Gauging Your Ideal Exercise Intensity: The Basics
Understanding what a good heart rate when working out is crucial for maximizing the benefits of physical activity while minimizing risks. Heart rate serves as a vital indicator of exercise intensity, reflecting how hard the cardiovascular system is working. By monitoring heart rate during workouts, individuals can effectively gauge whether they are exercising at an appropriate level. This measurement is essential for optimizing training results and ensuring safety. The heart’s rhythm changes in response to physical exertion, differentiating between its state of rest and work. A resting heart rate, typically measured when the body is at ease, provides a baseline. In contrast, a working heart rate reflects the cardiovascular system’s activity during physical exercise. It’s important to understand that a heart rate that is appropriate during a low intensity activity like a light walk will not be the same as the heart rate expected during a more intense activity like a run, and monitoring these changes is vital for creating a safe and effective exercise program. A good heart rate when working out will vary greatly based on the fitness goals and the exercise being performed. These changes in heart rate are important factors that help determine the level of effort being exerted by the body. Monitoring these metrics helps to tailor workouts to individual fitness goals and ensures that exercise is both beneficial and safe. While a good heart rate when working out is not static, understanding the difference between a resting heart rate and a working heart rate sets the stage for a deeper dive into understanding how to monitor heart rate effectively. This fundamental understanding of the relationship between exercise intensity and heart rate is the first step towards optimizing workout routines.
How to Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
Determining what a good heart rate when working out involves understanding your maximum heart rate (MHR) and then calculating your target heart rate zones. A common method to estimate MHR is by subtracting your age from 220. For instance, a 30-year-old would have an estimated MHR of 190 beats per minute (220 – 30 = 190). This number serves as a starting point for establishing your individual exercise intensity levels. Once you have your estimated MHR, you can calculate your target heart rate zones based on percentages of that MHR. Generally, these zones are categorized as moderate, vigorous, and peak. The moderate-intensity zone typically ranges from 50% to 70% of your MHR. This zone is ideal for activities like brisk walking or light jogging. The vigorous-intensity zone, often between 70% and 85% of MHR, is suitable for activities such as running, cycling, and high-intensity training. Finally, the peak zone, which is between 85% and 100% of MHR, is generally reserved for very short bursts of high-intensity exercise that are beneficial for advanced athletes. For example, a 40-year-old with an estimated MHR of 180 would have a moderate target zone ranging from 90 to 126 beats per minute (180 x 0.50 = 90, 180 x 0.70 = 126), a vigorous zone ranging from 126 to 153 beats per minute (180 x 0.70 = 126, 180 x 0.85= 153), and a peak zone ranging from 153 to 180 (180 x 0.85 = 153, 180 x 1 = 180). These target zones are guidelines, and they can vary based on individual fitness levels and goals. It’s also crucial to acknowledge that the MHR calculation is an estimation and may not be perfectly accurate for every individual. Furthermore, it’s extremely important that individuals, especially those with pre-existing health conditions, seek guidance from a healthcare professional before beginning an exercise program or trying to determine what a good heart rate when working out is for them. This consultation will help ensure that the exercise intensity is safe and appropriate for their health status. Consulting with a healthcare professional allows for a more personalized approach in determining a safe and effective heart rate strategy for exercising based on individual needs and health conditions.
Understanding Different Heart Rate Zones and Their Benefits
Understanding heart rate zones is crucial for optimizing workouts and achieving fitness goals. Different zones correspond to different intensities and offer distinct physiological benefits. Knowing what a good heart rate when working out is depends largely on which zone you’re targeting. The most commonly discussed zones are fat-burning, cardio, and peak performance zones, each demanding different levels of exertion and yielding unique advantages. The fat-burning zone, generally considered 50-70% of your maximum heart rate (MHR), is ideal for improving cardiovascular health and burning fat efficiently. Workouts in this zone are typically low to moderate intensity, such as brisk walking or cycling at a comfortable pace. Sustained activity in this zone can lead to significant improvements in endurance and overall fitness, helping to answer the question, “what a good heart rate when working out” for those aiming for weight management and improved cardiovascular health. It’s important to note that while this zone is effective for fat burning, it doesn’t necessarily lead to the most efficient calorie burn per unit of time.
