The Importance of Injury Rehabilitation for Athletes
Injury rehabilitation is a critical aspect of an athlete’s training program, as it can significantly impact recovery time, performance, and long-term health. By incorporating injury rehabilitation strategies into their training, athletes can reduce the risk of future injuries, improve mobility, and enhance overall performance. For instance, successful athletes such as Serena Williams and Adrian Peterson have credited injury rehabilitation with helping them return to the top of their respective sports after significant injuries.
Injury rehabilitation involves a comprehensive approach that includes identifying the cause and type of injury, setting rehabilitation goals, designing a rehabilitation program, and incorporating rehabilitation exercises into an athlete’s training program. By taking a proactive approach to injury rehabilitation, athletes can optimize their recovery and reduce the risk of future injuries, ultimately leading to improved performance and long-term health.
Effective injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes involve a combination of exercises, techniques, and frequency that are tailored to the individual athlete’s needs and goals. These strategies may include stretching, strengthening, and mobility work, as well as other innovative and creative concepts that provide value and usefulness to the athlete. By incorporating injury rehabilitation into their training program, athletes can achieve their goals and reach their full potential, both on and off the field.
Understanding the Injury: Identifying the Cause and Type
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes rely heavily on the accurate identification of the cause and type of injury. This information is crucial in developing an effective rehabilitation plan that addresses the root cause of the injury and prevents future occurrences. Athletes can assess their injuries by paying attention to symptoms such as pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility. If an injury causes severe pain, significant swelling, or difficulty moving, athletes should seek medical attention immediately.
Identifying the type of injury is also essential in developing a rehabilitation plan. Common sports injuries include sprains, strains, fractures, and dislocations. Sprains occur when ligaments stretch or tear, while strains involve the stretching or tearing of muscles or tendons. Fractures involve breaks in bones, and dislocations occur when joints are forced out of their normal position. Accurately identifying the type of injury is critical in determining the appropriate rehabilitation exercises and techniques.
To ensure a proper diagnosis, athletes should consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sports medicine. These professionals have the knowledge and expertise to accurately diagnose and treat sports injuries, as well as the ability to develop a comprehensive rehabilitation plan that addresses the root cause of the injury. By working with a sports medicine specialist, athletes can ensure that they receive the appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, ultimately leading to a faster and more effective recovery.
In addition to seeking medical attention, athletes can also take steps to prevent injuries from occurring in the first place. These steps include proper warm-up and cool-down routines, maintaining proper form and technique during exercise, and using appropriate protective gear. By taking a proactive approach to injury prevention, athletes can reduce the risk of injury and optimize their performance on the field.
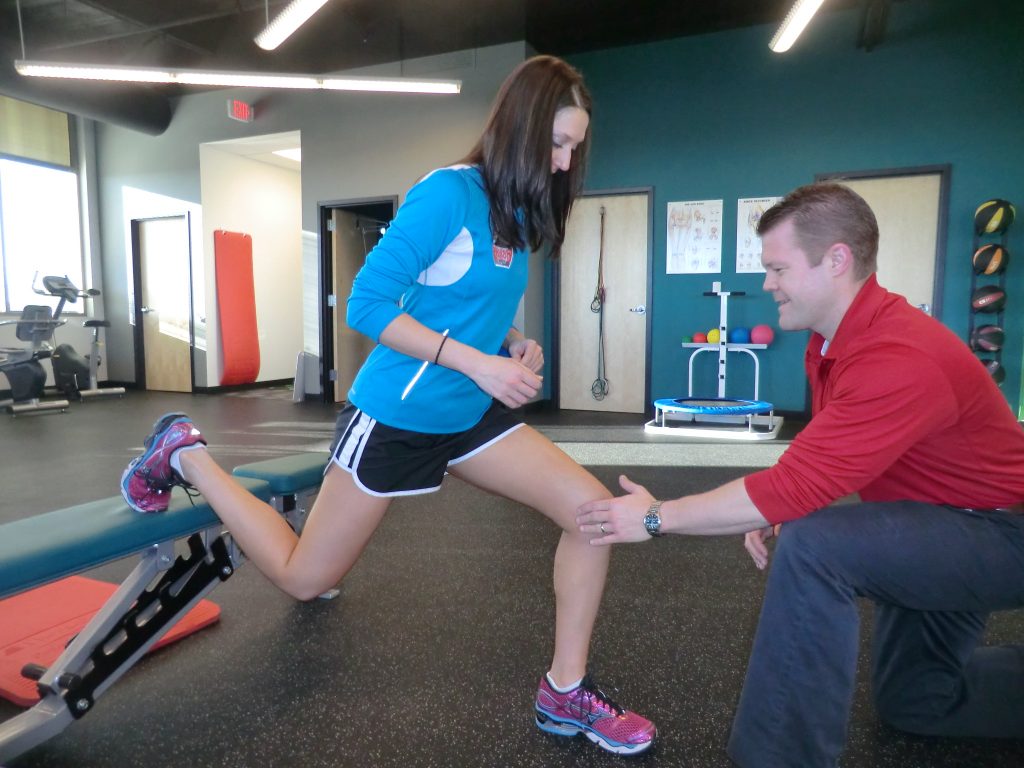

Setting Rehabilitation Goals: Focusing on Recovery and Prevention
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes should include setting specific and measurable goals that focus on both recovery and injury prevention. By setting clear goals, athletes can stay motivated and track their progress throughout the rehabilitation process. Here are some examples of specific goals that athletes can set during injury rehabilitation:
- Range of motion: Increase the range of motion in the affected joint or muscle group.
