, depending on the severity of the injury.
It is essential to differentiate quad strain from other leg injuries, such as a pulled hamstring or a muscle contusion. A pulled hamstring typically causes pain at the back of the thigh, while a muscle contusion usually results in bruising and swelling without the sharp pain associated with quad strain. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and recovery, so seeking medical attention when in doubt is always recommended.
Immediate Response: First Aid Measures for Quad Strain
Taking swift action following a quad strain is essential to facilitate healing and minimize the risk of further damage. Implementing first aid measures is crucial to support the recovery process, especially during the initial stages of the injury.
The R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) method is a widely recommended first aid approach for quad strain. Rest is vital to prevent aggravating the injury, while ice helps reduce swelling and numb the pain. Compression with an elastic bandage can further limit swelling, and elevating the affected leg above the heart level can help minimize inflammation and accelerate recovery.
Pain management is another critical aspect of first aid measures for quad strain. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can provide temporary relief. However, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage and avoid relying solely on medication, as it may mask the severity of the injury and hinder proper healing.
In some cases, seeking medical attention might be necessary. If the pain is severe, swelling is significant, or mobility is limited, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. A healthcare provider can assess the injury, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options, including physical therapy or, in rare cases, surgery.
Restoring Mobility: Gentle Stretching and Exercises
As the initial swelling and pain subside, gradually reintroducing mobility to the affected quadriceps muscle becomes a key focus. Gentle stretching and exercise techniques can promote blood flow, reduce muscle stiffness, and maintain flexibility during the recovery process.
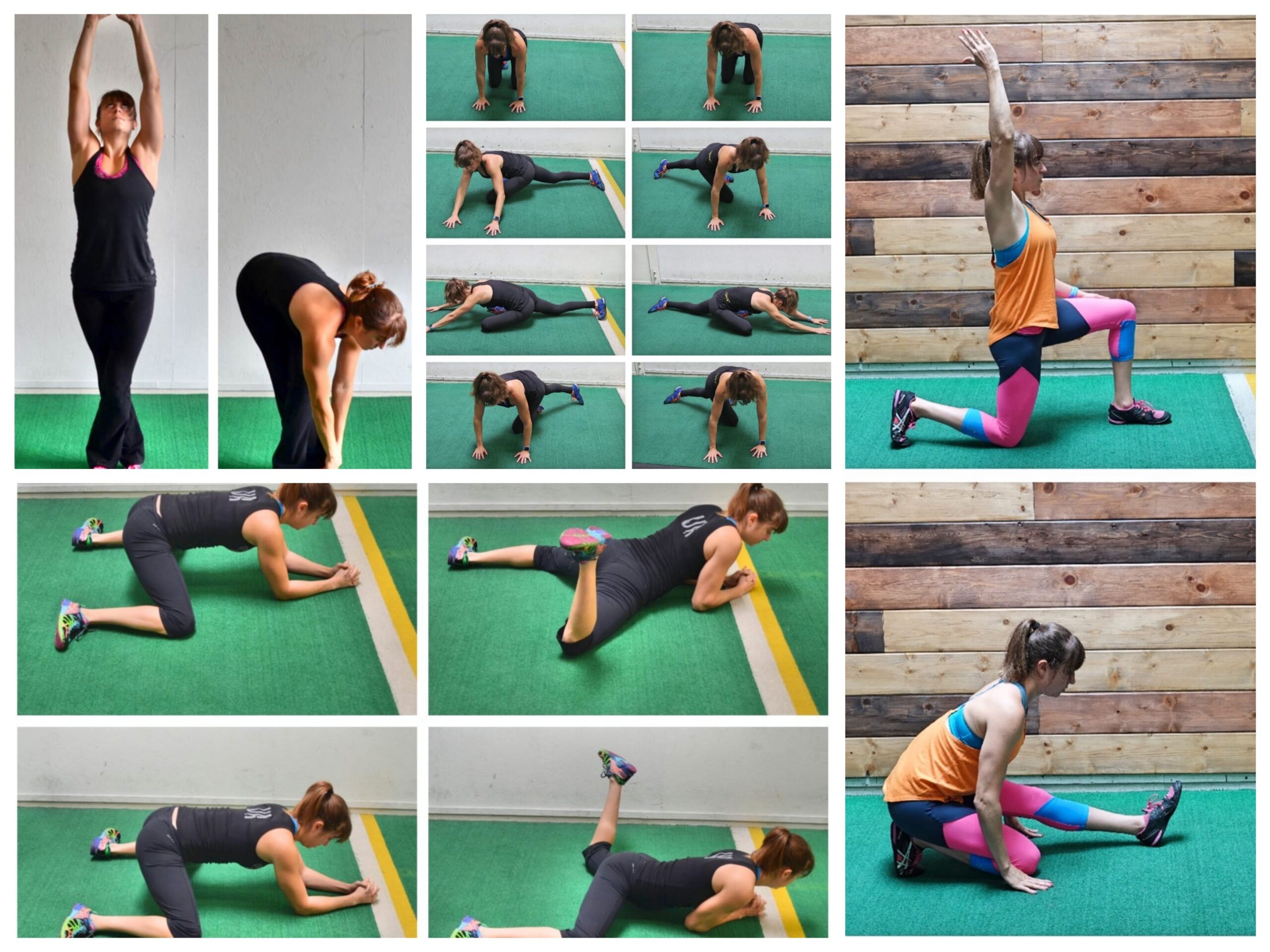
Begin with light stretching to alleviate muscle tension and improve range of motion. Focus on static stretches, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds without bouncing or causing discomfort. Examples of suitable stretches for a strained quad include the standing quad stretch, the kneeling lunge stretch, and the hamstring stretch. Perform these stretches 2-3 times a day, ensuring you warm up the muscles with a few minutes of light cardio before starting.
