Understanding the Normal Heart Rate Range During Exercise
During exercise, the heart rate increases to supply more oxygen and nutrients to the working muscles. The normal heart rate range during exercise varies based on individual factors such as age, fitness level, and exercise intensity. For a healthy adult, the heart rate may double or even triple during intense exercise compared to resting rates. A common method to estimate target heart rate zones during exercise is to calculate 220 beats per minute (bpm) minus the individual’s age. This formula provides a rough estimate, and it is essential to consider personal differences and specific fitness levels.
How to Measure Your Heart Rate
Accurately monitoring your heart rate during exercise is crucial for understanding your cardiovascular response and ensuring that your workout remains within a safe and effective range. Various methods are available to measure your heart rate, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Manual counting, wearable devices, and smartphone apps are the most common techniques.
Manual counting: To measure your heart rate manually, locate your pulse either on your wrist (radial artery) or neck (carotid artery). Using your index and middle fingers, gently press on the artery and count the number of beats you feel in a 15-second interval. Multiply the result by four to obtain your beats per minute. This method is simple and free but may be less accurate and more time-consuming than other techniques.
Wearable devices: Heart rate monitors integrated into smartwatches, fitness trackers, or chest straps provide continuous and accurate heart rate measurements. These devices use either optical or electrical sensors to detect the heart rate. Optical sensors, typically found in wrist-worn devices, emit light through the skin to measure blood flow, while electrical sensors, commonly used in chest straps, detect the electrical signals generated by the heart. Wearable devices offer convenience and accuracy but may be more expensive than manual counting.