The cardio zone, ranging from 70-80% of MHR, pushes the body into a more intense cardiovascular workout. Activities like jogging, swimming laps, or a spin class fall into this range. Working in this zone enhances cardiovascular fitness, increases endurance, and helps improve lung capacity. Determining what a good heart rate when working out is in this zone requires finding a challenging but sustainable pace. This range is a sweet spot for many individuals looking to improve overall cardiovascular health and increase their fitness levels. Focusing on heart rate in this zone ensures the workout remains effective, pushing the cardiovascular system without becoming overly strenuous.
The peak performance or anaerobic zone (80-90% of MHR) is reserved for high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or vigorous activity. This zone is characterized by short bursts of intense exertion followed by periods of recovery. Examples include sprinting, intense weightlifting sessions, or high-intensity circuit training. While the effort is significantly higher and determining what a good heart rate when working out is requires a careful approach, this zone maximizes calorie burn and enhances both cardiovascular and muscular strength. However, this intensity should be approached cautiously and gradually increased as fitness improves to avoid injury or overtraining. It is extremely important to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too far, especially when initiating high-intensity workouts.
Beyond these main zones, some individuals also include an active recovery zone (below 50% MHR) for light activities like walking, stretching, or yoga, assisting with recovery and reducing muscle soreness. The choice of heart rate zone depends greatly on individual fitness levels, training goals, and personal preferences. A marathon runner will likely spend more time in lower heart rate zones than a competitive weightlifter. Understanding your target heart rate zones is key to designing effective and safe workouts tailored to your specific needs and aspirations. Knowing what a good heart rate when working out is will contribute significantly to your training’s success and overall well-being. This personalized approach ensures both efficiency and safety, optimizing fitness progress without compromising health.
Heart Rate Variability: A Deeper Look
