What is a Resting Heart Rate?
A resting heart rate, often abbreviated as RHR, is the number of times your heart beats per minute when you are at rest. It serves as a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health and fitness levels. Typically, a lower resting heart rate implies a more efficient heart function and better physical fitness. This is because a fitter heart pumps blood more effectively, reducing the need for frequent beats. As a result, the heart rate at rest decreases. A resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is often considered a good benchmark, but individual factors and overall health status can influence its interpretation.
How to Measure Your Resting Heart Rate
To accurately determine your resting heart rate, follow these simple steps:
- Find a quiet and comfortable place where you can relax.
- Ensure you are in a seated or lying position.
- Locate your pulse by placing your index and middle fingers on your wrist or the side of your neck.
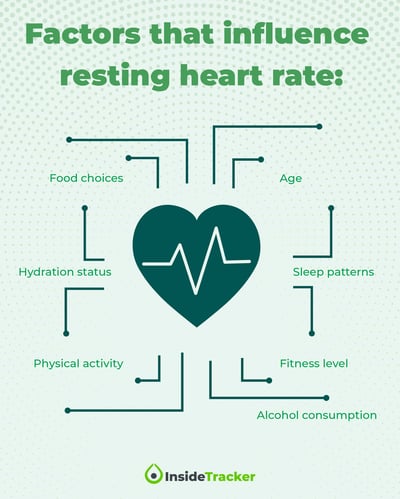
- Age: As individuals grow older, their resting heart rates tend to increase due to natural physiological changes. Consequently, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute might be more favorable for older adults than for younger individuals.
- Fitness level: Highly trained athletes often have lower resting heart rates, reflecting their superior cardiovascular fitness. In this context, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute might be considered average or even slightly elevated for elite athletes.
- Overall health: Chronic health conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or thyroid disorders, can affect resting heart rate. In such cases, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute might have different implications depending on the specific health issue and its severity.
- Athlete: Highly trained athletes often have resting heart rates between 40 and 60 beats per minute. This is due to their superior cardiovascular fitness, which allows their hearts to pump blood more efficiently. In this context, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute might be considered average or even slightly elevated.
- Average: For the general population, resting heart rates typically range from 60 to 100 beats per minute. A resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute falls within this range, indicating average cardiovascular health and fitness. However, individual factors and overall health status should still be taken into account when interpreting this value.
- High-risk: Individuals with resting heart rates above 100 beats per minute are often at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. A resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is significantly lower than this high-risk threshold, suggesting a lower risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, particularly aerobic exercises like running, swimming, or cycling, can help strengthen your heart and reduce your resting heart rate. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as recommended by the American Heart Association.
- Stress management: High stress levels can increase heart rate and blood pressure. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation, can help lower your resting heart rate.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: Maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco products, and limiting alcohol consumption can contribute to better cardiovascular health and a lower resting heart rate.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body weight can strain the heart and increase resting heart rate. Losing weight through a combination of regular exercise and a balanced diet can help lower your resting heart rate.
- Adequate sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall heart health and can help regulate resting heart rate. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and establish a consistent sleep schedule.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as beta blockers or calcium channel blockers, can lower resting heart rate as a side effect. If you are taking medication and notice a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute, consult your healthcare provider to ensure your heart rate is within the expected range for your specific situation.
- Illness: Acute or chronic illnesses, such as infections, fever, or heart conditions, can temporarily or persistently increase resting heart rate. If you experience a sudden change in your resting heart rate or are concerned about any symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
- Other health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as thyroid disorders, anemia, or electrolyte imbalances, can affect resting heart rate. Regular check-ups and consultations with your healthcare provider can help monitor and manage these conditions, ensuring your resting heart rate remains within a healthy range.
- Case Study 1: Sarah, a 35-year-old recreational runner, has a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute. She maintains an active lifestyle, running 30 miles per week and incorporating strength training twice a week. Sarah also focuses on stress management through meditation and ensures she gets 7-8 hours of sleep each night. Her healthy diet, active lifestyle, and stress management techniques contribute to her low resting heart rate and overall cardiovascular health.
- Case Study 2: John, a 50-year-old office worker, has a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute. While he does not engage in regular exercise, he maintains a healthy diet and ensures he gets 7-9 hours of sleep each night. John’s healthcare provider has recommended that he incorporate more physical activity into his routine to further improve his cardiovascular health and maintain his resting heart rate.
- Case Study 3: Emily, a 40-year-old nurse, has a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute. She leads a relatively sedentary lifestyle but maintains a healthy diet and ensures she gets adequate sleep. Emily’s healthcare provider has suggested that she incorporate regular exercise into her routine to further enhance her cardiovascular health and lower her resting heart rate.
- Understanding the factors that can influence resting heart rate, such as age, fitness level, and overall health, is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Comparing your resting heart rate to other categories, like athlete, average, and high-risk, can offer additional context and help you assess your cardiovascular health.
- Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, stress management, and a balanced diet, can contribute to a lower resting heart rate and improved cardiovascular health.
Is a Resting Heart Rate of 52 Good?
A resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute generally indicates good cardiovascular health and fitness. However, several factors can influence the interpretation of this value.
In summary, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is generally considered good, but individual factors and overall health status should be taken into account when interpreting this value.
Comparing Resting Heart Rate Ranges
To better understand the implications of a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute, it is helpful to compare it with other resting heart rate ranges. These categories include athlete, average, and high-risk.
In conclusion, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is generally considered good, as it falls within the average range and is significantly lower than the high-risk threshold. However, individual factors and overall health status are crucial when interpreting this value.
How to Improve Your Resting Heart Rate
A resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is a positive indicator of cardiovascular health, but there are still ways to further enhance it through lifestyle modifications. Here are some practical tips and advice to improve your resting heart rate:
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can work towards improving your resting heart rate and enhancing your cardiovascular health.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GrZG0BRog7Y
Potential Limitations and Considerations
While a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is generally considered good, there are certain limitations and considerations to keep in mind when interpreting this value. Various factors, such as medication, illness, and other health conditions, can influence resting heart rate.
In summary, while a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is generally a positive indicator of cardiovascular health, it is essential to consider potential limitations and seek professional advice when necessary. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations to ensure your resting heart rate is within the expected range for your age, fitness level, and overall health status.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
To offer a more comprehensive understanding of the implications of a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute, let’s explore some real-life examples and case studies of individuals with similar resting heart rates.
These examples demonstrate that a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute can be influenced by various factors, including age, fitness level, and lifestyle habits. While Sarah and John have resting heart rates of 52 beats per minute due to their active lifestyles and healthy habits, Emily’s resting heart rate may be influenced by factors other than fitness, such as her occupation and stress levels. Overall, monitoring resting heart rate and incorporating healthy lifestyle habits can contribute to better cardiovascular health and well-being.
Conclusion: The Importance of Monitoring Resting Heart Rate
In conclusion, a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute can be a positive indicator of cardiovascular health and fitness. Regularly monitoring your resting heart rate can provide valuable insights into your overall health status and help you identify potential issues early on.
While a resting heart rate of 52 beats per minute is generally considered good, it is essential to consider individual factors and overall health status when interpreting this value. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations to ensure your resting heart rate is within the expected range for your age, fitness level, and health status. By monitoring your resting heart rate and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can take a proactive approach to your health and well-being.