The Significance of Heart Rate Zones in Exercise
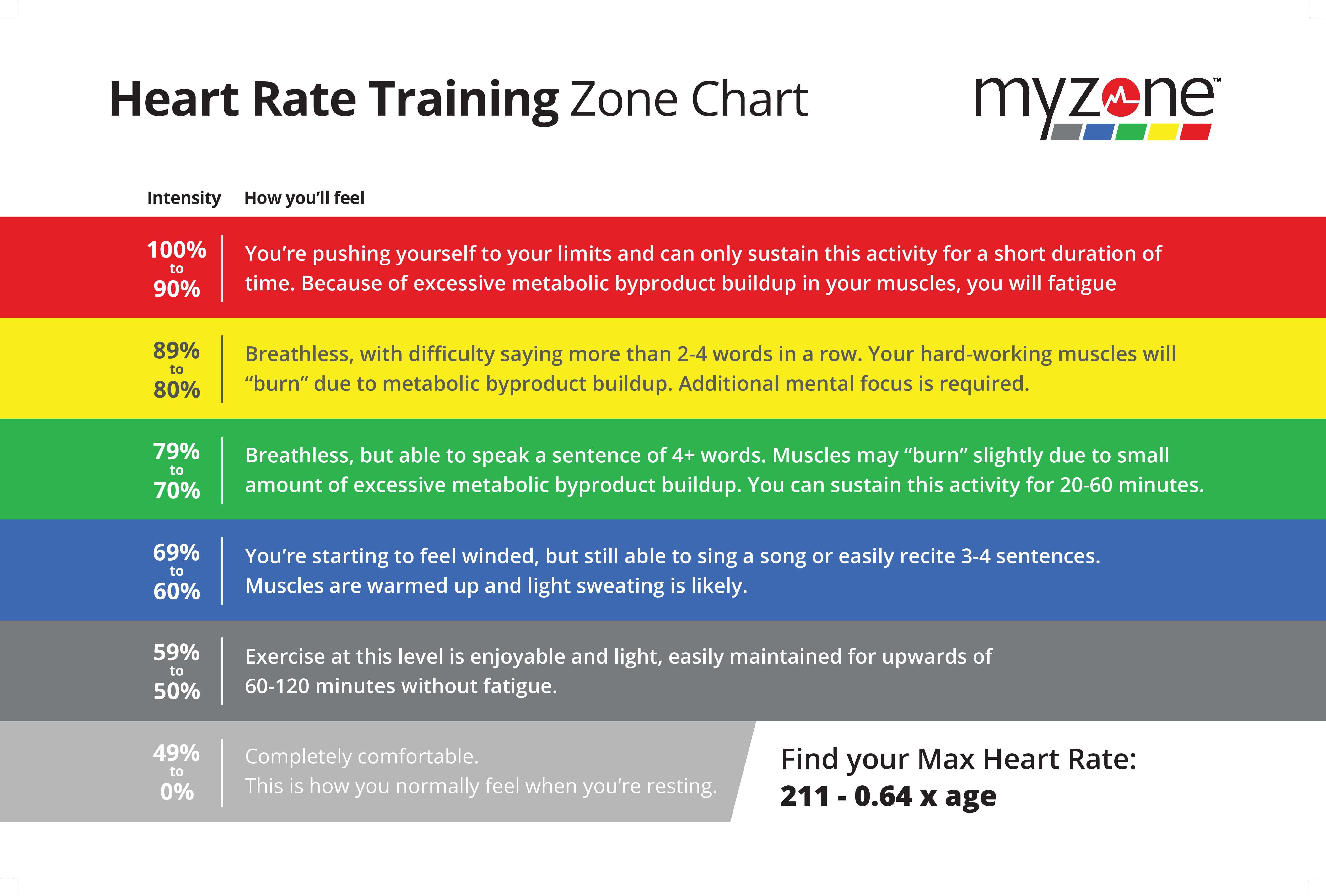
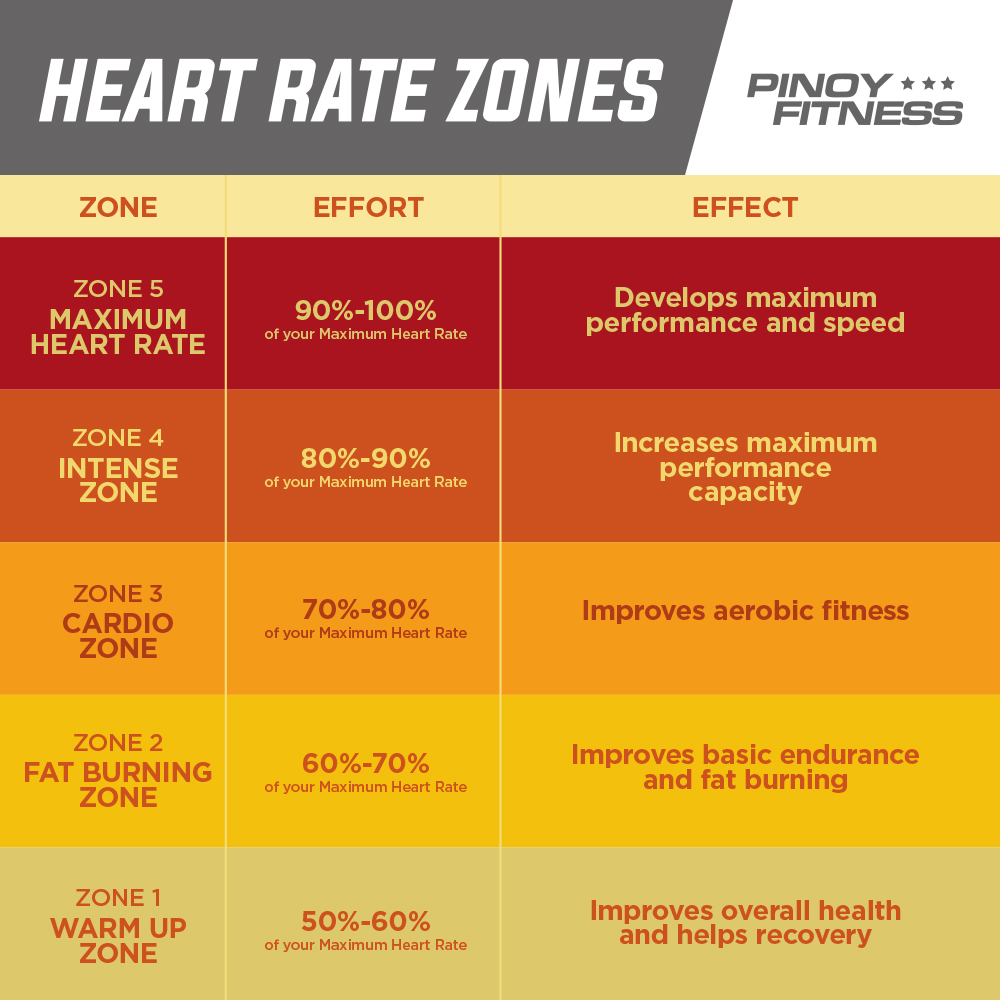
Understanding the concept of heart rate zones is crucial for optimizing your exercise routine and achieving your fitness goals. Heart rate zones are divided based on a percentage of your maximum heart rate, providing a range of exercise intensities. Among these zones, Zone 2 training has gained significant attention due to its numerous benefits, including improved cardiovascular fitness, increased fat burning, and enhanced endurance. Consequently, learning how to calculate Zone 2 heart rate is essential for any fitness enthusiast.
Monitoring your heart rate during exercise can help you gauge your intensity, ensuring that you’re training at the appropriate level to meet your objectives. By understanding your target heart rate zones, you can tailor your workouts to focus on specific aspects of fitness, such as aerobic capacity, anaerobic threshold, or recovery. Consequently, this knowledge empowers you to make data-driven decisions about your training, ultimately leading to more effective and efficient workouts.
What is Zone 2 Heart Rate?
Zone 2 heart rate is a specific range of heartbeats per minute that corresponds to a moderate level of exercise intensity. It is typically defined as a percentage of your maximum heart rate, usually between 50% and 70%. To calculate your personalized Zone 2 heart rate, you can use the following formula:
Zone 2 Heart Rate = (Maximum Heart Rate x 0.5) to (Maximum Heart Rate x 0.7)
For example, if your maximum heart rate is 180 beats per minute, your Zone 2 heart rate would be between 90 and 126 beats per minute. This range represents the ideal intensity for endurance training and improving cardiovascular fitness.
Zone 2 training is particularly beneficial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to build a solid aerobic base, increase fat burning, and enhance overall exercise efficiency. By training at this moderate intensity, you can improve your body’s ability to utilize fat as a fuel source, reduce the risk of injury, and promote recovery. Furthermore, Zone 2 training can help you develop a strong aerobic foundation, which is crucial for more intense workouts and competitive events.
