Understanding Supination: Causes and Consequences
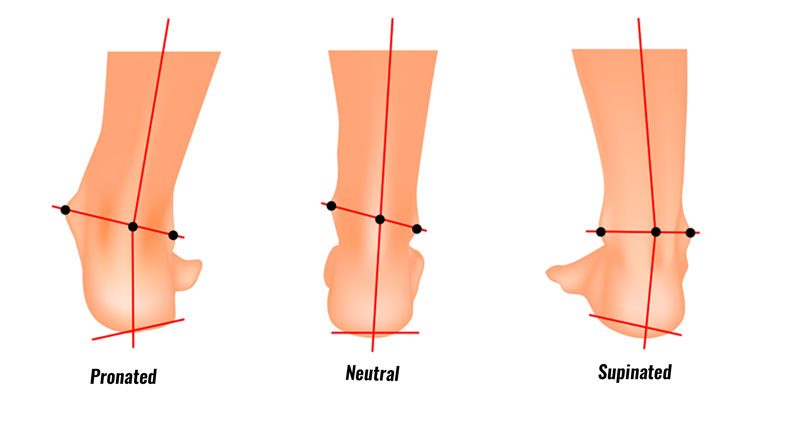
Supination of the foot, also known as underpronation, is a common biomechanical issue that occurs when the outer edge of the foot bears the majority of the weight during walking or running. This condition can result from various factors, including structural abnormalities, muscle imbalances, or inadequate footwear. The consequences of supination can extend beyond the foot, affecting the ankle, knee, hip, and even the lower back.
Individuals with supination often experience issues such as ankle sprains, plantar fasciitis, and knee pain. Ankle sprains occur due to the foot’s inability to provide adequate support during movement, leading to excessive strain on the ligaments. Plantar fasciitis, a painful inflammation of the tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes, can develop due to the increased tension on the plantar fascia caused by supination. Lastly, knee pain may arise from the altered alignment and biomechanics of the lower limb, resulting in excessive stress on the knee joint.
Identifying Supination: Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of supination is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Common indicators of supination include excessive wear on the outer edge of the shoe sole, foot pain, and poor shock absorption. These symptoms may worsen over time if left untreated, potentially leading to chronic issues and discomfort.
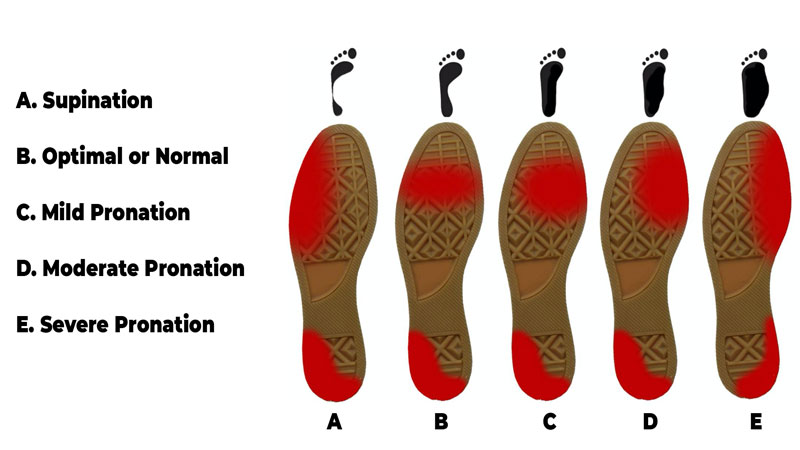
To self-assess for supination, examine the soles of your shoes for uneven wear patterns. If the outer edge of the sole shows significantly more wear than the inner edge, this may suggest supination. Additionally, observe your feet during weight-bearing activities, such as walking or running. A supinated foot often appears to roll outward, causing the arch to become more pronounced. This motion can lead to inefficient shock absorption and increased stress on the foot and leg muscles.
