Understanding Shin Splints: Causes and Symptoms
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are a common ailment among athletes and individuals engaging in high-impact activities. This condition manifests as pain and tenderness along the tibia, or shin bone. The discomfort arises from inflammation of the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue surrounding the tibia. Several factors contribute to the development of shin splints. Overuse is a primary cause, frequently observed in runners who increase their mileage or intensity too rapidly. Improper footwear, which does not provide adequate support or cushioning, can also place excessive stress on the lower leg. Muscle imbalances, particularly between the calf and shin muscles, can further contribute to the onset of shin splints. These imbalances can lead to uneven distribution of stress on the tibia, triggering inflammation. The typical symptoms include a dull ache or sharp pain along the inner edge of the shin bone, which may worsen during or after exercise. Tenderness to the touch in the affected area is also common. Understanding these causes and symptoms is crucial for anyone experiencing discomfort and looking to manage it effectively; this includes considering how to tape your leg for shin splints. Recognizing the symptoms early enables timely intervention, which could include methods such as learning how to tape your leg for shin splints, alongside rest and other conservative treatments. The objective is to minimize further aggravation and promote healing, utilizing a combination of strategies that address the root causes and alleviate the discomfort. As part of a comprehensive approach, learning how to tape your leg for shin splints can provide essential support to the lower leg, thus contributing to pain relief and facilitating the recovery process. When seeking solutions, it’s imperative to differentiate between mild discomfort and more severe symptoms, guiding the appropriate course of action. Therefore, understanding why this pain appears is vital, before applying any method like learning how to tape your leg for shin splints, to effectively manage the condition. It’s also important to remember that understanding the causes of shin splints and the potential benefits of taping is essential before applying techniques to effectively handle and alleviate the condition.
When is Leg Taping Appropriate for Shin Splints Relief
Taping the leg can be a beneficial strategy for managing shin splints, particularly in mild to moderate cases. This method provides support to the lower leg, helping to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with this condition. Understanding when and why taping is appropriate can greatly enhance its effectiveness. When considering how to tape your leg for shin splints, it is crucial to evaluate the severity of the symptoms. Taping is often a good option when the pain is manageable and does not significantly hinder daily activities. It works best when integrated into a broader treatment plan that includes rest, ice application, and gentle stretching exercises. The purpose of taping is to reduce stress on the affected muscles and tissues, allowing them to heal. However, it is important to recognize that taping is not a standalone solution for shin splints but an adjunct therapy that complements other conservative treatments. Taping can be particularly helpful for athletes and individuals who need some level of activity, offering extra support and comfort during movement. This temporary relief can assist in maintaining some level of physical activity while managing shin splint discomfort. Another benefit of learning how to tape your leg for shin splints is the potential to reduce inflammation and provide proprioceptive feedback, which can help in correcting any underlying biomechanical issues. Nevertheless, one must be aware of situations where taping is not advisable. For example, in cases of severe pain that does not improve with rest, suspected stress fractures, or significant swelling and bruising, taping should be avoided. In such scenarios, a medical professional should be consulted for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Applying tape when the underlying condition is more serious may mask the symptoms, delay appropriate medical care, and worsen the injury. The appropriate use of taping for shin splints also means understanding the limitations of this technique. It’s essential to combine taping with proper rest periods, appropriate footwear, and tailored exercises to promote healing and prevent recurrence. Taping should be viewed as a part of an encompassing strategy focused on long-term shin splint management. Therefore, if considering how to tape your leg for shin splints, remember that it’s a valuable tool when used correctly and in combination with other conservative methods, but should not replace professional medical advice, especially in more severe cases.