- Strength: Improve the strength of the affected muscle or muscle group.
- Flexibility: Increase the flexibility of the affected muscle or muscle group.
- Balance: Improve balance and stability in the affected limb or muscle group.
- Endurance: Increase endurance and stamina in the affected muscle or muscle group.
To set effective rehabilitation goals, athletes should consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sports medicine. These professionals can help athletes develop a comprehensive rehabilitation plan that includes specific goals tailored to their individual needs and injury. By setting clear and measurable goals, athletes can stay motivated and focused throughout the rehabilitation process, ultimately leading to a faster and more effective recovery.
It’s also important to note that injury rehabilitation is not just about recovering from an injury but also preventing future injuries. By incorporating injury prevention exercises and techniques into their rehabilitation program, athletes can reduce the risk of future injuries and optimize their performance on the field. These exercises may include balance training, mobility work, and strengthening exercises that target the affected muscle or muscle group.
In addition to setting specific goals, athletes should also track their progress throughout the rehabilitation process. This can include tracking exercises, reps, and goals to ensure that they are making progress towards their rehabilitation goals. By tracking their progress, athletes can identify areas where they may need to adjust their rehabilitation program and make changes accordingly. This can help optimize the rehabilitation process and lead to a faster and more effective recovery.

Designing a Rehabilitation Program: Incorporating Exercises and Techniques
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes should include a comprehensive rehabilitation program that incorporates various exercises and techniques to promote recovery and injury prevention. Here is a guide to designing an effective injury rehabilitation program for athletes:
Exercises
The following exercises are essential components of an injury rehabilitation program:
- Stretching: Stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and prevent injury. Dynamic stretching, which involves moving the muscles and joints through a full range of motion, is particularly effective for athletes. Examples of dynamic stretching exercises include leg swings, arm circles, and lunges with a twist.
- Strengthening: Strengthening exercises can help improve muscle strength, endurance, and power. These exercises should target the affected muscle or muscle group, as well as surrounding muscles that provide stability and support. Examples of strengthening exercises include bodyweight squats, resistance band rows, and single-leg deadlifts.
- Mobility work: Mobility exercises can help improve joint range of motion, reduce stiffness, and prevent injury. These exercises should focus on the affected joint or muscle group, as well as surrounding joints that contribute to overall mobility. Examples of mobility exercises include hip circles, shoulder rolls, and ankle rotations.
Techniques
The following techniques can be used to complement the exercises in an injury rehabilitation program:
- Manual therapy: Manual therapy techniques, such as massage, mobilization, and manipulation, can help reduce muscle tension, improve joint range of motion, and promote healing. These techniques should be performed by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or chiropractor.
- Modalities: Modalities, such as heat, cold, and electrical stimulation, can help reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms. These modalities should be used in conjunction with exercises and techniques that promote recovery and injury prevention.
- Education: Education is a critical component of an injury rehabilitation program. Athletes should be educated on proper exercise technique, injury prevention strategies, and the importance of rest and recovery. Education can help athletes make informed decisions about their rehabilitation program and optimize their recovery.
The frequency and duration of an injury rehabilitation program will depend on the type and severity of the injury. In general, rehabilitation exercises should be performed 2-3 times per week, with each session lasting 20-30 minutes. As the athlete progresses, the frequency and duration of the exercises can be increased to further promote recovery and injury prevention.

