Vitamin B12: A Vital Nutrient for Optimal Health
Vitamin B1
Understanding Vitamin B12: Sources and Absorption
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the human body. It is vital for the production of red blood cells, nerve cells, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to various health issues, making it essential to recognize the signs and seek appropriate measures. Natural sources of Vitamin B12 are primarily found in animal-based foods, such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. The absorption of Vitamin B12 in the body is a complex process that involves intrinsic factor, a protein secreted by the stomach’s parietal cells. This protein binds to Vitamin B12, facilitating its absorption in the small intestine.
Individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet may be at a higher risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency due to the lack of dietary sources. Moreover, certain conditions, such as pernicious anemia, gastrointestinal disorders, and the use of certain medications, can also affect the absorption of Vitamin B12, leading to deficiency.
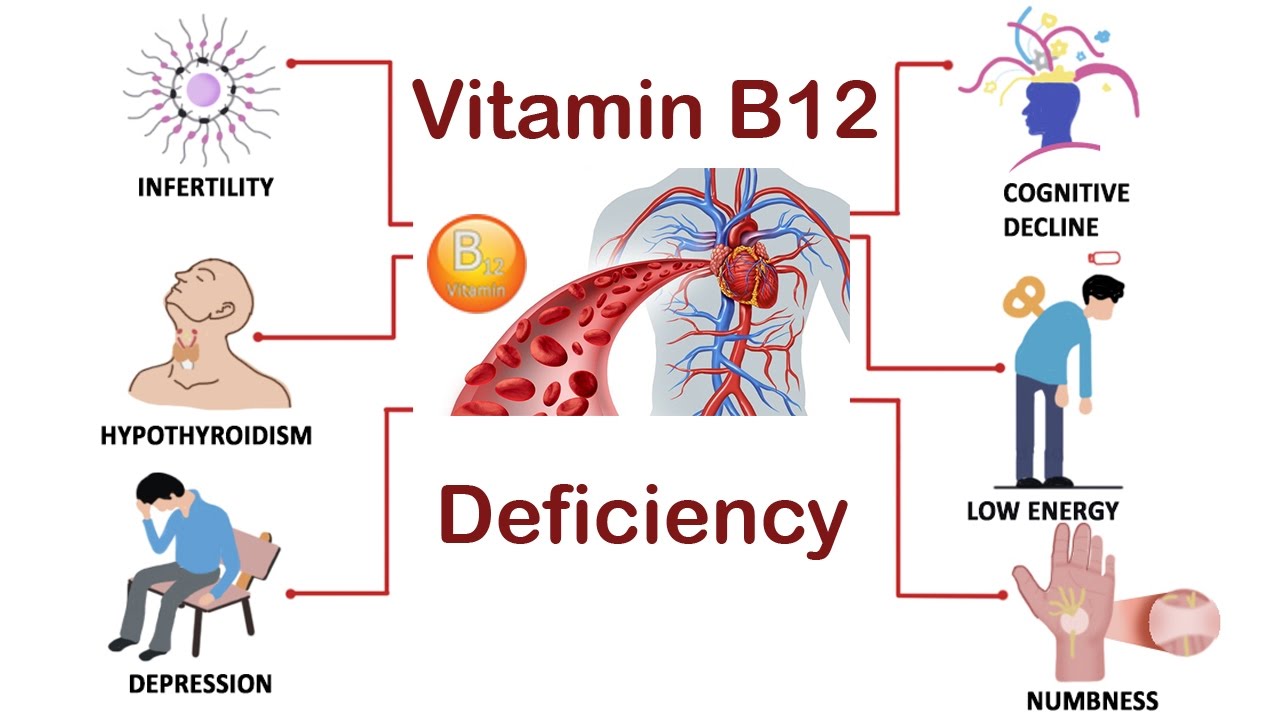
Recognizing the Subtle Signs of Vitamin B1
The Progression of Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Serious Health Concerns
Vitamin B12 deficiency, if left untreated, can lead to severe health consequences. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent these potential complications. Anemia is one of the most common long-term health consequences of Vitamin B12 deficiency. This condition occurs when the body lacks sufficient red blood cells to carry oxygen to its tissues. As a result, individuals with anemia may experience fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Neurological disorders are another serious health concern associated with Vitamin B12 deficiency. The lack of this essential nutrient can damage the protective covering of nerves, known as the myelin sheath, leading to neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling sensations, and balance problems. In severe cases, Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause cognitive decline, memory loss, and even dementia.
Furthermore, Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of depression, mood disorders, and mental health issues. Research suggests that this essential nutrient plays a vital role in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain. Therefore, a deficiency in Vitamin B12 can affect mood and cognitive function.
Preventing these severe health consequences requires early detection and intervention. If you suspect that you have a Vitamin B12 deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and guidance. By addressing the deficiency promptly, you can prevent long-term health complications and maintain optimal health.
Diagnosing Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Lab Tests and Medical Evaluation
If you suspect that you have a Vitamin B12 deficiency, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and guidance. The diagnostic process for Vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves laboratory tests and medical evaluations. A common blood test used to diagnose Vitamin B12 deficiency measures the level of this essential nutrient in the blood. This test can help healthcare professionals determine if your Vitamin B12 levels are within the normal range. However, it is important to note that a low Vitamin B12 level in the blood does not always indicate a deficiency, as other factors can affect the test results.
In addition to blood tests, healthcare professionals may also perform medical evaluations to assess the severity of the deficiency and its impact on the body. These evaluations may include a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and a discussion of your symptoms.
It is important to note that diagnosing Vitamin B12 deficiency can be complex, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other medical conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and guidance. Self-diagnosis and self-treatment can be dangerous and may lead to further health complications.
Treatment Options for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
If you have been diagnosed with Vitamin B12 deficiency, there are various treatment options available to help restore your levels to normal. The appropriate treatment plan will depend on the severity and underlying cause of the deficiency. Dietary Changes: If your Vitamin B12 deficiency is due to a lack of dietary sources, incorporating more animal-based foods into your diet can help increase your intake of this essential nutrient. Foods rich in Vitamin B12 include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. However, if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, you may need to consider other options, such as fortified foods or supplements.
Oral Supplements: Oral supplements are another option for treating Vitamin B12 deficiency. These supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquids. They can be taken daily or as directed by a healthcare professional. It is important to note that oral supplements may not be as effective as injections for individuals with severe deficiencies or absorption issues.
Injections: Injections are a common treatment option for Vitamin B12 deficiency, particularly for individuals with severe deficiencies or absorption issues. These injections can be administered in a healthcare professional’s office or at home, depending on the severity of the deficiency and the individual’s preferences. The frequency and duration of the injections will depend on the severity of the deficiency and the individual’s response to treatment.
It is important to seek professional medical advice when considering treatment options for Vitamin B12 deficiency. A healthcare professional can help determine the appropriate treatment plan based on the underlying cause and severity of the deficiency. Self-treatment can be dangerous and may lead to further health complications.
Preventing Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Dietary Strategies and Supplementation
Preventing Vitamin B12 deficiency is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing serious health consequences. Here are some practical tips for preventing Vitamin B12 deficiency through dietary strategies and supplementation: Dietary Strategies: Incorporating more animal-based foods into your diet can help increase your intake of Vitamin B12. Foods rich in this essential nutrient include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, consider incorporating fortified foods, such as fortified cereals, plant-based milk, and nutritional yeast, into your diet. However, it is important to note that dietary strategies may not be enough to prevent Vitamin B12 deficiency in some individuals, particularly those with absorption issues.
Supplementation: Supplementation is another option for preventing Vitamin B12 deficiency. Oral supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquids. They can be taken daily or as directed by a healthcare professional. It is important to choose a high-quality supplement and follow the recommended dosage to ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Combination Approach: A combination approach that includes both dietary strategies and supplementation may be the most effective way to prevent Vitamin B12 deficiency. By incorporating both strategies, you can ensure that you are getting enough Vitamin B12 to meet your body’s needs and prevent deficiency.
It is important to note that the benefits and drawbacks of various options may vary depending on the individual’s dietary preferences, absorption capabilities, and overall health. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and advice on preventing Vitamin B12 deficiency. By taking proactive measures to prevent Vitamin B12 deficiency, you can maintain optimal health and prevent serious health consequences.
Maintaining Optimal Vitamin B12 Levels: Regular Monitoring and Lifestyle Adjustments
Maintaining optimal Vitamin B12 levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Regular monitoring of Vitamin B12 levels can help ensure that you are getting enough of this essential nutrient and prevent deficiency. Here are some tips for maintaining optimal Vitamin B12 levels through regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments: Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of Vitamin B12 levels can help detect deficiency early and prevent serious health consequences. Blood tests are the most common method for measuring Vitamin B12 levels. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and guidance on monitoring Vitamin B12 levels.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Lifestyle adjustments can also play a role in maintaining optimal Vitamin B12 levels. Here are some tips to consider:
Balanced Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet that includes animal-based foods can help ensure that you are getting enough Vitamin B12. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, consider incorporating fortified foods or supplements into your diet.
Cooking Techniques: Cooking techniques can affect the absorption of Vitamin B12. For example, cooking meat, fish, and poultry thoroughly can help increase the absorption of Vitamin B12.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can affect the absorption of Vitamin B12 and lead to deficiency. Limiting alcohol consumption can help maintain optimal Vitamin B12 levels.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect the absorption and utilization of Vitamin B12. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help maintain optimal Vitamin B12 levels.
Regular Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve the absorption and utilization of Vitamin B12. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
It is important to note that individual needs and responses to lifestyle adjustments may vary. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and advice on maintaining optimal Vitamin B12 levels. By prioritizing your health and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can maintain optimal Vitamin B12 levels and prevent deficiency.