If you suspect supination, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. A qualified healthcare provider, such as a podiatrist or physical therapist, can perform a gait analysis to determine if supination is present and recommend appropriate treatment options. Early intervention and addressing the root cause of supination can significantly improve symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Addressing Supination: Conservative Treatment Options
Addressing the root cause of supination is essential for long-term improvement and the prevention of chronic issues. Various conservative treatment options are available, including stretching and strengthening exercises, orthotics, and modifying footwear. These methods aim to improve foot biomechanics, increase stability, and reduce the risk of injury.
Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility, range of motion, and arch strength. Regularly performing these exercises can alleviate supination-related symptoms and promote overall foot health. Incorporating exercises targeting the calf, ankle, and foot muscles into your routine can significantly contribute to addressing supination of the foot.
Orthotics are specialized devices designed to provide additional support and correct biomechanical issues. Custom-made or over-the-counter orthotics can help correct supination by realigning the foot and redistributing pressure more evenly across the sole. Consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable orthotic device for your needs.
Modifying footwear is another crucial aspect of addressing supination. Shoes with adequate arch support, shock absorption, and motion control can significantly improve foot biomechanics and alleviate supination symptoms. When selecting running shoes or everyday footwear, look for models that offer the necessary features to support your feet and promote a more natural gait.
In summary, addressing the root cause of supination is vital for long-term improvement. Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises, using orthotics, and modifying footwear can help alleviate supination-related symptoms and promote overall foot health. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
Stretching Exercises for Supination
Stretching exercises play a crucial role in alleviating supination-related symptoms by improving flexibility and range of motion in the calf, ankle, and foot muscles. Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can significantly contribute to addressing supination of the foot.
Calf Stretch
Instructions: Stand facing a wall with one foot forward and one foot back, both feet flat on the ground. Lean forward, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in your calf muscles. Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides. Repeat three times on each side.
Ankle Circles
Instructions: Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Lift one foot off the ground and rotate your ankle in a circular motion, first clockwise, then counterclockwise. Perform 10 rotations in each direction, then switch to the other foot. This exercise helps improve ankle mobility and range of motion.
Toe Curls
Instructions: Sit on a chair with a towel placed under your feet. Using only your toes, scrunch the towel towards you, then push it back out. Repeat this exercise for 30 seconds, then rest for 30 seconds. Perform three sets.
Arch Stretch
Instructions: Sit on the floor with your legs extended in front of you. Loop a resistance band or a towel around the ball of one foot. Gently pull back on the band or towel, keeping your knee straight, until you feel a stretch in your arch. Hold for 30 seconds, then switch to the other foot. Repeat three times on each side.
Incorporating these stretching exercises into your daily routine can help alleviate supination symptoms and promote overall foot health. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
Strengthening Exercises for Supination
Strengthening the muscles responsible for maintaining the foot’s arch can help improve stability and alleviate supination-related symptoms. Incorporating these exercises into your routine can contribute to addressing the root cause of supination of the foot.
Short Foot Exercise
Instructions: Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Without curling your toes, try to slide your big toe towards the heel of your foot while keeping the ball of your foot on the ground. Hold for 5 seconds, then relax. Perform three sets of 10 repetitions.
Heel Raises
Instructions: Stand behind a chair or a sturdy object for support. Slowly lift your heels off the ground, rising onto the balls of your feet. Hold for 3 seconds, then slowly lower your heels back to the ground. Perform three sets of 10 repetitions.
Toe Walking
Instructions: Stand up straight and walk on your tiptoes for 20 seconds. Rest for 20 seconds, then repeat. Perform three sets.
Arch Lifts
Instructions: Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Lift the arch of your foot by contracting the muscles on the bottom of your foot. Hold for 5 seconds, then relax. Perform three sets of 10 repetitions.
Incorporating these strengthening exercises into your daily routine can help enhance the foot’s arch strength and stability, ultimately addressing the root cause of supination. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
Selecting the Right Footwear for Supination
Proper footwear plays a crucial role in managing supination by providing adequate arch support, shock absorption, and motion control. Choosing the right running shoes and everyday footwear can significantly contribute to addressing the root cause of supination of the foot.
