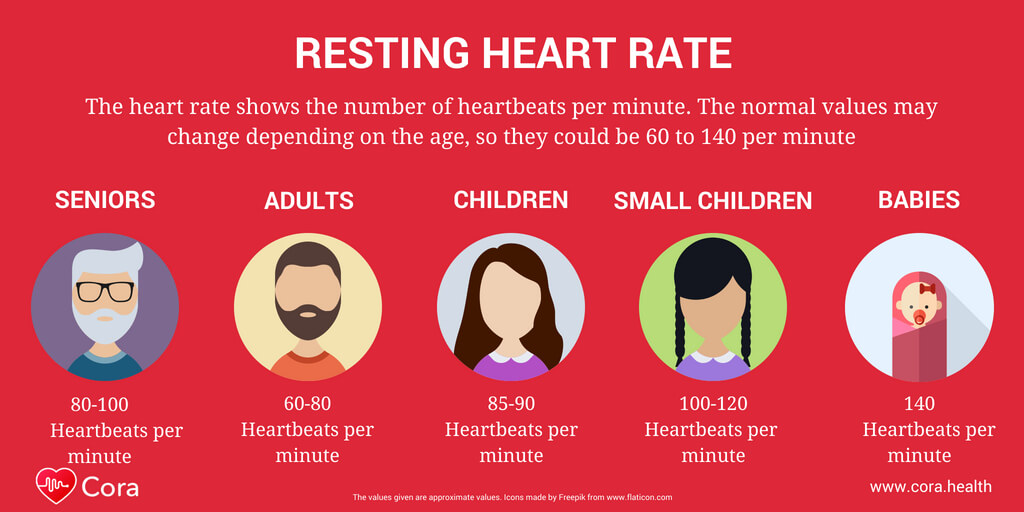
What Constitutes a High Resting Heart Rate?
A high resting heart rate, also known as tachycardia, refers to a heart rate that exceeds the normal range when an individual is at rest. Generally, a resting heart rate above 100 beats per minute (bpm) is considered high. However, several factors can influence the resting heart rate, including age, fitness level, and overall health. For instance, highly trained athletes may have a lower resting heart rate due to their enhanced cardiovascular fitness. In contrast, older individuals or those with preexisting health conditions may have a higher resting heart rate. It is essential to consider these factors when evaluating whether one’s heart rate falls within a healthy range. While it is normal for heart rate to fluctuate throughout the day, consistently having a high resting heart rate may indicate potential health concerns, making it important to monitor and address this issue in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Is It Harmful to Have a High Heart Rate?
The question of whether it is bad to have a high heart rate is not a straightforward one, as a consistently elevated heart rate is not always indicative of poor health. However, there are potential risks and consequences associated with a high resting heart rate that warrant attention. Research has shown that a higher resting heart rate may be linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as a higher mortality rate. Moreover, individuals with a resting heart rate above 80 bpm may be more susceptible to developing hypertension, or high blood pressure. It is important to note that these risks are often compounded by other health markers, such as obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Therefore, while a high heart rate is not a definitive sign of poor health, it can serve as a valuable indicator of potential health concerns. Regular monitoring of one’s resting heart rate, in conjunction with other health metrics, can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their health and wellness. By addressing underlying factors contributing to a high heart rate, such as stress, anxiety, and physical inactivity, individuals can take proactive steps towards improving their overall health and reducing the risk of associated health complications.
How Does Exercise Impact Resting Heart Rate?
Regular exercise has a significant influence on the resting heart rate, offering a valuable strategy for managing and reducing a high heart rate. Engaging in consistent physical activity helps to strengthen the heart muscle, enabling it to pump a greater volume of blood with each beat. As a result, the heart does not need to work as hard to maintain blood flow, leading to a lower resting heart rate. Research has demonstrated that individuals who participate in regular aerobic exercise, such as running, swimming, or cycling, can achieve a resting heart rate that is 10-20 bpm lower than those who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Moreover, lowering the resting heart rate through exercise has been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. To maximize the benefits of exercise on resting heart rate, it is essential to adopt a well-rounded fitness routine that incorporates both cardiovascular and strength training exercises. By doing so, individuals can not only lower their resting heart rate but also improve their overall cardiovascular health and well-being.
The Connection Between Stress and Heart Rate
Stress and anxiety can significantly impact the heart rate, contributing to a high resting heart rate in some individuals. When an individual experiences stress or anxiety, their body responds by releasing stress hormones such as adrenaline, which in turn increases the heart rate. Over time, chronic stress and anxiety can lead to a consistently elevated heart rate, raising concerns about potential health implications. To manage stress and reduce its impact on heart rate, consider incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation have been shown to effectively lower stress levels and decrease heart rate. Additionally, maintaining a healthy work-life balance, engaging in regular physical activity, and fostering supportive relationships can help mitigate the effects of stress on heart rate. By addressing stress and anxiety, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their resting heart rate and improving their overall health and well-being.