How to Measure Your Heart Rate
To effectively incorporate Zone 2 training into your exercise routine, you need to know how to measure your heart rate accurately. There are several methods available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common techniques:
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices, such as heart rate monitors, smartwatches, and fitness trackers, offer a convenient and accurate way to measure your heart rate during exercise. These devices typically use a chest strap or wrist-based sensor to detect your heartbeat and display your heart rate in real-time. The primary advantage of wearable devices is their accuracy and ease of use. However, they can be expensive and may require charging or battery replacement.
Manual Methods
Manual methods for measuring heart rate involve locating your pulse and counting the number of beats per minute. You can find your pulse on your wrist, neck, or chest. While manual methods are less expensive and more accessible than wearable devices, they can be less accurate and more challenging to use during exercise, especially if your hands are sweaty or moving rapidly.
Smartphone Apps
Several smartphone apps can measure your heart rate using your phone’s camera or built-in sensors. These apps can be a cost-effective alternative to wearable devices, although their accuracy may vary depending on the app and your phone’s capabilities. Smartphone apps are convenient and easy to use, making them a popular choice for many fitness enthusiasts.
When choosing a method for measuring your heart rate, consider factors such as accuracy, convenience, cost, and ease of use. By selecting a method that meets your needs and preferences, you can effectively monitor your heart rate during Zone 2 training and optimize your exercise routine for maximum benefit.
Calculating Your Personalized Zone 2 Heart Rate
To calculate your personalized Zone 2 heart rate, you’ll need to consider several factors, including your age, resting heart rate, and maximum heart rate. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine your Zone 2 heart rate:
- Determine your maximum heart rate: The most common formula for estimating maximum heart rate is 220 minus your age. For example, if you’re 30 years old, your estimated maximum heart rate would be 190 beats per minute (bpm).
- Calculate your resting heart rate: Measure your heart rate while at rest, typically upon waking up in the morning. Count the number of beats per minute for 60 seconds or use a smartphone app to measure your heart rate automatically.
- Calculate your heart rate reserve (HRR): Subtract your resting heart rate from your maximum heart rate. For example, if your maximum heart rate is 190 bpm and your resting heart rate is 60 bpm, your HRR would be 130 bpm (190 – 60).
- Calculate your Zone 2 heart rate: Multiply your HRR by 0.55 and 0.7 to get the lower and upper limits of your Zone 2 heart rate. For example, if your HRR is 130 bpm, your Zone 2 heart rate would be between 71.5 bpm (130 x 0.55) and 91 bpm (130 x 0.7).
Remember that these calculations provide an estimate of your Zone 2 heart rate. Individual differences in fitness levels, genetics, and other factors can affect your actual Zone 2 heart rate. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor your heart rate during exercise and adjust your training intensity accordingly.
By calculating your personalized Zone 2 heart rate, you can tailor your exercise routine to your unique physiology and maximize the benefits of Zone 2 training. This targeted approach can help you improve your cardiovascular fitness, increase fat burning, and promote recovery, ultimately leading to better overall health and fitness.
Incorporating Zone
Maximizing the Benefits of Zone 2 Training
Zone 2 training offers numerous benefits for endurance athletes and fitness enthusiasts, including improved cardiovascular fitness, increased fat burning, and enhanced recovery. To maximize these benefits, consider the following tips:
Monitor Your Progress
Tracking your heart rate and exercise intensity during Zone 2 training can help you ensure that you’re staying within your target heart rate zone. Use a heart rate monitor or smartphone app to monitor your heart rate in real-time, and record your workouts to track your progress over time. This data can help you identify trends, adjust your training intensity, and stay motivated as you see your fitness levels improve.
Gradually Increase Intensity
While consistency is crucial in Zone 2 training, it’s also essential to gradually increase your exercise intensity to continue making progress. Aim to increase your training duration or intensity by no more than 10% per week to avoid overtraining and injury. This gradual progression can help you build a strong aerobic base, improve your cardiovascular fitness, and boost your overall exercise efficiency.
Mix Up Your Workouts
While Zone 2 training should form the foundation of your exercise routine, incorporating other types of workouts can help you achieve well-rounded fitness and prevent boredom. Consider adding high-intensity interval training (HIIT), strength training, or flexibility exercises to your workout routine to challenge your body in different ways and promote overall health and fitness.
Prioritize Recovery
Rest and recovery are just as important as exercise in Zone 2 training. Aim to get at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and take rest days as needed to allow your body to recover and rebuild. Additionally, consider incorporating active recovery techniques, such as foam rolling, stretching, or light exercise, to promote blood flow and aid in recovery.
