The Connection Between Eating and Weight Gain
When exploring the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?”, it is essential to understand the relationship between food consumption and weight changes. While it is common to experience temporary fluctuations in weight after eating, sustained weight gain is typically the result of long-term dietary patterns and lifestyle habits. Emphasizing overall diet and lifestyle is crucial for long-term weight management, rather than focusing solely on individual meals or eating occasions.
Short-Term Weight Gain After Eating
Addressing the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?” involves understanding the temporary fluctuations in weight that can occur following a meal. After consuming food, the digestive process begins, leading to an increase in water retention as the body processes and stores nutrients. This water retention can cause a short-term rise in weight, which is often misperceived as fat gain. However, it is essential to recognize that this water weight is typically lost within a few days as the body eliminates excess fluids. To better understand these short-term weight changes, consider tracking weight trends over a more extended period, such as a week or a month, rather than focusing on daily fluctuations.
The Impact of Different Foods on Weight
When considering the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?”, it is crucial to examine the influence of various types of food on weight. Different foods can have unique effects on the body due to their macronutrient composition and other properties. For instance, high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote satiety and support healthy digestion, potentially minimizing weight fluctuations. On the other hand, processed foods, high in sugar and unhealthy fats, can contribute to weight gain and related health issues.
Understanding the impact of macronutrients on weight management is essential. Proteins, for example, can help build muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and promote weight loss or maintenance. Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can support satiety and hormone balance, while carbohydrates, particularly those from whole food sources, provide energy and support overall health. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, individuals can optimize their weight management efforts and reduce the likelihood of experiencing significant weight fluctuations after eating.
How to Monitor Weight Changes
To effectively track weight changes and better understand the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?”, consider implementing a variety of monitoring methods. Utilizing a digital scale can provide daily weight measurements, but it is essential to focus on overall trends rather than individual data points. Additionally, incorporating body measurements, such as waist and hip circumference, can offer a more comprehensive view of health and weight distribution. Progress photos can also serve as valuable visual indicators of physical changes over time.
When tracking weight changes, it is crucial to maintain a balanced perspective. Daily fluctuations, whether due to food consumption, hydration levels, or other factors, are common and should not be a cause for concern. Instead, focus on long-term progress and overall health improvements. Regularly reviewing monitoring data can help identify patterns and trends, allowing for adjustments to diet and lifestyle habits as needed. By adopting a holistic approach to weight management, individuals can better understand their bodies and make informed decisions about their health.
The Role of Hormones in Weight Management
Hormones play a critical role in weight management, and understanding their functions can help answer the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?”. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels and influences fat storage. Consuming meals high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to increased insulin secretion, promoting fat storage and potentially contributing to weight gain.
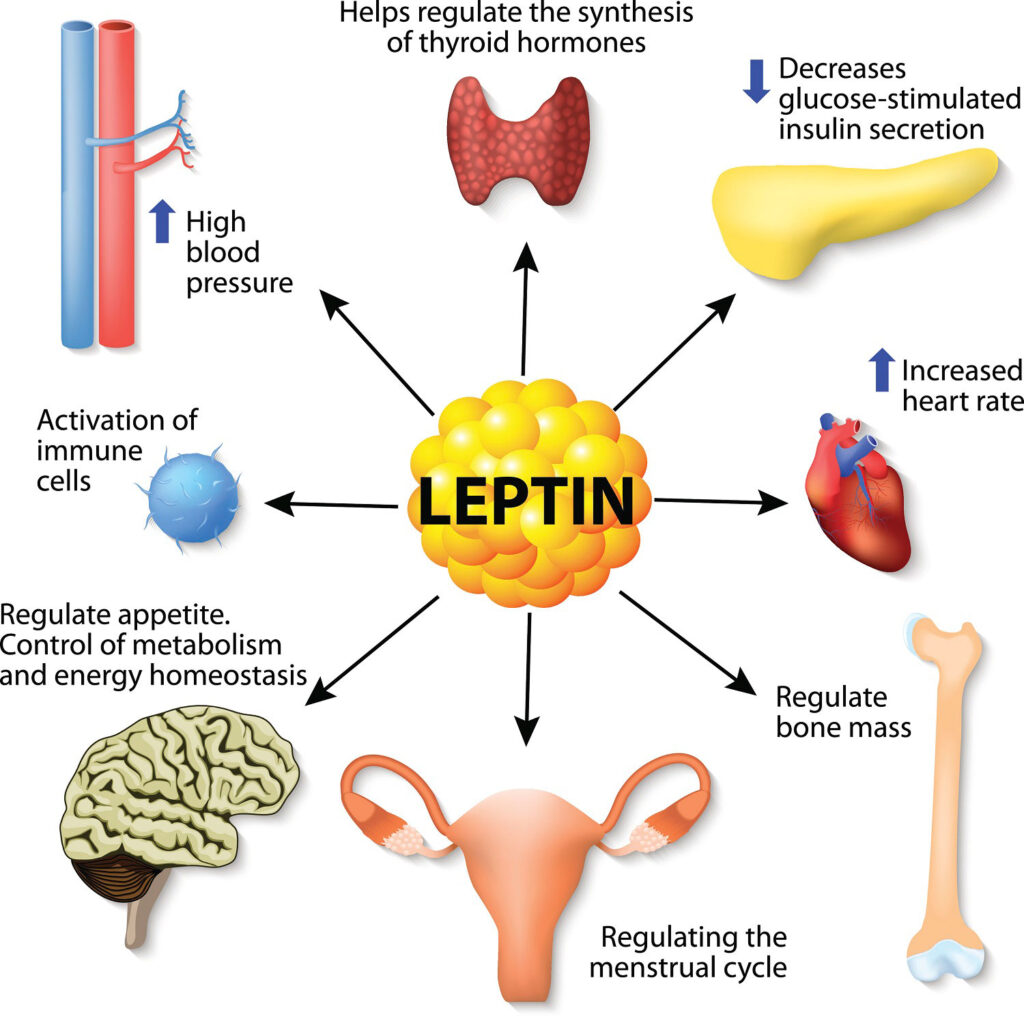
Ghrelin, often referred to as the “hunger hormone,” is produced by the stomach and signals the brain when it’s time to eat. Leptin, another hormone involved in weight management, is released by fat cells and communicates with the brain to suppress appetite and regulate energy balance. Imbalances in these hormones can lead to overeating, weight gain, and difficulty losing weight. Additionally, cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, can contribute to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area, by increasing appetite and promoting fat storage.