How to Measure Your Resting Heart Rate
To accurately assess your resting heart rate, it is essential to follow a consistent and proper measurement technique. Begin by finding a quiet and comfortable space where you can relax and focus on your heart rate. Ideally, perform the measurement first thing in the morning, before engaging in any physical activity or consuming caffeine. To measure your resting heart rate, follow these steps:
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position, ensuring your body is relaxed and still.
- Locate your pulse by placing your index and middle fingers on your wrist, just below the base of your thumb, or on the side of your neck, near your windpipe.
- Once you have found your pulse, use a watch, clock, or timer to count the number of beats you feel over a 60-second period. Alternatively, you can count the beats over a 15-second interval and multiply the result by four to obtain your heart rate per minute.
- Record your heart rate, and repeat the measurement two more times to ensure accuracy. Use the average of the three measurements as your resting heart rate.
By consistently measuring your resting heart rate, you can establish a baseline for comparison and track changes over time. This information can be invaluable in assessing your cardiovascular health and identifying potential health concerns related to a high heart rate. Regular monitoring of your resting heart rate, in conjunction with other health markers, can help inform health and wellness decisions and contribute to an overall improvement in your well-being.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
While a high heart rate is not always indicative of poor health, there are certain scenarios when it is appropriate to consult a healthcare professional regarding your heart rate. These situations include:
- Persistent tachycardia: If you consistently experience a resting heart rate above 100 bpm, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Persistent tachycardia may indicate an underlying health condition, such as heart disease, that requires medical attention.
- Associated symptoms: If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, or fatigue in conjunction with a high heart rate, seek medical advice. These symptoms may suggest a more serious health concern and warrant further investigation.
- Family history: If you have a family history of heart disease or other cardiovascular conditions, it is advisable to discuss your heart rate and overall cardiovascular health with a healthcare professional. Early detection and intervention can help manage potential health risks and improve long-term outcomes.
- Pre-existing health conditions: If you have pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or thyroid disorders, it is crucial to monitor your heart rate and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. These conditions can impact your heart rate and may require specialized care or management strategies.
By consulting a healthcare professional when appropriate, you can ensure that you receive the necessary guidance and care to manage your heart rate and maintain optimal cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups and discussions with your healthcare provider can help identify potential health concerns and inform appropriate lifestyle modifications or treatment interventions.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Heart Rate
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly contribute to lowering a high heart rate. By incorporating the following modifications, you can effectively manage your heart rate and improve your overall cardiovascular health:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in consistent physical activity, such as aerobic exercises like running, swimming, or cycling, can help lower your resting heart rate. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week to experience the benefits.
- Stress management: Implementing stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce the impact of stress on your heart rate. By effectively managing stress, you can contribute to a lower resting heart rate and improved overall well-being.
- Healthy diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight and support cardiovascular health. Avoiding processed foods, excessive caffeine, and alcohol can also contribute to a lower heart rate.
- Adequate sleep: Ensuring you receive sufficient sleep each night is essential for maintaining a healthy heart rate. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support your body’s natural recovery processes and contribute to a lower resting heart rate.
- Limit stimulants: Reducing your consumption of stimulants, such as caffeine and nicotine, can help lower your heart rate. Consider limiting your intake of these substances or avoiding them altogether to support a healthier heart rate.
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, you can effectively manage your heart rate and contribute to an overall improvement in your cardiovascular health. Regularly monitoring your heart rate and tracking trends over time can help inform your health and wellness decisions, ensuring you remain on the path towards optimal well-being.
Monitoring Heart Rate Trends Over Time
Tracking your heart rate trends over time can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular health and overall well-being. By consistently monitoring your heart rate, you can identify patterns, assess the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications, and detect potential health concerns. Here are some ways to monitor your heart rate trends:
- Manual tracking: Use a wristwatch or clock to manually measure your heart rate at the same time each day, recording the results in a journal or spreadsheet. This method, while time-consuming, allows you to visually track changes in your heart rate over time.
- Smartwatch or fitness tracker: Invest in a wearable device, such as a smartwatch or fitness tracker, that automatically measures and records your heart rate throughout the day. Many of these devices offer features that allow you to view trends, set goals, and receive alerts when your heart rate falls outside of a specified range.
- Health apps: Utilize health apps that enable you to track and analyze your heart rate data. Some apps even offer features that allow you to share your data with healthcare professionals, facilitating more informed decision-making regarding your health and wellness.
By monitoring heart rate trends over time, you can better understand the impact of lifestyle modifications on your heart rate and overall health. Regularly reviewing your heart rate data can help you identify areas for improvement, ensure you remain on track towards your health goals, and inform discussions with healthcare professionals. Ultimately, tracking heart rate trends can contribute to a more proactive approach to managing your health and well-being, enabling you to make data-driven decisions that support your long-term cardiovascular health.