Running Shoes for Supination
When selecting running shoes for supination, look for models that offer the following features:
- Adequate arch support: Shoes with a firm midsole and built-in arch support can help maintain the foot’s natural arch and prevent excessive pronation or supination.
- Stability features: Look for shoes with dual-density midsoles or medial posts, which provide additional support and help control motion.
- Shock absorption: Cushioning materials in the heel and forefoot can help absorb impact and reduce stress on the foot and leg muscles.
- Motion control: Shoes with motion control features can help guide the foot through the gait cycle and prevent excessive supination.
Everyday Footwear for Supination
For everyday footwear, prioritize the following features:
- Adequate arch support: Choose shoes with a firm sole and built-in arch support to maintain the foot’s natural arch.
- Shock absorption: Opt for shoes with cushioning materials in the heel and forefoot to absorb impact and reduce stress on the foot and leg muscles.
- Motion control: Select shoes with a stable heel counter and a firm sole to help guide the foot through the gait cycle and prevent excessive supination.
Some recommended shoe models for supination include the Brooks Adrenaline GTS, ASICS Gel-Kayano, and New Balance 860. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional or a specialized shoe store to ensure the best fit for your specific needs.
Orthotics and Supination: Finding the Right Support
Orthotics are specialized devices designed to support, align, or correct the foot’s biomechanics, providing additional arch support and addressing supination. Both custom-made and over-the-counter orthotics can help alleviate supination-related symptoms and contribute to long-term improvement.
Custom-Made Orthotics
Custom-made orthotics are designed based on a mold or digital scan of your foot, taking into account your unique foot structure, biomechanics, and specific needs. These devices typically offer a higher level of support, control, and durability compared to over-the-counter options. However, they tend to be more expensive and may require a prescription from a healthcare professional.
Over-the-Counter Orthotics
Over-the-counter orthotics are prefabricated devices available at pharmacies, sporting goods stores, or online. These orthotics are generally more affordable and can be a good starting point for individuals with mild to moderate supination. However, they may not provide the same level of support and customization as custom-made orthotics.
Selecting the Right Orthotic Device
When choosing an orthotic device, consider the following factors:
- Comfort: Ensure the orthotic feels comfortable and supportive, without causing excessive pressure or discomfort in any area.
- Support: Look for orthotics that provide adequate arch support and motion control to help correct supination.
- Durability: Opt for devices made from durable materials that can withstand regular use and maintain their shape and support over time.
- Activity level: Select orthotics that are suitable for your specific activities, such as running, walking, or standing for long periods.
Some recommended over-the-counter orthotic options for supination include Superfeet Green or Blue insoles and Powerstep Pinnacle insoles. However, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific needs.
Red Flags and When to Seek Professional Help
While conservative treatment options can be effective for many individuals with supination, certain situations warrant professional medical intervention. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience any red flags or if your symptoms do not improve with conservative treatment.
Red Flags
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe pain or swelling in the foot, ankle, or leg
- Limited mobility or inability to walk
- A history of injuries or fractures in the affected area
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in the foot
- Visible deformity or abnormal growths in the foot or ankle
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Consider consulting a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the foot, ankle, or leg despite trying conservative treatment options
- Difficulty finding appropriate footwear or orthotics that provide adequate support and relief
- A noticeable change in foot structure or gait pattern
- Concerns about the progression or severity of your symptoms
Healthcare professionals who can help diagnose and treat supination include podiatrists, orthopedic surgeons, sports medicine physicians, and physical therapists. These professionals can perform a thorough evaluation, recommend appropriate treatment options, and monitor your progress to ensure long-term improvement.
Remember, addressing the root cause of supination is crucial for long-term improvement and the prevention of further complications. If you are unsure about your symptoms or treatment options, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations.