The Crucial Role of Adequate Hydration in Athletic Performance
Proper hydration is an essential aspect of athletic performance, recovery, and overall health. Adequate water intake helps maintain the body’s fluid balance, regulates core temperature, and supports vital physiological functions. Neglecting hydration can lead to dehydration, negatively impacting physical performance and increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses. Therefore, understanding how much water athletes should drink a day is crucial for optimal performance and well-being.
How to Estimate Daily Water Needs for Athletes: A Step-by-Step Process
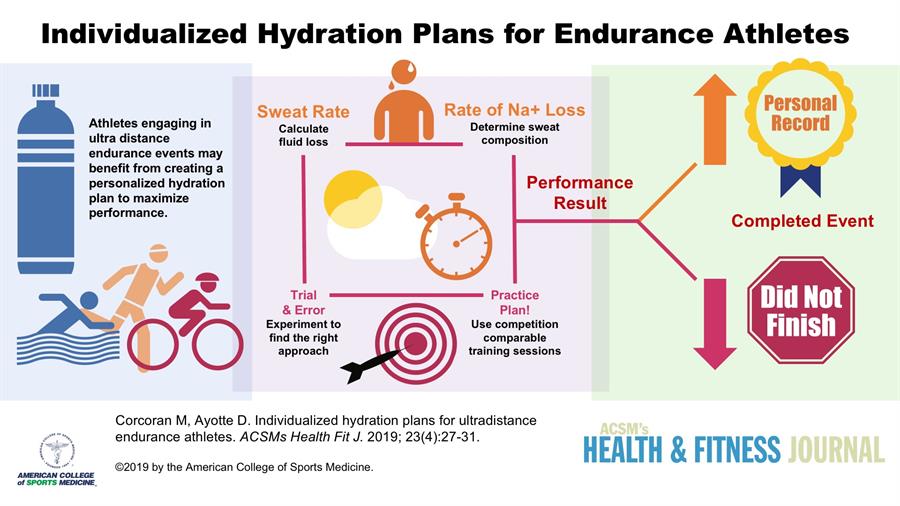
Estimating daily water needs for athletes involves considering several factors that influence hydration requirements. To create a personalized hydration plan, follow these steps:
- Calculate your body weight in kilograms (kg) by dividing your weight in pounds by 2.2.
- Determine your daily sweat rate by weighing yourself before and after exercise, accounting for any fluids consumed during the activity. Your sweat rate is the difference in body weight (in kg) divided by the duration of exercise (in hours).
- Factor in the intensity of your workouts. High-intensity exercise typically requires more water than low-intensity activities.
- Consider the environmental conditions. Hot and humid environments can increase water needs due to increased sweat production.
- Estimate your daily water intake needs by adding up your fluid losses from sweat, urine, and respiration. A general recommendation is to aim for a daily fluid intake of 25-35 milliliters per kilogram of body weight. For example, an 80 kg athlete would require 2,000-2,800 milliliters (67-94 ounces) of water per day.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual needs may vary. Adjust your hydration plan based on your unique circumstances, such as sweat rate, personal preferences, and specific sport requirements.
General Recommendations for Daily Water Intake for Athletes
While individual water needs may vary, general guidelines can help athletes estimate their daily water intake requirements. For athletes, the recommended daily water intake is typically higher than the standard recommendation for the general population. Aim for the following daily water intake guidelines:
- 16-20 fluid ounces (473-591 milliliters) of water 2-3 hours before exercise
- 8-12 fluid ounces (237-355 milliliters) of water 10-20 minutes before exercise
- 3-8 fluid ounces (89-237 milliliters) of water every 15-20 minutes during exercise, depending on individual sweat rate and environmental conditions
- 16-24 fluid ounces (473-710 milliliters) of water for every pound (0.45 kilograms) lost during exercise, consumed after exercise
- Additionally, aim for a daily water intake of 25-35 milliliters per kilogram of body weight, accounting for fluids lost through sweat, urine, and respiration
It’s essential to adjust these recommendations based on individual needs and circumstances, such as body weight, exercise intensity, duration, and environmental conditions. Proper hydration can significantly impact athletic performance, recovery, and overall health, making it a critical aspect of any athlete’s routine.
Personalizing Hydration Strategies for Athletes
Athletes can optimize their hydration plans by considering individual factors that influence water needs. Personalizing hydration strategies can help ensure adequate hydration while avoiding overhydration and its associated risks. Here’s how athletes can customize their hydration plans:
- Assess sweat rate: Measure body weight before and after exercise, accounting for fluids consumed, to estimate sweat rate. This can help athletes determine their unique fluid needs during exercise.
- Consider personal preferences: Some athletes may prefer cold or flavored beverages, which can encourage fluid consumption. However, avoid beverages with excessive sugar or artificial ingredients, as they can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort during exercise.
- Factor in specific sport requirements: Sports with prolonged or intense physical activity may require additional hydration strategies, such as the use of hydration packs or bottles, to ensure adequate fluid intake.
