Plyometric Exercises: Unleashing Athletic Potential
The realm of sports and athletics has always been driven by the pursuit of peak physical performance. One method that has proven instrumental in this is “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance”. These exercises, often referred to as plyos, involve quick, powerful movements that aim to increase speed and power.
Plyometric training involves the Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) where a muscle is quickly stretched before being contracted, providing an explosive reaction. By doing so, plyometric exercises help to enhance the muscle’s contractile response, improving overall athletic performance.

For an athlete, the benefits of plyometric exercises are manifold. They help to improve speed, boost strength, increase power, and enhance agility. These are all crucial components for athletic success, regardless of the sport in question. A sprinter can improve their start off the blocks, a basketball player can enhance their jump shot, or a football player can increase their tackling power – the possibilities are indeed vast.
The Science of Plyometrics: A Closer Look
At the heart of plyometric exercises lies the principle of dynamic resistance training. These exercises work on the muscles, stimulating the fast-twitch fibers responsible for powerful, explosive movements. When an athlete performs a plyometric exercise, they are essentially training these fibers to respond more quickly and forcefully, thereby enhancing their athletic performance.
It is essential, however, to approach plyometric training with a thorough understanding of the science behind it. Without proper form and technique, the risk of injury can be significant. It is, therefore, crucial to start slow, maintain proper form, and progressively increase the intensity of the exercises.
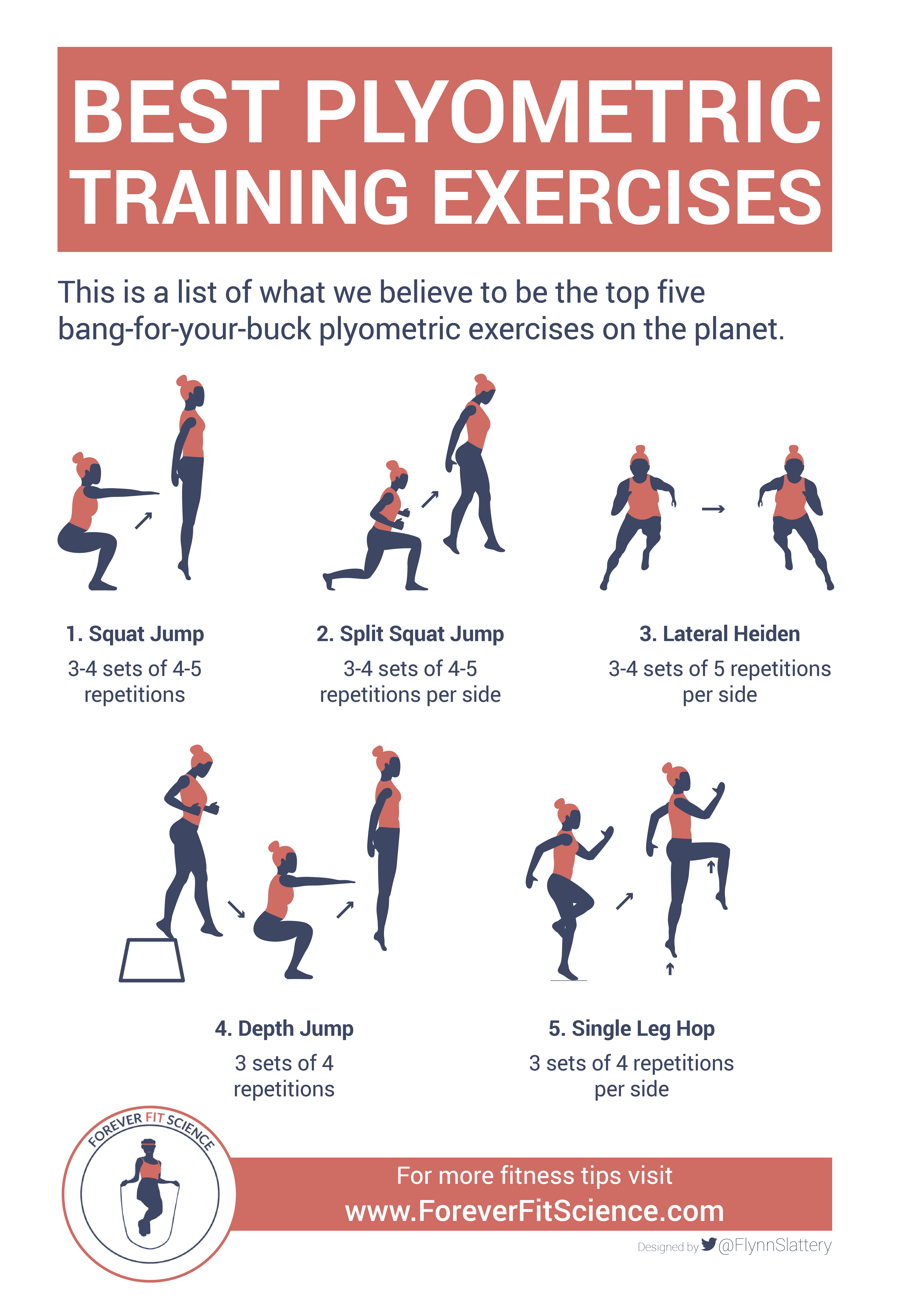
Key Plyometric Exercises for Boosting Athletic Performance
There are several key plyometric exercises that athletes can incorporate into their training routines. Box jumps, for instance, are excellent for building explosive power and enhancing vertical jump. Depth jumps, on the other hand, can help with improving reaction times and increasing lower body strength.
Other exercises like burpees are not only effective for increasing power and endurance, but also provide a comprehensive full-body workout. Each of these exercises can be tailored to suit the athlete’s specific requirements, making plyometric training a versatile and effective tool for enhancing athletic performance.
As the world of sports continues to evolve, so does the need for innovative and effective training methods. Plyometric exercises, with their focus on enhancing speed, power, and agility, are proving to be a game-changer in athletic performance. By understanding the science behind these exercises and incorporating them effectively into training routines, athletes can unlock their full potential and reach new heights in their performance.
Understanding the Science of Plyometrics
Plyometric exercises, also known as “jump training” or “plyos”, are exercises in which muscles exert maximum force in short intervals of time, with the goal of increasing power (speed-strength). These exercises are central to the development of an athlete’s explosive power, the rapid exertion of strength, a key component of athletic performance. But what’s the science behind plyometrics and how do these exercises enhance “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance”?
The science of plyometrics is rooted in the understanding of muscle contraction. Our muscles contract in three ways: concentrically (muscle shortens), eccentrically (muscle lengthens), and isometrically (length remains constant). Plyometrics primarily use the eccentric and concentric contractions. The “stretch-shortening cycle” (SSC) is a powerful human movement pattern that combines these two types of contractions. Plyometric exercises utilize this cycle to produce powerful movements.

When an athlete lands from a jump, the muscles lengthen (eccentric contraction) and store potential energy. If the following movement, such as a second jump, is immediate, the stored energy is released (concentric contraction), resulting in a more forceful action. This is the principle that powers plyometrics and enhances athletic performance.
At the cellular level, plyometric exercises target the fast-twitch muscle fibers. These fibers fatigue quickly but are capable of rapid, forceful contractions, making them essential for explosive movements. The more these fibers are trained, the better their performance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9tfbVvfm96Y
With the integration of plyometric exercises into an athlete’s training routine, the fast-twitch fibers are repeatedly stimulated. Over time, this leads to an increase in the size and efficiency of these fibers, enabling the athlete to perform explosive movements with greater speed and power. This is how plyometrics enhance athletic performance.
However, it’s important for athletes and coaches to remember that while plyometrics can be incredibly beneficial when done correctly, they can also lead to injuries if performed improperly. Proper form, adequate rest, and gradual progression are key to a successful and safe plyometric training.
The science of plyometrics is a fascinating field that continues to evolve with new research. By harnessing the power of this training method, athletes can push the boundaries of their performance to new heights.
How to Incorporate Plyometrics into Your Training Routine
Integrating “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance” into your training routine can be a game-changer. However, it’s crucial to do it correctly to maximize benefits and minimize injury risk. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to incorporate plyometrics into your training regimen.
Firstly, it’s essential to have a solid fitness foundation before starting plyometric training. This includes good overall strength, flexibility, and balance. Plyometrics are high-intensity exercises, and diving in without a proper fitness base could lead to injuries.

Once you’re ready to start, begin with lower intensity plyometric exercises. This could include exercises like squat jumps or box jumps. As your strength and power improve, you can gradually incorporate more intense exercises into your routine.
Proper form is crucial in plyometric training. Incorrect form not only reduces the effectiveness of the exercise but also significantly increases the risk of injury. It’s a good idea to work with a trained professional who can guide you on the correct technique.
Another key aspect of plyometric training is the principle of progressive overload. This means gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts over time. You can do this by adding more repetitions, increasing the height of your jumps, or reducing the rest time between sets.
Rest and recovery are just as important as the exercises themselves. Plyometrics are intense and can be taxing on the muscles and joints. Ensure you’re giving your body ample time to recover between workouts. This not only helps prevent injuries but also allows your muscles to grow and adapt.
Lastly, remember to listen to your body. If you feel pain or discomfort during an exercise, stop and rest. It’s better to miss one workout than to be sidelined for weeks with an injury.
By following these guidelines, you can safely incorporate plyometric exercises into your training routine and start reaping the benefits. Whether you’re a sprinter looking to improve your start off the blocks, a basketball player wanting to enhance your jump shot, or a football player aiming to increase your tackling power, plyometrics can help you reach your athletic potential.
Key Plyometric Exercises for Enhancing Athletic Performance
When it comes to “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance”, there are several key exercises that stand out for their effectiveness in enhancing speed, power, and agility. These exercises, when performed correctly and consistently, can significantly improve an athlete’s performance in their chosen sport.
Box Jumps: Box jumps are a classic plyometric exercise that primarily targets the lower body, including the glutes, hamstrings, and quads. The athlete starts in a squat position and jumps onto a sturdy box or platform, landing softly in a squat position. This exercise not only improves lower body strength and power but also enhances coordination and balance.