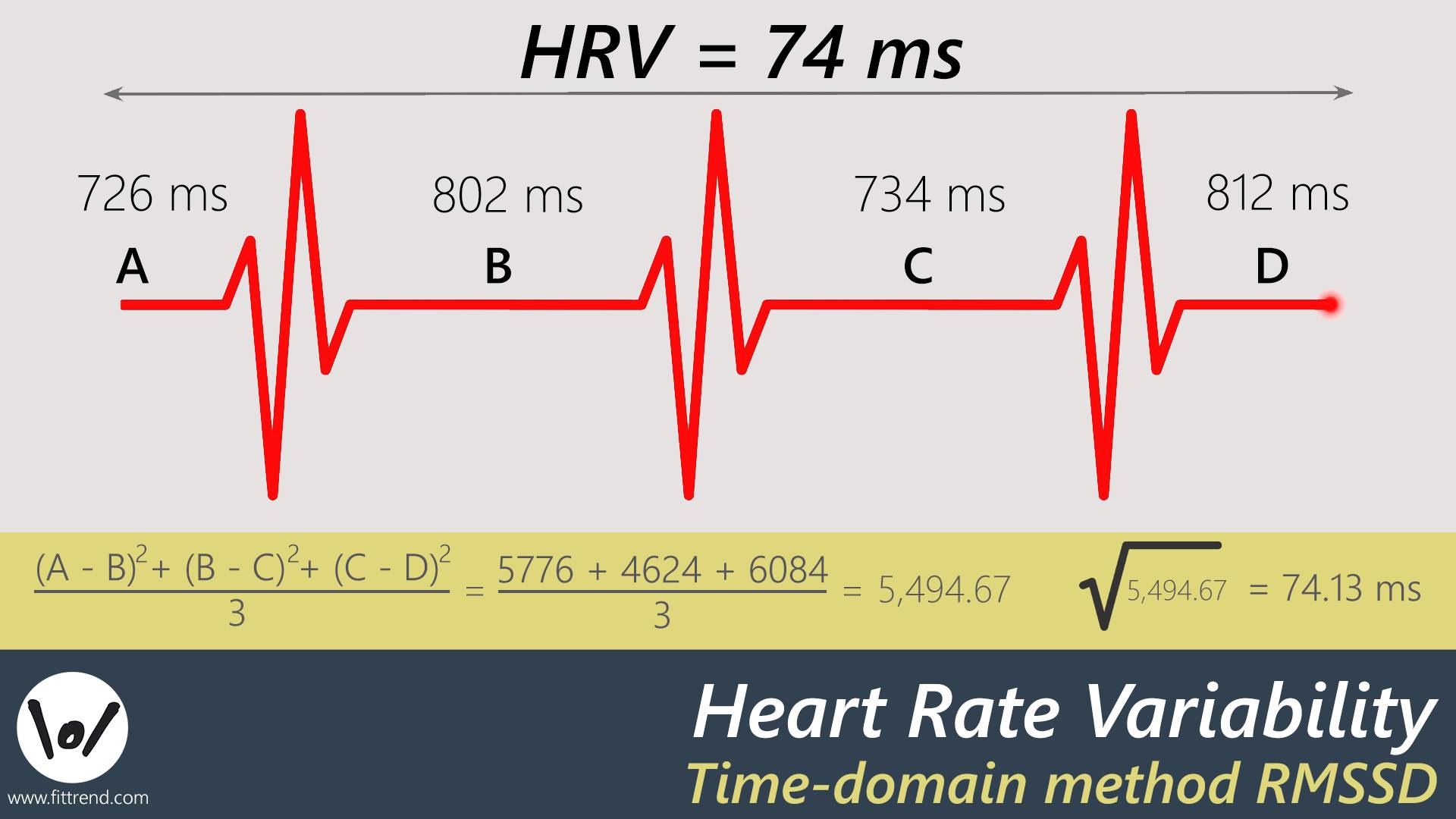
Heart rate variability (HRV) offers a more nuanced perspective on cardiovascular health and recovery, moving beyond the simple measure of heart rate. HRV refers to the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. It’s not merely about how fast your heart is beating, but also about the consistency of those beats. A higher HRV generally indicates a healthier, more resilient cardiovascular system capable of adapting to various stressors. When the body is in a state of rest and recovery, the variability between heartbeats tends to be greater, reflecting the parasympathetic nervous system’s influence. Conversely, during stress or exertion, HRV tends to decrease, indicating the dominance of the sympathetic nervous system. Understanding HRV is crucial because it provides insights into the body’s readiness to handle physical demands. A consistently low HRV can suggest overtraining, insufficient recovery, or underlying health concerns, whereas a healthy, fluctuating HRV suggests the body is responding well to training and stressors. To monitor HRV, many utilize fitness trackers, smartwatches, or dedicated HRV apps, which record the intervals between heartbeats and present a variety of metrics that help users understand their cardiovascular health. The data from these devices can be incredibly valuable for tailoring workout plans to match the body’s readiness. For example, if HRV is low one day, it might be better to take it easy, while a high HRV could indicate it’s a good day for a high-intensity workout. Interpreting HRV data, however, isn’t always straightforward; it’s important to track the trends over time and, if necessary, to seek guidance from healthcare or fitness professionals who can provide context and advice. It’s important to understand what a good heart rate when working out is, but understanding HRV also helps to adjust exercises based on the body’s readiness to perform. HRV can provide a unique insight into when to push the body and when to take a step back. By incorporating HRV data, individuals can make more informed decisions about their workouts, helping to avoid overtraining and maximize their fitness gains, making it an important factor for determining what a good heart rate when working out should be, along with other measurements and factors.
