Delving into the Concept: What is the Typical Women’s Height?
The term “average women’s height” refers to the statistical mean or median height of adult females within a specific population or demographic group. This measurement is often used as a benchmark for comparing the heights of individuals and assessing the distribution of heights across different populations. Understanding the average women’s height is crucial in various fields, including health, anthropology, and demographics, as it can provide valuable insights into factors such as genetics, nutrition, and socio-economic conditions.
The average women’s height can vary significantly across different populations and ethnicities due to a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and societal factors. For instance, women from populations with a history of adequate nutrition and healthcare tend to have taller average heights compared to those from populations with a history of malnutrition or limited access to healthcare. Moreover, the average women’s height can also be influenced by factors such as socio-economic status, education, and urbanization, further highlighting the importance of considering the broader context when examining this measurement.
As a key indicator of overall health and well-being, the average women’s height has garnered considerable attention from researchers and policymakers alike. By examining trends and variations in the average women’s height, it is possible to identify potential health disparities and inequalities, and develop targeted interventions to address these issues. Additionally, understanding the average women’s height can also provide valuable insights into broader population trends, such as changes in living standards, health outcomes, and societal development.
Exploring the Global Perspective: Women’s Height Distributions Worldwide
The global distribution of women’s height showcases significant variations across different countries and regions, reflecting the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and societal factors. For instance, women from countries with a history of adequate nutrition, healthcare, and socio-economic stability tend to have taller average heights compared to those from countries with a history of malnutrition, limited access to healthcare, or political instability.
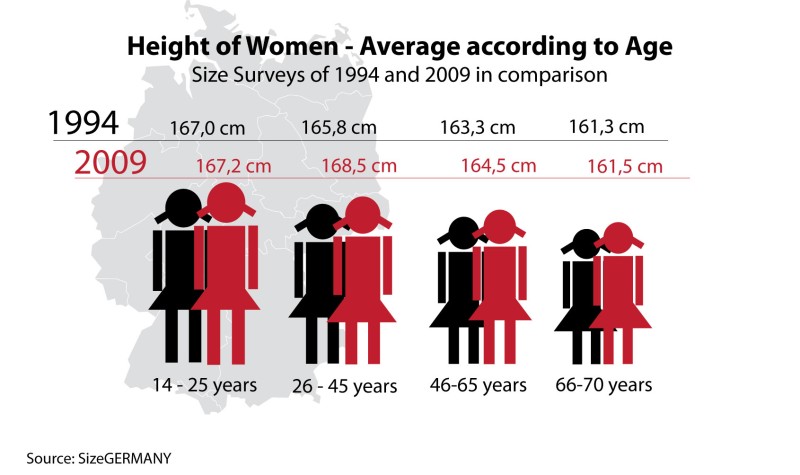
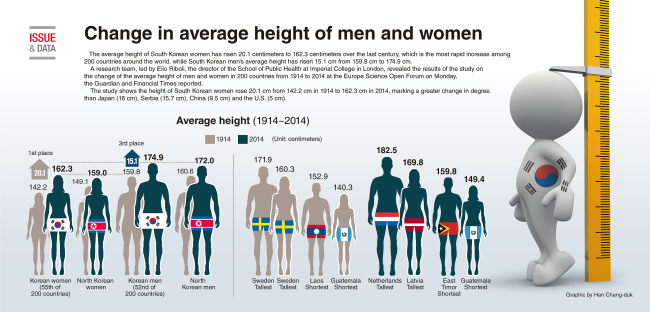
According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the average women’s height ranges from approximately 149 cm (4 feet 10 inches) in Guatemala to 171 cm (5 feet 7 inches) in the Netherlands. Other countries with relatively tall average women’s heights include Denmark, Finland, and Estonia, all of which have average heights above 168 cm (5 feet 6 inches). In contrast, countries with relatively short average women’s heights include India, China, and Indonesia, all of which have average heights below 158 cm (5 feet 2 inches).
Several factors contribute to these global variations in women’s height, including genetics, nutrition, and socio-economic conditions. For instance, women from populations with a history of adequate nutrition and healthcare tend to have taller average heights compared to those from populations with a history of malnutrition or limited access to healthcare. Additionally, factors such as socio-economic status, education, and urbanization can also influence women’s height, further highlighting the importance of considering the broader context when examining this measurement.