Maintaining a balanced hormonal environment is crucial for effective weight management. Strategies to support hormonal health include consuming a nutrient-dense diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep. By addressing hormonal imbalances, individuals can optimize their weight management efforts and minimize the impact of hormonal fluctuations on their weight.
The Influence of Emotional Eating on Weight
Emotional eating, or the practice of turning to food to cope with emotions, can significantly impact weight management. Addressing the question “is it normal to gain weight after eating?” requires acknowledging the role of emotional eating in weight fluctuations. People often consume high-calorie, palatable foods to alleviate negative emotions, such as stress, sadness, or boredom, leading to overeating and potential weight gain.
To combat emotional eating, individuals can develop self-awareness around their emotional triggers and adopt healthier coping mechanisms. Keeping a food diary to track eating patterns, practicing mindfulness meditation, and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage emotional eating. Additionally, seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can provide valuable guidance and encouragement during the weight management journey.
Long-Term Weight Management Strategies
Effective long-term weight management relies on a sustainable, balanced lifestyle. Adopting a holistic approach that addresses diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep can help individuals maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of weight fluctuations. Here are evidence-based recommendations to support long-term weight management:
-
Consume a nutrient-dense diet: Focus on whole, minimally processed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit intake of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
-
Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
-
Manage stress: Identify and address stressors in your life, and adopt stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises. Reducing stress can help prevent emotional eating and support weight management.
-
Prioritize sleep: Ensure adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night for adults) to support weight management. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormone levels and metabolism, leading to weight gain.
By incorporating these strategies into a balanced lifestyle, individuals can effectively manage their weight and improve their overall health. Remember, small, consistent changes are more likely to result in long-term success than drastic, unsustainable measures.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Weight Management
Navigating the complex world of weight management can be challenging, and seeking expert guidance and support is often essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Consulting healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide numerous benefits, including:
-
Personalized advice: Professionals can evaluate your individual needs, preferences, and health status to create a tailored weight management plan that considers your unique circumstances.
-
Evidence-based strategies: Healthcare providers and dietitians stay up-to-date with the latest research and guidelines, ensuring that their recommendations are based on sound scientific evidence.
-
Motivation and accountability: Regular appointments with a professional can help keep you motivated and accountable, increasing the likelihood of long-term success.
-
Debunking myths: Professionals can help dispel common weight management myths and misconceptions, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health.
-
Addressing underlying issues: Healthcare providers can identify and address any underlying health issues, such as hormonal imbalances or medical conditions, that may be contributing to weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
By working with a qualified professional, you can develop a customized weight management plan that addresses your specific needs and goals. This partnership can help you navigate the challenges of weight management, ensuring that you have the tools and support necessary to achieve and maintain a healthy weight over time.