Stay Hydrated and Fueled
Proper hydration and nutrition are essential for optimal performance and recovery during Zone 2 training. Aim to drink at least 8-10 cups of water per day, and increase your fluid intake as needed based on your exercise duration and intensity. Additionally, fuel your body with a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, to support your exercise goals and overall health.
By following these tips, you can maximize the benefits of Zone 2 training and improve your cardiovascular fitness, fat burning, and overall health. Remember to stay consistent, track your progress, and prioritize recovery to achieve your desired results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Zone 2 Training
Zone 2 training can be a powerful tool for improving cardiovascular fitness, increasing fat burning, and promoting recovery. However, there are several common mistakes that beginners and experienced athletes alike can make when incorporating Zone 2 training into their exercise routine. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid and strategies for staying on track:
Going Too Hard
One of the most common mistakes in Zone 2 training is pushing too hard and exceeding your target heart rate zone. Exercising at a higher intensity can lead to fatigue, injury, and suboptimal results. To avoid this mistake, focus on maintaining a conversational pace during your Zone 2 workouts, and use a heart rate monitor or smartphone app to ensure that you’re staying within your target heart rate range.
Going Too Easy
On the other hand, some athletes may not push themselves hard enough during Zone 2 training, leading to suboptimal results. While it’s essential to maintain a moderate intensity, you should still feel challenged during your Zone 2 workouts. To avoid this mistake, aim for a perceived exertion level of 3-4 out of 10, and focus on maintaining a steady, sustainable pace throughout your workout.
Neglecting Recovery
Recovery is just as important as exercise in Zone 2 training. Neglecting recovery can lead to fatigue, injury, and suboptimal results. To avoid this mistake, prioritize rest and recovery, and take rest days as needed. Additionally, consider incorporating active recovery techniques, such as foam rolling, stretching, or light exercise, to promote blood flow and aid in recovery.
Lack of Consistency
Consistency is key in Zone 2 training. Neglecting to consistently incorporate Zone 2 training into your exercise routine can lead to suboptimal results. To avoid this mistake, aim to incorporate Zone 2 training into your workout routine 2-3 times per week, and gradually increase your training duration and intensity over time.
Ignoring Progress
Ignoring progress can lead to stagnation and suboptimal results in Zone 2 training. To avoid this mistake, track your heart rate, exercise duration, and perceived exertion level during your Zone 2 workouts. Use this data to identify trends, adjust your training intensity, and stay motivated as you see your fitness levels improve.
By avoiding these common mistakes and focusing on consistency, patience, and progress, you can maximize the benefits of Zone 2 training and achieve your desired results. Remember to stay within your target heart rate zone, prioritize recovery, and track your progress to stay on track and avoid common pitfalls.
Success Stories and Real-Life Applications
Zone 2 training has helped countless athletes and fitness enthusiasts achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall health. Here are some success stories and real-life applications of Zone 2 training, demonstrating its effectiveness and versatility:
From Couch Potato to Marathon Runner
After years of sedentary living, Jane decided to take up running to improve her health and fitness. She started with walk/run intervals, gradually increasing her running time and distance. As she progressed, she incorporated Zone 2 training into her routine, focusing on building a strong aerobic base and improving her cardiovascular fitness. Over time, she was able to complete several marathons, achieving a personal best time of 4 hours and 30 minutes. Jane’s story demonstrates the power of Zone 2 training to transform even the most sedentary individuals into accomplished endurance athletes.
From Injury-Prone to Ironman
John had a history of sports injuries, limiting his ability to train consistently and achieve his fitness goals. However, after incorporating Zone 2 training into his routine, he noticed a significant reduction in injuries and an improvement in his overall fitness. By focusing on building a strong aerobic base and improving his cardiovascular fitness, John was able to complete several Ironman races, achieving a personal best time of 11 hours and 30 minutes. John’s story highlights the importance of Zone 2 training in preventing injuries and improving overall fitness.
From Overweight to Healthy and Fit
Sarah struggled with her weight for years, trying various diets and exercise programs without success. However, after incorporating Zone 2 training into her routine, she noticed a significant improvement in her overall health and fitness. By focusing on building a strong aerobic base and improving her cardiovascular fitness, Sarah was able to lose weight, reduce her body fat percentage, and improve her blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Sarah’s story demonstrates the power of Zone 2 training to improve overall health and fitness, even for those struggling with weight loss.
These success stories demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of Zone 2 training. By incorporating Zone 2 training into your exercise routine, you too can improve your cardiovascular fitness, increase fat burning, and promote recovery. Remember to stay consistent, track your progress, and adjust your training intensity as needed to achieve your desired results. Share your own Zone 2 training success stories and experiences with others to inspire and motivate them on their fitness journey.