Preparing for the Leg Taping Process
Before starting the process of how to tape your leg for shin splints, meticulous preparation is essential to ensure the tape adheres properly and provides maximum support. Begin by thoroughly cleaning the lower leg area with mild soap and water, removing any dirt, oils, or lotions that may interfere with the tape’s grip. If there is significant hair on the lower leg, consider gently shaving the area to allow the tape to adhere directly to the skin; this step is crucial for the efficacy of the taping and to reduce discomfort upon removal. Gather all the necessary supplies before you begin. The key items include athletic tape, which is often preferred for its rigidity and support, or kinesiology tape, known for its flexibility and ability to mimic the skin’s elasticity. It’s also advisable to have a sharp pair of scissors on hand to cut the tape to the desired length. Understanding how to tape your leg for shin splints effectively requires accurate measurement of the tape to ensure the correct support without restricting movement. To measure the tape, start from just above the ankle bone and extend the tape along the shin towards the area of tenderness or the lower part of the knee. It is always better to cut a piece longer than you anticipate, because you can always trim the excess, so start long rather than short, or you may have to restart. This measured length will serve as the base piece of tape for the first application, and each piece after should be measured using the initial measurement as a guide. For areas that require additional support, you may need to measure smaller pieces. The goal is to have enough tape available to complete the initial application and any additional techniques you may be considering. Lay out the tape on a clean surface to keep it from getting contaminated or inadvertently stuck to other materials. All of these preparations before you proceed how to tape your leg for shin splints will optimize the process, minimizing skin irritation and maximizing therapeutic benefits.
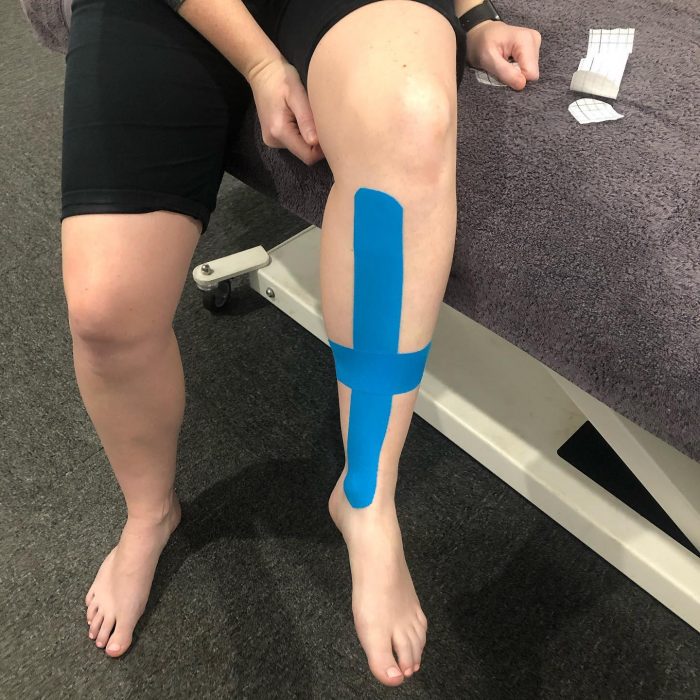
How to Tape Your Leg for Shin Support: Step-by-Step Instructions
To effectively apply tape for shin splint relief, start by positioning the leg with the foot flexed upward, as this will stretch the muscles and allow for proper tape application. The initial step in how to tape your leg for shin splints involves anchoring the tape just below the knee. Take the end of the athletic tape or kinesiology tape and, without any stretch, adhere it to the front of your lower leg, a few inches below the kneecap. It is crucial to ensure this anchor point is secure before proceeding, as this provides the foundation for the rest of the application. Once anchored, begin to apply the tape down the shin, directly over the area of pain. The key here is to maintain a light to moderate tension, depending on the type of tape used; athletic tape should be applied with minimal stretch, while kinesiology tape can be applied with slight stretch for additional support. Gently apply the tape along the shin bone, following the path of the pain. Avoid pulling the tape too tightly, as this can cause discomfort or skin irritation. The tape should extend down towards the ankle, finishing a few inches above the ankle bone. For some individuals, a second strip of tape may be beneficial. If required, apply this second strip parallel to the first, overlapping by about half the width of the tape. This additional strip adds further support and stability. It is also crucial to smooth the tape down and avoid any wrinkles, to maximize comfort and prevent the tape from pulling on the skin. The correct application of how to tape your leg for shin splints can greatly enhance support and alleviate pain. For individuals using kinesiology tape, you can round the corners before applying to reduce the possibility of the tape peeling. After application, lightly rub the tape to activate the adhesive, ensuring it’s firmly adhered to the skin. When working on how to tape your leg for shin splints using athletic tape, do not stretch the tape on the skin, but rather stretch the muscle by flexing your foot upwards. In contrast, kinesiology tape can be stretched to provide extra support. In the case of kinesiology tape, it can be applied in a ‘Y’ shape. Anchor the base of the ‘Y’ below the pain point. The tails of the ‘Y’ go up towards the knee, flanking the shinbone. Visual aids can prove invaluable when learning how to tape your leg for shin splints. Be sure to follow any specific recommendations provided by your healthcare professional for your particular case. The direction of application, and the level of tension used, are all variables that can impact the effectiveness of the tape, thus attention to detail during application is paramount. This method is a great way to learn how to tape your leg for shin splints to support the lower leg muscles.
Advanced Taping Techniques for Added Stability
While the basic method of how to tape your leg for shin splints provides a foundational level of support, advanced taping techniques can offer enhanced stability and compression for those needing extra relief. These methods, however, are generally recommended for individuals who have some experience with taping and are comfortable with the application process. One such technique involves applying additional strips of tape in a criss-cross pattern over the initial taping. To execute this, begin by placing the first strip diagonally across the previously taped area, starting from the inner side of the lower leg and moving towards the outer side, applying moderate tension. A second strip of tape should be applied in the opposite diagonal direction, forming an ‘X’ over the primary tape, ensuring a consistent overlap of about half the tape width for secure adhesion. This criss-cross method provides multi-directional support and is particularly useful for controlling excessive pronation of the foot, which can contribute to shin splint pain. This method reinforces how to tape your leg for shin splints, improving support.
Another advanced method involves creating a ‘tear drop’ configuration. This is achieved by anchoring the tape on the inner side of the leg just below the knee, then bringing the tape down and around the area where the shin splints pain is most intense, and then back up to the original anchoring point, creating a tear drop shape. The ‘tear drop’ provides targeted compression and support around the affected area. When using this method, it’s crucial to avoid wrapping the tape too tightly, as this can restrict blood flow and exacerbate discomfort. It’s also vital that the skin is clean and free of any lotions or oils to ensure proper tape adhesion and to help reduce the chance of skin irritation. The goal of these advanced approaches is to improve the effectiveness of how to tape your leg for shin splints, so individuals can continue their activities with decreased pain and the needed support. Keep in mind, these advanced techniques are not for beginners and it is important to learn basic taping properly first, and then move on to advanced techniques to ensure the best outcomes. This guidance provides a more comprehensive understanding of how to tape your leg for shin splints using these methods.
Post-Taping Considerations: Care and Removal
Proper care of the taped area following the application is essential to maximize the benefits of how to tape your leg for shin splints and to prevent skin irritation or other complications. Once the tape is applied, it is generally recommended to keep it in place for a specific duration, often ranging from a few hours to a few days, depending on the type of tape and the individual’s response. It’s important to avoid exposing the tape to excessive moisture, which can weaken the adhesive and potentially cause skin maceration. Activities that cause excessive sweating or immersion in water should be limited or avoided. When showering, consider using a waterproof cover or carefully patting the tape dry afterward without rubbing. Rubbing the tape is not recommended; friction can lead to skin irritation and might cause the tape to peel prematurely, impacting the effectiveness of how to tape your leg for shin splints. Furthermore, tight clothing should be avoided, as it can also cause the tape to lift. Regularly check the skin beneath the tape for any signs of irritation, such as redness, itching, or blistering. If these symptoms appear, the tape should be removed immediately, and further taping may not be advisable without consulting a healthcare professional. Removing the tape carefully is crucial. Avoid abruptly pulling the tape off, as this can cause pain and skin damage. Instead, gently peel the tape off slowly, preferably in the direction of hair growth, to minimize discomfort and potential for tearing the skin. Using baby oil or adhesive remover can facilitate the process if the tape is particularly stubborn. Apply the oil or remover along the edge of the tape and allow it to seep underneath for a few minutes before slowly and carefully peeling it away. After the tape is removed, the skin should be assessed for any lingering irritation or damage. Applying a gentle moisturizer can help to soothe any discomfort and restore the skin’s natural moisture. This step is particularly useful if the skin was slightly irritated by the adhesive. It is also important to allow the skin to breathe and avoid re-taping the same area immediately, especially if any signs of irritation were present. If planning to reapply the tape, ensure that the skin is clean, dry, and free of any residue from previous applications. How to tape your leg for shin splints effectively includes understanding the importance of proper aftercare and removal techniques, which are equally as crucial as the application itself. Understanding these post-taping guidelines can improve the experience, effectiveness, and overall benefits of taping, while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Combining Taping with Other Shin Splints Treatments