Understanding the global distribution of women’s height can provide valuable insights into broader population trends and health disparities. By examining variations in the average women’s height across different countries and regions, it is possible to identify potential health disparities and inequalities, and develop targeted interventions to address these issues. Additionally, understanding the global distribution of women’s height can also provide valuable insights into factors such as living standards, health outcomes, and societal development.
How to Measure Height Accurately: Best Practices and Common Mistakes
Measuring height accurately is crucial for obtaining reliable and consistent results, particularly when examining the average women’s height. To ensure accuracy, it is essential to follow standardized procedures and avoid common mistakes that can lead to measurement errors. Here, we outline the proper techniques for measuring height and provide tips for obtaining reliable results.
To measure height accurately, follow these steps:
- Remove shoes, heavy clothing, and any accessories that may interfere with height measurement.
- Stand with heels together, against a flat surface such as a wall or door frame.
- Ensure that the back of the head, shoulders, buttocks, and heels are all touching the flat surface.
- Keep the arms at the sides, and avoid flexing or bending them.
- Use a level or spirit level to ensure that the head is in a neutral position, neither tilted up nor down.
- Mark the position of the top of the head on the flat surface with a pencil or other non-permanent marker.
- Measure the distance from the marked point to the floor using a tape measure or ruler, ensuring that the measuring device is held vertically and in contact with the flat surface.
Common mistakes to avoid when measuring height include:
- Wearing heavy clothing or accessories that can add several centimeters to the measured height.
- Failing to maintain proper posture, such as standing with the shoulders slouched or the head tilted.
- Measuring from the wrong point, such as the top of the headpiece or the mid-point of the back, rather than the actual top of the head.
- Using an inaccurate or improperly calibrated measuring device, such as a flexible tape measure or a ruler that is not graduated in centimeters or inches.
By following these best practices and avoiding common mistakes, it is possible to obtain reliable and accurate height measurements for women, providing valuable insights into the average women’s height and its various implications.
The Evolution of Women’s Height: Historical Trends and Future Projections
Understanding the historical trends in women’s height is crucial for gaining insights into the factors that influence this measurement and predicting potential changes in future generations. Over time, various genetic, environmental, and societal factors have contributed to the evolution of women’s height, resulting in significant variations across different populations and ethnicities.
Historically, women’s height has been influenced by factors such as nutrition, healthcare, and socio-economic conditions. For instance, in populations with a history of malnutrition or limited access to healthcare, women tend to have shorter average heights compared to those from populations with a history of adequate nutrition and healthcare. Moreover, factors such as urbanization, education, and economic development can also influence women’s height, further highlighting the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors that shape this measurement.
According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the average women’s height has increased globally over the past century. For instance, in the United States, the average women’s height has increased from approximately 152 cm (5 feet) in the early 20th century to around 163 cm (5 feet 4 inches) today. Similarly, in Europe, the average women’s height has increased from approximately 157 cm (5 feet 2 inches) in the early 20th century to around 165 cm (5 feet 5 inches) today.
However, it is important to note that these trends may not continue indefinitely, and that various factors may influence the future evolution of women’s height. For instance, changes in nutrition, healthcare, and socio-economic conditions may impact women’s height in different ways, depending on the population and region. Additionally, the potential for epigenetic influences on height, such as the impact of environmental factors on gene expression, may also play a role in shaping the future evolution of women’s height.
In conclusion, the evolution of women’s height has been shaped by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and societal factors, resulting in significant variations across different populations and ethnicities. By understanding these trends and predicting potential changes in future generations, it is possible to develop targeted interventions to address health disparities and inequalities, and promote overall health, well-being, and height potential for women.
The Impact of Women’s Height on Health and Well-being: A Multidimensional Analysis
Understanding the relationship between women’s height and their health and well-being is crucial for promoting overall health and wellness. While the average women’s height can vary significantly across different populations and ethnicities, it is important to consider the potential advantages and disadvantages associated with different height ranges, and to provide evidence-based insights to debunk common stereotypes and misconceptions.
Physical Aspects: Women’s height can influence various physical aspects of health, including cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and musculoskeletal health. For instance, taller women may have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, while shorter women may have a higher risk of respiratory issues. Moreover, women’s height can also impact their musculoskeletal health, with taller women potentially having a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis or other joint-related issues.
Mental Aspects: Women’s height can also influence various mental aspects of health, including self-esteem, body image, and mental health. For instance, women who are significantly taller or shorter than their peers may experience lower self-esteem or body dissatisfaction, which can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety or depression. Moreover, women’s height can also impact their social interactions and relationships, with taller women potentially facing discrimination or bias in certain contexts.