Smartphone apps: Several smartphone apps allow users to measure their heart rate using the device’s camera. These apps work by detecting subtle color changes in the user’s fingertip or face as blood flows through the capillaries. While these apps are generally inexpensive or free, their accuracy may vary depending on the app and the user’s device.
When selecting a heart rate measurement method, consider factors such as accuracy, convenience, and cost. Choosing a technique that suits your needs and preferences will help you monitor your heart rate effectively during exercise and ensure a safe and productive workout.
What Constitutes a High Heart Rate During Exercise?
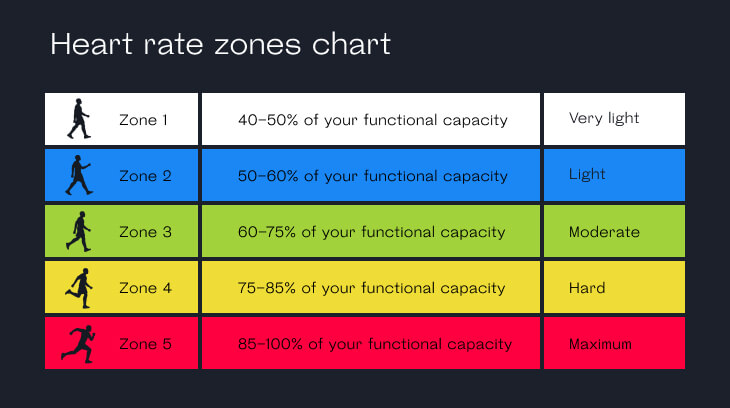
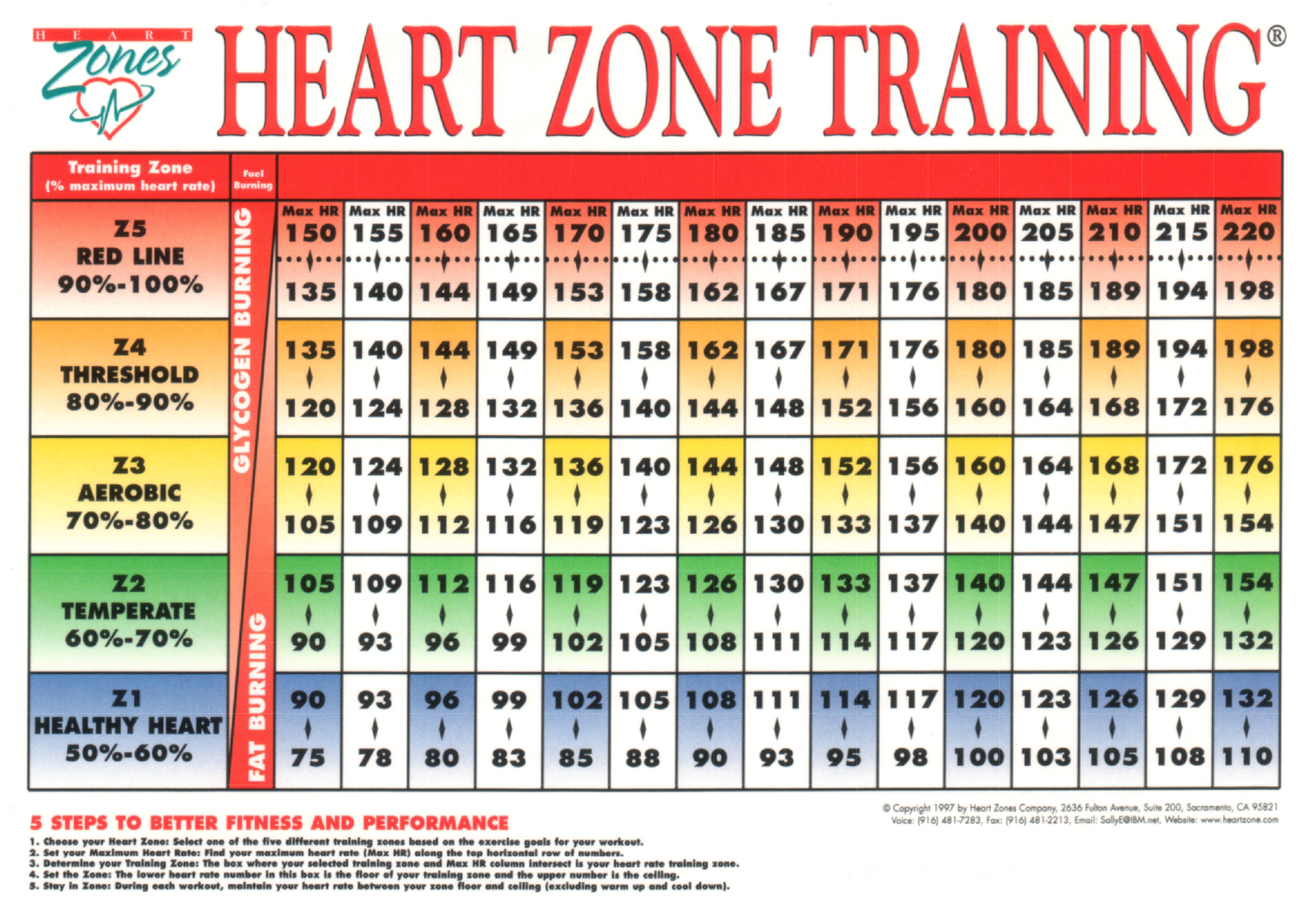
Understanding the upper limits of heart rate zones is essential for recognizing potentially excessive heart rates during exercise. The American Heart Association (AHA) identifies maximum heart rate as 220 beats per minute (bpm) minus an individual’s age. Within this maximum heart rate, various heart rate zones exist, each corresponding to different exercise intensities.
For most healthy adults, the following heart rate zones are generally accepted:
- Moderate-intensity exercise (50-70% of maximum heart rate): This zone is suitable for activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming at a comfortable pace. It is essential to maintain a conversation during these activities without feeling out of breath.
- Vigorous-intensity exercise (70-85% of maximum heart rate): Activities in this zone, such as running, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), or intense swimming, cause shortness of breath and make carrying on a conversation challenging.
Several factors can contribute to an elevated heart rate during exercise, including dehydration, stress, and medication. Dehydration reduces blood volume, causing the heart to work harder to maintain adequate circulation. Stress, whether physical or mental, can also increase heart rate, as can certain medications, such as stimulants or decongestants. It is essential to be aware of these factors and monitor heart rate accordingly to ensure a safe and effective workout.
Potential Risks and Consequences of High Heart Rates
Consistently high heart rates during exercise can have several health implications, including the risks of cardiovascular events, fatigue, and reduced performance. Recognizing the signs of excessive heart rates and addressing them is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and optimizing workout efficiency.
Cardiovascular events: Exercising at excessively high heart rates for extended periods can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially leading to cardiovascular events such as heart attacks or strokes. Although the risk is relatively low for healthy individuals, those with preexisting heart conditions should be particularly cautious when engaging in high-intensity exercise.
Fatigue: Training with consistently high heart rates can lead to increased fatigue, both during and after workouts. Over time, this can negatively impact motivation, exercise adherence, and overall performance. Monitoring and managing heart rate during exercise can help maintain energy levels and promote more efficient workouts.
Reduced performance: High heart rates during exercise can result in premature muscle fatigue, impairing overall performance. By maintaining a heart rate within the appropriate zones, athletes can optimize their training, ensuring that their workouts are both challenging and productive. Additionally, proper recovery and cross-training can help reduce the risk of overtraining and maintain optimal performance levels.
To mitigate the risks and consequences of high heart rates during exercise, it is essential to monitor heart rate regularly, employ appropriate training strategies, and consult with healthcare professionals when necessary. By doing so, individuals can enjoy the benefits of exercise while minimizing potential health risks.
Strategies to Lower Your Heart Rate During Exercise
Managing and reducing heart rate during exercise is essential for maintaining a safe and productive workout. Various techniques can help lower heart rate, including pacing, breathing exercises, and hydration management. Implementing these strategies can contribute to improved exercise efficiency, reduced fatigue, and enhanced overall performance.
Pacing
Proper pacing is crucial for maintaining a steady heart rate during exercise. Adjusting the intensity of your workout to match your fitness level and goals can help prevent excessive heart rate elevations. For example, when running or cycling, start with a slower pace and gradually increase the speed as your heart rate and breathing adjust to the activity. This approach allows your cardiovascular system to adapt to the exercise, reducing the risk of overexertion and excessive heart rate increases.
Breathing exercises
Deep, controlled breathing can help lower heart rate during exercise. By focusing on your breath and using techniques such as diaphragmatic or pursed-lips breathing, you can improve oxygen delivery to your muscles, reduce stress, and promote relaxation. These benefits can contribute to a more stable heart rate during physical activity.
Hydration management
Staying adequately hydrated before, during, and after exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy heart rate. Dehydration can cause the heart to work harder, increasing heart rate. Consuming water or electrolyte-rich beverages before, during, and after exercise can help maintain fluid balance, reduce heart rate, and support overall cardiovascular health.
By incorporating these strategies into your exercise routine, you can effectively manage and reduce your heart rate during physical activity. Remember to listen to your body, adjust your workout intensity as needed, and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any warning signs or symptoms related to high heart rate during exercise.
When to Consult a Medical Professional
Recognizing the warning signs and symptoms that necessitate medical attention is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health during exercise. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider when experiencing chest pain, dizziness, or severe shortness of breath, as these symptoms may indicate an underlying health issue or an excessive heart rate during physical activity.
Chest pain: Although mild chest pain or discomfort during exercise can be a normal response to increased heart rate and physical exertion, severe or persistent chest pain requires immediate medical attention. Chest pain could be a sign of a cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack, or another underlying health condition. If you experience chest pain during or after exercise, seek medical help promptly.
Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy during exercise can be a symptom of various factors, including dehydration, low blood sugar, or an excessive heart rate. While occasional dizziness may not be a cause for concern, frequent or severe episodes may indicate an underlying health issue. If dizziness persists or worsens during exercise, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Severe shortness of breath: While it is normal to experience some shortness of breath during intense exercise, severe or worsening shortness of breath can be a sign of a problem. This symptom may indicate an excessive heart rate, asthma, or another underlying health condition. If you experience severe shortness of breath during or after exercise, consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
By being aware of these warning signs and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can help ensure your safety and maintain a healthy heart rate during exercise. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals can also help identify and manage any underlying health issues that may contribute to excessive heart rates during physical activity.
Personalizing Your Exercise Program Based on Heart Rate
Tailoring exercise programs to individual heart rate zones can help maximize workout efficiency, support fitness goals, and minimize the risk of excessive heart rates during physical activity. By understanding the relationship between heart rate and exercise intensity, individuals can create personalized workout plans that consider personal fitness levels, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
Establishing heart rate zones
To personalize your exercise program, first, determine your heart rate zones based on your age, resting heart rate, and maximum heart rate. The most common method for calculating maximum heart rate is 220 minus your age. From there, you can establish various heart rate zones, such as warm-up, fat-burning, cardio, and anaerobic zones, each corresponding to different exercise intensities.
Considering personal factors
When personalizing your exercise program based on heart rate, consider factors such as fitness level, medical history, and lifestyle. For instance, individuals with lower fitness levels or chronic health conditions may need to exercise at lower heart rate zones to minimize the risk of excessive heart rates and related complications. Conversely, experienced athletes may require higher heart rate zones to challenge their cardiovascular system and achieve their fitness goals.
Setting fitness goals
Incorporate heart rate zones into your fitness goals by adjusting exercise intensity accordingly. For example, if your goal is to improve cardiovascular endurance, focus on exercises that keep your heart rate within the cardio or anaerobic zones for extended periods. If your aim is to burn fat, concentrate on exercises that maintain your heart rate within the fat-burning zone.
Monitoring and adjusting
Regularly monitor your heart rate during exercise to ensure you are training within the appropriate heart rate zones. Utilize wearable devices, smartphone apps, or manual counting to track your heart rate and make adjustments as needed. Over time, you may find it necessary to adjust your heart rate zones based on changes in fitness level, medical history, or lifestyle factors.
By personalizing your exercise program based on heart rate zones, you can optimize your workouts, enhance overall performance, and minimize the risk of excessive heart rates during physical activity. Regularly reassess your heart rate zones and adjust your workout routine as needed to maintain a safe and effective exercise program.
Maintaining a Balanced Exercise Program
Incorporating a variety of exercises and intensities into your workout routine is essential for promoting overall cardiovascular health and well-being. By regularly challenging your heart and cardiovascular system through diverse activities, you can minimize the risk of excessive heart rates during exercise and optimize your fitness gains.
Cross-training
Cross-training involves participating in various exercises and activities to improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of injury. By incorporating cross-training into your workout routine, you can challenge your heart rate in different ways, promoting cardiovascular adaptations and minimizing the potential for excessive heart rates during specific exercises.
Incorporating interval training
Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with lower-intensity recovery periods. This approach can help improve cardiovascular fitness, increase caloric expenditure, and reduce the risk of excessive heart rates during exercise. By adjusting the intensity and duration of the intervals, you can create a challenging and balanced workout tailored to your fitness level and heart rate zones.
Including low-impact exercises
Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, or using elliptical machines, can help reduce the stress on joints and minimize the risk of injury. These activities can also provide a valuable alternative for individuals with chronic health conditions or those experiencing excessive heart rates during high-impact exercises.
Prioritizing recovery
Adequate recovery is crucial for maintaining a balanced exercise program and minimizing the risk of excessive heart rates during physical activity. Schedule rest days between intense workout sessions, allowing your body to recover and rejuvenate. Implementing active recovery techniques, such as light stretching, walking, or yoga, can further support cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
By maintaining a balanced exercise program that incorporates various exercises, intensities, and recovery techniques, you can promote overall cardiovascular health, minimize the risk of excessive heart rates during exercise, and optimize your fitness journey.