Incorporating Rehabilitation into Training: Balancing Recovery and Performance
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes should not only focus on recovery but also on injury prevention and maintaining performance levels. Incorporating rehabilitation exercises into an athlete’s training program can be challenging, but it is crucial for optimal recovery and long-term health. Here are some tips on how to balance recovery and performance during injury rehabilitation:
When to Perform Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehabilitation exercises should be performed at the right time to optimize recovery and prevent further injury. Athletes should perform rehabilitation exercises:
- As soon as possible after the injury, once cleared by a medical professional.
- On days when they are not training or competing, to avoid overloading the affected area.
- Before training or competition, as part of a warm-up routine, to prepare the affected area for activity.
How to Progress
Progressing rehabilitation exercises is essential for optimal recovery and injury prevention. Athletes should:
- Start with basic exercises and gradually progress to more advanced exercises as the injury heals.
- Increase the intensity, frequency, and duration of the exercises as the injury heals.
- Listen to their body and adjust the exercises accordingly, seeking medical attention if necessary.
How to Avoid Overtraining
Overtraining can hinder recovery and lead to further injury. Athletes should:
- Allow adequate rest and recovery time between rehabilitation exercises and training sessions.
- Monitor their body for signs of fatigue, such as muscle soreness, stiffness, and reduced performance.
- Adjust their training program if necessary, reducing the volume and intensity of training to avoid overloading the affected area.
Balancing Recovery and Performance
Balancing recovery and performance during injury rehabilitation can be challenging, but it is essential for optimal recovery and long-term health. Athletes should:
- Set specific and measurable rehabilitation goals that focus on both recovery and injury prevention.
- Incorporate rehabilitation exercises into their training program gradually, avoiding overloading the affected area.
- Listen to their body and adjust their training program accordingly, seeking medical attention if necessary.
Incorporating injury rehabilitation exercises into an athlete’s training program can be challenging, but it is crucial for optimal recovery and long-term health. By balancing recovery and performance, athletes can optimize their rehabilitation program and reduce the risk of future injuries. Remember to progress gradually, avoid overtraining, and seek medical attention when necessary.

The Benefits of Injury Rehabilitation for Athletes: Improved Performance and Reduced Risk of Future Injuries
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are essential for optimal recovery, improved performance, and reduced risk of future injuries. Successful athletes understand the importance of incorporating injury rehabilitation exercises into their training programs, and they reap the benefits of their efforts. Here are some of the benefits of injury rehabilitation for athletes:
Improved Performance
Injury rehabilitation exercises can help athletes improve their performance by increasing mobility, strength, and flexibility. For example, a runner who has suffered a knee injury can benefit from rehabilitation exercises that target the muscles surrounding the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings. By strengthening these muscles, the runner can improve their running form, increase their speed, and reduce their risk of future injuries.
Increased Mobility
Injury rehabilitation exercises can help athletes increase their mobility by improving their range of motion and reducing stiffness. For example, a basketball player who has suffered an ankle injury can benefit from rehabilitation exercises that target the ankle joint, such as ankle circles and heel-to-toe walks. By increasing their ankle mobility, the basketball player can improve their agility, reduce their risk of future ankle injuries, and enhance their overall performance.
Reduced Risk of Future Injuries
Injury rehabilitation exercises can help athletes reduce their risk of future injuries by addressing muscle imbalances, weaknesses, and mobility restrictions. For example, a tennis player who has suffered a shoulder injury can benefit from rehabilitation exercises that target the rotator cuff muscles, which are essential for shoulder stability and mobility. By addressing these muscle imbalances, the tennis player can reduce their risk of future shoulder injuries and improve their overall performance.
Successful athletes such as Serena Williams, Tom Brady, and Usain Bolt have incorporated injury rehabilitation strategies into their training programs, and they have reaped the benefits of their efforts. By prioritizing injury rehabilitation exercises, these athletes have been able to maintain their mobility, strength, and flexibility, which has contributed to their long-term success and reduced their risk of future injuries.
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are essential for optimal recovery, improved performance, and reduced risk of future injuries. By incorporating injury rehabilitation exercises into their training programs, athletes can improve their mobility, strength, and flexibility, reduce their risk of future injuries, and enhance their overall performance. Successful athletes understand the importance of injury rehabilitation, and they prioritize it in their training programs.