Social Aspects: Women’s height can also influence various social aspects of health, including education, employment, and income. For instance, taller women may have an advantage in certain educational or professional contexts, as they may be perceived as more confident or competent. However, women who are significantly taller or shorter than their peers may also face discrimination or bias in certain contexts, which can impact their employment and income potential.
In conclusion, women’s height can influence various aspects of health and well-being, including physical, mental, and social factors. By understanding the potential advantages and disadvantages associated with different height ranges, and by providing evidence-based insights to debunk common stereotypes and misconceptions, it is possible to promote overall health, well-being, and height potential for women.
The Role of Genetics and Environment in Determining Women’s Height
Understanding the complex interplay between genetics and environment is crucial for gaining insights into the factors that determine women’s height. While genetics plays a significant role in determining height, environmental and societal factors can also influence this measurement, resulting in significant variations across different populations and ethnicities.
Genetic Factors: Genetic factors are estimated to account for approximately 60-80% of the variation in women’s height. These factors include the number and size of the bones in the body, as well as the production and regulation of growth hormones. Moreover, certain genetic variations have been associated with increased or decreased height, highlighting the potential for genetic influences on height.
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as nutrition, healthcare, and socio-economic conditions, can also influence women’s height. For instance, women who have access to adequate nutrition and healthcare during critical growth periods, such as childhood and adolescence, are more likely to reach their full height potential. Additionally, women who live in environments with clean air, safe water, and adequate sanitation are also more likely to have better health outcomes, including increased height potential.
Societal Factors: Societal factors, such as cultural norms, gender roles, and discrimination, can also impact women’s height. For instance, women who face discrimination or bias based on their height may experience lower self-esteem or body dissatisfaction, which can impact their overall health and well-being. Moreover, women who are expected to conform to certain cultural norms or beauty standards may also experience pressure to alter their height, either through cosmetic procedures or other means.
Epigenetic Factors: Epigenetic factors, such as the impact of environmental factors on gene expression, may also play a role in determining women’s height. For instance, women who experience trauma, stress, or other adverse experiences during critical growth periods may have altered gene expression, which can impact their height potential. Moreover, women who are exposed to certain environmental toxins or pollutants may also have altered gene expression, which can impact their overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, the complex interplay between genetics, environment, and societal factors determines women’s height. By understanding the relative contributions of these factors, and by considering the potential for epigenetic influences on height, it is possible to promote overall health, well-being, and height potential for women.
Strategies for Optimizing Women’s Health and Height Potential: A Holistic Approach
Understanding the various factors that influence women’s height and health is crucial for promoting overall well-being and optimizing height potential. By taking a holistic approach that addresses both genetic and environmental factors, women can improve their health, well-being, and height potential, regardless of their starting point.
1. Prioritize Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is crucial for promoting overall health and well-being, including height potential. Women should aim to consume a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Additionally, women should ensure that they are getting adequate amounts of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients for bone health and growth.
2. Engage in Regular Exercise: Regular exercise is essential for promoting overall health and well-being, including height potential. Women should aim to engage in a variety of physical activities, including cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Additionally, women should focus on exercises that promote good posture and spinal health, such as yoga, Pilates, and other core-strengthening exercises.
3. Address Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins, pollutants, and other harmful substances, can impact women’s health and height potential. Women should aim to minimize their exposure to these substances, and should take steps to promote a healthy and safe living environment. This may include using air and water filters, avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, and taking steps to reduce exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants.
4. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can impact women’s health and height potential, and can lead to a variety of negative health outcomes. Women should aim to manage stress through a variety of techniques, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and other relaxation techniques. Additionally, women should prioritize self-care and self-compassion, and should seek support from friends, family, or mental health professionals as needed.
5. Seek Genetic Counseling: While genetics plays a significant role in determining height, women who are concerned about their height potential or other genetic factors may benefit from seeking genetic counseling. Genetic counselors can provide information and guidance on genetic testing, risk assessment, and other factors that may impact women’s health and height potential.
In conclusion, by taking a holistic approach that addresses both genetic and environmental factors, women can optimize their health, well-being, and height potential. By prioritizing nutrition, exercise, environmental factors, stress management, and genetic counseling, women can improve their overall health and well-being, and can achieve their full height potential.