Factors That Affect Your Heart Rate During Exercise
Numerous elements can influence what a good heart rate when working out should be, and understanding these factors is crucial for effective and safe training. Age is a primary determinant; as individuals age, their maximum heart rate tends to decrease, thus affecting target heart rate zones. An individual’s fitness level also plays a significant role. Those who are more physically fit typically exhibit a lower resting heart rate and may experience a less dramatic increase in heart rate during exercise, compared to individuals who are less active. This difference emphasizes the importance of personalized heart rate monitoring to understand what a good heart rate when working out is for each individual. Hydration status is another key factor; dehydration can cause the heart to work harder, leading to an elevated heart rate during physical activity. Similarly, sleep quality has a notable impact; inadequate sleep can increase resting heart rate and affect how the heart responds to exertion. Poor sleep can contribute to a higher heart rate when working out than what would otherwise be normal for an individual. Stress, whether physical or mental, can also elevate heart rate, making it essential to manage stress levels, especially before physical activity. Medications can also affect heart rate; certain medications can either increase or decrease heart rate, highlighting the need to be mindful of these effects during workouts. External conditions, such as temperature and altitude, also exert an influence. High temperatures can cause the heart rate to increase as the body works harder to regulate its internal temperature. Exercising at high altitudes can lead to a higher heart rate due to lower oxygen levels in the atmosphere. Individual responses to these factors can vary significantly. It is essential to understand that what a good heart rate when working out is for one person might not be the same for another. Therefore, paying close attention to one’s body signals and adjusting the intensity of workouts accordingly is essential. This personalized understanding of heart rate, which considers the interplay of these influencing factors, will ensure both the effectiveness and safety of any exercise regimen. These various factors highlight the dynamic nature of heart rate and why it’s important to take a holistic view of well-being when monitoring what a good heart rate when working out is. Listening to the body is the single best piece of advice, and if a person is experiencing unusual heart rate responses, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Utilizing Fitness Trackers: Garmin and Fitbit Options for Heart Rate Monitoring
Garmin and Fitbit devices stand out as popular choices for individuals seeking to monitor their heart rate during physical activity. These wearable technologies provide a convenient way to track various aspects of fitness, with heart rate monitoring being a key feature. Garmin devices often cater to more serious athletes, offering a wide range of metrics and advanced features, such as detailed workout analysis and GPS tracking. Users can typically view their real-time heart rate, heart rate zones, and performance data directly on the device or through a connected smartphone app. This allows for precise adjustments to workout intensity, ensuring that the user is working within the desired heart rate zone. What a good heart rate when working out is a central question for many users and these trackers aim to help find the answer. Fitbit, on the other hand, generally focuses on a broader user base with an emphasis on overall wellness. Fitbit devices monitor heart rate, track steps, sleep patterns, and offer insights into daily activity levels. While they may not provide as many advanced performance metrics as some Garmin models, they offer a more user-friendly interface and are well-suited for those who are new to fitness tracking or who prioritize overall health. In addition to Garmin and Fitbit, there are many other options for heart rate tracking including chest straps, smartwatches from other brands, and even some phone apps. Chest straps, while not wearable in the same sense as a smartwatch, are known for their accuracy and are often preferred by individuals seeking precise heart rate data. Smartwatches from brands like Apple and Samsung also incorporate heart rate sensors, offering features similar to those found in fitness trackers. Phone apps that rely on the phone camera and flash can also offer estimates of heart rate, though their accuracy may vary. Each option comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. Wearable tech, like Garmin and Fitbit, offer convenient, real-time data, but can sometimes have issues with accuracy, especially if not worn correctly. Chest straps provide excellent accuracy but may be less comfortable to wear for extended periods. Smartwatches, while convenient, often have shorter battery life compared to simpler fitness trackers. The key is finding a device or system that fits the user’s individual needs, goals and what a good heart rate when working out means for them. These tracking technologies offer a wealth of data, empowering individuals to take more control of their exercise routines, and make informed decisions based on their specific heart rate readings, while remembering that individual experiences may vary.