Common Mistakes to Avoid in Injury Rehabilitation: Focusing on Short-Term Relief
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are essential for optimal recovery, improved performance, and reduced risk of future injuries. However, athletes often make common mistakes during injury rehabilitation that can hinder their progress and lead to further injuries. One of the most significant mistakes is focusing too much on short-term relief, neglecting long-term recovery and injury prevention.
When athletes focus solely on short-term relief, they may rely on pain medication or other quick fixes to alleviate their symptoms. While these methods may provide temporary relief, they do not address the underlying cause of the injury. As a result, the injury may not heal properly, and the athlete may be at risk of re-injury.
To avoid this mistake, athletes should prioritize long-term recovery and injury prevention in their injury rehabilitation strategies. This means taking a holistic approach to injury rehabilitation, addressing the root cause of the injury, and incorporating exercises and techniques that promote mobility, strength, and flexibility. By focusing on long-term recovery and injury prevention, athletes can reduce their risk of future injuries and improve their overall performance.
Another common mistake that athletes make during injury rehabilitation is neglecting mobility work. Mobility exercises are essential for improving range of motion, reducing stiffness, and preventing future injuries. However, athletes often overlook mobility work, focusing instead on strength and flexibility exercises. By neglecting mobility work, athletes may not fully recover from their injuries and may be at risk of re-injury.
To avoid this mistake, athletes should incorporate mobility exercises into their injury rehabilitation programs. This may include exercises such as ankle circles, hip circles, and shoulder rolls, which can improve range of motion and reduce stiffness. By incorporating mobility exercises into their injury rehabilitation programs, athletes can promote long-term recovery and injury prevention.
Finally, athletes may make the mistake of performing exercises with poor form during injury rehabilitation. Poor form can lead to further injuries and hinder recovery. To avoid this mistake, athletes should focus on proper form and technique when performing injury rehabilitation exercises. This may include working with a physical therapist or coach to ensure that they are performing exercises correctly.
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are essential for optimal recovery, improved performance, and reduced risk of future injuries. To optimize injury rehabilitation, athletes should avoid common mistakes such as focusing too much on short-term relief, neglecting mobility work, and performing exercises with poor form. By prioritizing long-term recovery and injury prevention, athletes can promote optimal recovery and improve their overall performance.

Measuring Progress and Adjusting Your Rehabilitation Program: Tracking Exercises and Goals
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each athlete’s injury and recovery process is unique, and it’s essential to measure progress and adjust the rehabilitation program accordingly. By tracking exercises, reps, and goals, athletes can ensure that they are making progress and can adjust their program as needed to optimize recovery and injury prevention.
To measure progress in injury rehabilitation, athletes should track their exercises, reps, and goals regularly. This may include keeping a rehabilitation journal or using a fitness app to log exercises and reps. By tracking their progress, athletes can identify areas where they are improving and areas where they may need to focus more attention. For example, if an athlete notices that they are struggling with a particular exercise, they may need to adjust their form or seek additional guidance from a physical therapist or coach.
In addition to tracking exercises and reps, athletes should also set specific goals for their injury rehabilitation. These goals should focus on both recovery and injury prevention. For example, an athlete may set a goal to regain full range of motion in a joint or to improve their strength and flexibility. By setting specific goals, athletes can stay motivated and focused during injury rehabilitation.
As athletes progress in their injury rehabilitation, they may need to adjust their program to continue making progress. This may include increasing the intensity or frequency of exercises, adding new exercises, or adjusting the form or technique. By regularly measuring progress and adjusting their program, athletes can ensure that they are making optimal progress and reducing their risk of future injuries.
To optimize injury rehabilitation, athletes should avoid common mistakes such as focusing too much on short-term relief, neglecting mobility work, and performing exercises with poor form. By prioritizing long-term recovery and injury prevention, athletes can promote optimal recovery and improve their overall performance. By measuring progress and adjusting their rehabilitation program accordingly, athletes can ensure that they are making optimal progress and reducing their risk of future injuries.
Injury rehabilitation strategies for athletes are essential for optimal recovery, improved performance, and reduced risk of future injuries. By measuring progress and adjusting their rehabilitation program accordingly, athletes can ensure that they are making optimal progress and reducing their risk of future injuries. By avoiding common mistakes and prioritizing long-term recovery and injury prevention, athletes can optimize their injury rehabilitation and improve their overall performance.