In addition to stretching, low-impact exercises can help restore strength and mobility to the quadriceps. Consider incorporating exercises such as gentle leg presses, mini squats, or heel slides into your routine. Perform these exercises with minimal resistance, focusing on proper form and control. Aim for 1-2 sets of 10-12 repetitions, 2-3 times a week, gradually increasing the intensity as your quad strain improves.
Strengthening the Quad: Progressive Resistance Training
Progressive resistance training plays a vital role in rebuilding quad strength and endurance following a strain. By gradually increasing the resistance, you can safely and effectively promote muscle healing and improve overall functionality.
Begin with isometric exercises, which involve contracting the muscle without moving the joint. Examples include wall sits, plank variations, and quad sets. Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, 2-3 times a week, ensuring you maintain proper form and control throughout each exercise.
As your quad strain improves, incorporate dynamic exercises that involve movement. Leg presses, mini squats, and heel slides with added resistance can help further strengthen the quadriceps. Start with light weights or resistance bands, focusing on controlled movements and proper form. Gradually increase the resistance as your strength improves, aiming for 2-3 sets of 10-12 repetitions, 2-3 times a week.
Remember to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard, too quickly. Progressive resistance training should be challenging but not painful. If you experience increased pain or discomfort during or after exercise, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Gradual Return to Physical Activity: A Step-by-Step Approach
A gradual return to physical activity is crucial to ensure a smooth and safe transition following a quad strain. Rushing back into sports or high-impact exercises too quickly can exacerbate the injury and hinder recovery.
Begin with light cardio activities, such as walking or cycling, to gently increase blood flow and promote healing. Aim for 10-15 minutes of light cardio, 2-3 times a week, gradually increasing the duration and intensity as your quad strain improves.
Next, incorporate low-impact strength training exercises, focusing on the quadriceps and surrounding muscle groups. Leg presses, mini squats, and heel slides with minimal resistance can help rebuild strength and endurance. Perform 2-3 sets of 10-12 repetitions, 2-3 times a week, allowing ample rest between sessions for muscle recovery.
As your quad strain continues to heal, gradually reintroduce sport-specific movements and drills. Start with basic techniques and progress to more complex movements, ensuring you maintain proper form and control. Listen to your body and adjust your training plan as needed, seeking professional guidance if necessary.