Monitoring Your Heart Rate for Optimal Training
Effective heart rate monitoring during workouts is essential for maximizing fitness gains and preventing overexertion. To accurately track heart rate, one must first ensure proper use of a heart rate monitor. Whether using a chest strap or a wrist-based device, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for placement and wear. A snug fit is crucial for consistent readings. During the workout, regularly check the monitor display to observe real-time heart rate data. Understanding how the heart rate responds to varying levels of exertion is key to gauging workout intensity. If a target zone is established, adjust workout intensity accordingly. For instance, if aiming for the cardio zone but the heart rate is consistently lower than expected, one may need to increase the intensity through a greater range of motion or added resistance. Conversely, if the heart rate is consistently exceeding the target zone, slow down or take a brief break to allow the heart rate to return to the desired range. One should gradually increase the intensity of workouts over time. Attempting too much too soon increases the risk of injury and burnout. A progressive approach allows the cardiovascular system to adapt, improving fitness levels safely and sustainably. There are multiple factors that influence the answer to the question of what a good heart rate when working out is, which means individual needs should always be the priority. Listening to the body’s cues is equally important. If experiencing excessive fatigue, dizziness, or shortness of breath, one must slow down or stop exercising altogether. Heart rate monitoring should serve as a guide, not a rigid rulebook. By paying attention to both heart rate data and overall physical sensations, one can fine-tune workouts to make them safe, effective, and enjoyable. Understanding what a good heart rate when working out means requires a balanced approach to physical exertion. As one becomes more familiar with the body’s responses to exercise, one can make more informed decisions about training intensity, which helps to optimize workout results. Also, for effective training, one should take note of how fast the heart rate drops after exercising; this, in itself, is a measure of fitness and cardiovascular health. By using a heart rate monitor correctly, learning how the body responds to exercise, and gradually increasing intensity, one is much more likely to achieve training goals while ensuring a safe workout regime. What a good heart rate when working out depends on multiple factors, and having that data on hand during exercise is key. Understanding how to interpret the real time feedback allows for a more personalized approach to fitness.
When To Seek Professional Advice Regarding Heart Rate
Knowing when to seek professional advice about heart rate during exercise is crucial for maintaining safety and maximizing workout effectiveness. It is important to be aware of potential warning signs that indicate a need for medical consultation. If an individual experiences unusual heart rate responses to exercise, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. This may include a heart rate that is excessively high or low for the level of exertion, or a heart rate that takes an unusually long time to return to normal after exercise. Irregular heartbeats, also known as arrhythmias, during or after physical activity warrant immediate medical attention. These can manifest as palpitations, fluttering sensations, or skipped beats. Chest pain, even mild discomfort, should never be ignored, as it could be an indicator of underlying cardiovascular issues. Similarly, dizziness, lightheadedness, or shortness of breath during exercise are reasons to seek professional guidance. These symptoms could be signs that the heart is not effectively pumping blood or receiving enough oxygen. It’s vital to consider personal medical history, and people with pre-existing conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure should have personalized advice on what a good heart rate when working out should be. Healthcare professionals can provide tailored recommendations for target heart rate ranges and workout intensity. It’s important to not only understand what a good heart rate when working out should be, but also to recognize that individual responses to exercise can vary greatly, making professional advice essential for those with specific health considerations. Furthermore, having regular checkups and discussing any concerns about heart rate with a doctor is a preventive measure that can help identify and manage potential problems before they escalate. Open communication with healthcare professionals about heart rate responses, particularly during physical activity, enables proactive adjustments to exercise routines for optimal well-being. Understanding what a good heart rate when working out means to you in the context of your overall health requires collaboration with a medical expert who can provide personalized insights. Remember that the goal is to optimize your workout in a safe and effective way, and knowing when to get professional advice about heart rate will enable you to achieve that goal. Seeking timely medical advice is not a sign of weakness; it demonstrates a commitment to safe and effective fitness practices, and that will help clarify what a good heart rate when working out looks like for you.