Burpees: Burpees are a full-body plyometric exercise that combines a squat, push-up, and jump into one fluid movement. This exercise not only increases power and speed but also improves cardiovascular endurance and overall body strength.
Depth Jumps: Depth jumps involve stepping off a box or platform and immediately jumping vertically as high as possible upon landing. This exercise is particularly effective in improving reactive strength, a key component of athletic performance.
While these exercises are highly effective, it’s important to remember that plyometric training should be tailored to the individual athlete’s fitness level and sport-specific demands. For instance, a basketball player might focus more on vertical jumps to improve their jump shot, while a soccer player might incorporate more lateral movements into their plyometric training to enhance their agility on the field.
Furthermore, proper form and technique are crucial in plyometric training to prevent injuries. Athletes should always warm up thoroughly before starting their workout and cool down afterwards. It’s also recommended to perform plyometric exercises on a soft surface, such as a gym mat or grass, to reduce impact on the joints.
With the right approach and commitment, plyometric exercises can be a powerful tool in an athlete’s training arsenal, helping them to reach new heights in their athletic performance.
Real-Life Success Stories: Athletes Who Swear by Plyometrics
The effectiveness of “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance” is not just theoretical. Many athletes, both famous and lesser-known, have seen significant improvements in their performance through plyometric training. These real-life success stories serve as powerful testimonials to the benefits of plyometrics.
One such athlete is Usain Bolt, widely regarded as the fastest man in the world. Bolt’s explosive speed and power can be attributed in part to his rigorous plyometric training regimen, which includes exercises like bounding, box jumps, and depth jumps. These exercises have helped him develop the fast-twitch muscle fibers necessary for sprinting at world-record speeds.

Another athlete who has benefited from plyometric training is Serena Williams, one of the greatest tennis players of all time. Williams incorporates plyometric exercises like medicine ball throws and jump squats into her training routine to improve her power, agility, and endurance on the court.
Plyometric training is not just for elite athletes. Many amateur athletes and fitness enthusiasts have also found success with this training method. For example, a marathon runner might use plyometric exercises to improve their running economy and endurance, while a soccer player might use them to enhance their kicking power and agility on the field.
These success stories highlight the potential of plyometric training to enhance athletic performance across a wide range of sports. However, it’s important to remember that plyometrics is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each athlete’s training regimen should be tailored to their individual needs, fitness level, and sport-specific demands.
Furthermore, while plyometrics can yield impressive results, it’s not a magic bullet. Success in sports requires a holistic approach that includes not only physical training but also proper nutrition, adequate rest, mental preparation, and, above all, consistent effort and dedication.
With the right approach, plyometric exercises can be a powerful tool in an athlete’s training arsenal, helping them to reach new heights in their athletic performance.
Expert Tips for Maximizing Benefits from Plyometric Training
Maximizing the benefits of “Plyometric exercises for athletic performance” requires more than just performing the exercises. It involves a holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, adequate rest, and complementary training techniques. Here are some expert tips to help athletes get the most out of their plyometric training.
Nutrition: Proper nutrition is crucial for athletic performance. Athletes should consume a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel their workouts and aid in recovery. Hydration is also important, especially during intense plyometric sessions.

Rest: Adequate rest is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Athletes should aim for at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night and consider incorporating rest days into their training schedule to allow their muscles to recover from the intense demands of plyometric exercises.
Complementary Training Techniques: While plyometrics can significantly enhance athletic performance, they should be part of a well-rounded training program that includes strength training, cardio, flexibility exercises, and sport-specific drills. This balanced approach can help athletes improve their overall fitness and performance.
Furthermore, athletes should always listen to their bodies. If they feel pain or discomfort during plyometric exercises, they should stop and seek medical advice. Overtraining can lead to injuries and hinder performance.
Finally, athletes should remember that progress takes time. While plyometric exercises can yield impressive results, they won’t happen overnight. Consistency, patience, and dedication are key to achieving long-term success in any sport.
With these expert tips, athletes can maximize the benefits of plyometric training and take their performance to the next level.