While learning how to tape your leg for shin splints can offer significant pain relief, it is crucial to understand that taping is not a standalone solution for this condition. Effective management of shin splints requires a comprehensive approach that integrates taping with other conservative treatments. Resting the affected leg is paramount; it allows the inflamed tissues to recover and reduces the stress that initially caused the pain. Engaging in activities that aggravate the pain should be avoided, which provides an opportunity to heal. Complementary to rest, a routine of targeted stretching exercises contributes significantly to reducing the tightness in the calf muscles and around the shin. By increasing the flexibility of the muscles, individuals can prevent further strain on the shin bone. Strengthening exercises, especially those that focus on the lower leg and ankle, are also integral. Stronger muscles can provide better support and stability, thus minimizing the risk of future shin splint problems. Additionally, the type of footwear worn plays a critical role in preventing shin splints. Proper arch support and cushioning within shoes will help to absorb shock and reduce the pressure on the shins during activities. Individuals should be cognizant of their specific needs when selecting their athletic footwear, ensuring they align with the demands of the sport they engage in. When determining how to tape your leg for shin splints, understand that the benefits are enhanced when used in conjunction with these therapies. The tape serves as an external support mechanism, aiding in pain reduction and tissue stabilization but without addressing the underlying causes. Therefore, the synergistic effects of rest, stretching, strengthening, and appropriate footwear are essential to ensure a holistic and successful recovery from shin splints. Ignoring any of these complementary treatments might result in a slow recovery process or the potential for reoccurrence, even when individuals are diligent in how to tape your leg for shin splints. The proper combination of these methods forms a cornerstone for long-term management and recovery, ensuring that individuals can return to their activities without the worry of persistent shin splint pain. It should be emphasized that each of these components works together to facilitate healing, and therefore should not be considered optional.
Context_8: Concluding this guide, long-term management and prevention of shin splints are crucial for sustained comfort and athletic performance. A proactive approach, rather than solely relying on techniques like how to tape your leg for shin splints, is essential. Gradual progression in training intensity forms a cornerstone of prevention; suddenly increasing the duration or intensity of activities can overwhelm the muscles and bones of the lower leg, leading to shin splints. Wearing appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning is equally vital. Footwear should be selected based on activity type and individual foot structure, and should be replaced regularly as cushioning degrades. Furthermore, a targeted exercise routine incorporating both strengthening and flexibility exercises for the calf muscles, tibialis anterior, and surrounding tissues contributes significantly to long-term prevention. Strengthening exercises enhance muscle resilience, while flexibility exercises improve range of motion and reduce strain on the tibia and connective tissues. Paying close attention to body signals during exercise and rest periods is also of paramount importance. Discomfort or pain is a warning; ignoring these can lead to aggravated shin splints and possibly stress fractures. Therefore, when learning how to tape your leg for shin splints, one must remember this is a temporary tool in a larger recovery process. It’s also important to include adequate rest days in any training regimen to enable tissues to repair and adapt; a balance between activity and rest is essential to prevent overuse injuries. Additionally, addressing any underlying biomechanical issues, such as flat feet or overpronation, with custom orthotics can reduce stress on the lower legs. While knowing how to tape your leg for shin splints is beneficial for managing pain, it is more effective when integrated into a comprehensive preventative strategy. If these preventive measures are not enough and shin splints become a chronic issue, consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and personalized advice to address the root causes of the problem. Continuous monitoring of the leg, proper footwear selection, a thoughtful and gradual training program, and listening to your body are the best methods to avoid recurring shin splint injuries. Therefore, always prioritize prevention alongside knowing how to tape your leg for shin splints.