Remember that patience is key during the recovery process. Aim for consistent progress, rather than rapid improvement, to minimize the risk of reinjury and ensure a successful return to physical activity.
Preventing Future Quad Strain: Injury-Proofing Techniques
Implementing effective injury-proofing techniques can significantly reduce the risk of future quad strains. By focusing on proper warm-up and cool-down routines, maintaining flexibility, and addressing muscle imbalances, you can minimize the likelihood of recurring injuries.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares your muscles for physical activity, increasing blood flow and reducing the risk of injury. Begin with 5-10 minutes of light cardio, such as brisk walking or cycling, followed by dynamic stretches that mimic the movements of your chosen sport or activity. For quad-focused exercises, consider incorporating lunges, high knees, and leg swings into your warm-up routine.
A cool-down routine is equally important, as it helps your muscles recover and reduces the likelihood of soreness and stiffness. Finish your workout with 5-10 minutes of light cardio and static stretches that target the quadriceps and surrounding muscle groups. Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds, ensuring you feel a gentle pull but no pain.
Maintaining Flexibility
Regular stretching and flexibility exercises can help prevent quad strain by ensuring your muscles remain limber and supple. Aim to stretch daily, focusing on both dynamic and static stretches. Consider incorporating yoga or Pilates into your exercise routine to further improve flexibility and balance.
Addressing Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances, where one muscle group is stronger or more flexible than its opposing group, can contribute to quad strain. Regularly assess your muscle balance and address any imbalances through targeted strength training exercises. For example, if your quadriceps are stronger than your hamstrings, focus on exercises that strengthen the hamstrings, such as deadlifts and hamstring curls.
Nutritional Support for Quad Strain Recovery
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in promoting quad strain recovery, ensuring your muscles receive the necessary nutrients to heal and rebuild. Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals, while limiting processed foods and unhealthy fats.
Protein: The Building Block of Muscles
Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, making it a critical nutrient during the recovery process. Aim to consume 1.2-1.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. Include protein-rich foods in your diet, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Vitamins and Minerals: Supporting Muscle Healing
Vitamins and minerals are vital for muscle function, energy production, and overall health. Ensure your diet includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to meet your daily nutrient requirements. Particularly, focus on vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium, which support muscle healing and recovery.
Hydration: A Key Component of Recovery
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal muscle function and promoting recovery. Aim to drink at least 8-10 cups of water daily, increasing your intake if you engage in physical activity or live in a hot, dry climate. Additionally, consider consuming hydrating beverages, such as herbal tea or coconut water, to support your recovery.
Recovery-Boosting Foods and Supplements
Certain foods and supplements can aid in quad strain recovery. Consider incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids, into your diet to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, consider supplementing with branch-chain amino acids (BCAAs) or collagen peptides to support muscle repair and recovery.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
While self-care measures and at-home treatments can be effective in managing a strained quad, there are certain circumstances where professional medical attention is necessary. Consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms or conditions:
Persistent Pain
If pain persists or worsens despite rest, ice, compression, and elevation, it may be a sign of a more severe injury. A healthcare provider can assess your injury and recommend appropriate treatment options to alleviate pain and promote healing.
Limited Mobility
If you have difficulty walking, standing, or performing daily activities due to quad strain, seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can evaluate your injury and provide guidance on rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy to help restore mobility and function.
Signs of Infection
If you notice increasing redness, warmth, or swelling around the affected area, or if you develop a fever or chills, seek medical help immediately. These symptoms may indicate an infection, which requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Chronic or Recurring Injuries
If you have a history of quad strain or if your injury does not improve within a reasonable timeframe, consult a healthcare provider. A healthcare professional can help identify underlying issues, such as muscle imbalances or biomechanical problems, and provide personalized treatment and rehabilitation plans to prevent future injuries.
By understanding when to seek professional help, you can ensure a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment for your strained quad, promoting a swift and successful recovery.