- Monitor hydration status: Regularly assess hydration levels using methods such as urine color, body weight changes, and perceived thirst. This can help athletes adjust their hydration plan as needed.
- Account for environmental conditions: Hot and humid environments can increase sweat production, necessitating higher fluid intake. Conversely, cold or dry conditions may reduce fluid loss, requiring athletes to adjust their hydration plan accordingly.
Personalizing hydration strategies based on these factors can help athletes optimize their performance, recovery, and overall health. By understanding their unique needs, athletes can develop a tailored hydration plan that supports their athletic goals and promotes long-term success.
Assessing and Monitoring Hydration Levels in Athletes
Monitoring hydration status is crucial for athletes to ensure they are consuming adequate water and avoiding the negative effects of dehydration or overhydration. Various methods can help athletes track their hydration levels, including:
- Urine color: A common and easy-to-use method for assessing hydration status is monitoring urine color. Well-hydrated individuals typically have pale yellow urine, while darker shades may indicate dehydration. However, this method has limitations, as certain medications, supplements, and foods can affect urine color.
- Body weight changes: Weighing yourself before and after exercise can help estimate fluid loss during physical activity. Aim to replace any fluid loss within a few hours post-exercise. However, this method may not account for changes in hydration status throughout the day or in response to environmental conditions.
- Perceived thirst: Listening to your body’s signals for thirst can help maintain hydration. However, thirst may not always accurately reflect hydration status, as it can be delayed during or after exercise. Therefore, athletes should not rely solely on thirst as an indicator of hydration needs.
To track hydration effectively, athletes should combine these methods and monitor hydration levels throughout the day and during exercise. This can help ensure optimal hydration and support athletic performance, recovery, and overall health.
Pre-Exercise Hydration Techniques for Athletes
Proper hydration before exercise is essential for optimal performance, recovery, and overall health. Here are some recommendations for pre-exercise hydration and maintaining optimal hydration levels:
- Assess hydration status: Monitor hydration levels using methods such as urine color, body weight changes, and perceived thirst. Address any signs of dehydration before engaging in physical activity.
- Gradual hydration: Begin hydrating several hours before exercise to ensure adequate fluid distribution throughout the body. Avoid consuming large amounts of water immediately before exercise, as this can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Pre-exercise meals: Include hydrating foods in pre-exercise meals, such as fruits, vegetables, and yogurt. These foods can help maintain hydration and provide essential nutrients for energy and endurance.
- Fluid balance: Aim for a balanced fluid intake, considering both water and electrolytes. Sports drinks containing electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, can help maintain fluid balance and prevent hyponatremia (low sodium levels) during prolonged exercise.
By following these pre-exercise hydration techniques, athletes can support their performance, recovery, and overall health. Proper hydration before exercise is a crucial aspect of an athlete’s routine and should not be overlooked.
Staying Hydrated During Exercise: Best Practices and Tips for Athletes
Maintaining proper hydration during exercise is essential for optimal performance, endurance, and overall health. Here are some practical tips and best practices for staying hydrated during physical activity:
- Fluid consumption rates: Aim to consume 3-8 ounces (89-237 milliliters) of water every 15-20 minutes during exercise. Adjust the amount based on individual sweat rate, environmental conditions, and exercise intensity.
- Electrolyte balance: Consider incorporating sports drinks containing electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, during prolonged or intense exercise. These drinks can help maintain fluid balance and prevent hyponatremia (low sodium levels).
- Hydration packs or bottles: Use hydration packs or bottles designed for athletes to ensure easy access to fluids during exercise. Choose packs or bottles that are comfortable, easy to use, and can hold enough water for your specific exercise duration.
- Pacing fluid intake: Avoid consuming large amounts of water at once, as this can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. Instead, pace fluid intake throughout the exercise session, taking small, frequent sips.
- Avoid overhydration: Be cautious not to overhydrate, as this can lead to hyponatremia. Monitor hydration levels using methods such as urine color, body weight changes, and perceived thirst, and adjust fluid intake accordingly.
By following these tips and best practices, athletes can maintain proper hydration during exercise, ensuring optimal performance, endurance, and overall health. Staying hydrated is a crucial aspect of an athlete’s routine and should be a top priority during physical activity.
Post-Exercise Hydration: Enhancing Recovery and Rehydration for Athletes
Proper post-exercise hydration is essential for optimal recovery, replenishing fluids, and restoring electrolyte balance. Here are some strategies and tips for effective post-exercise hydration and rehydration:
- Fluid replacement: Aim to replace 125-150% of the fluid lost during exercise within the first 4-6 hours post-exercise. This can help ensure proper rehydration and prevent dehydration from impacting future performance.
- Electrolyte replenishment: Incorporate electrolyte-rich foods and beverages, such as sports drinks, coconut water, or bananas, to help restore electrolyte balance. This is particularly important for athletes who have engaged in prolonged or intense exercise, as significant electrolyte losses can occur through sweat.
- Post-exercise meals: Consume a balanced meal containing carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats within 60 minutes post-exercise. This meal can help replenish glycogen stores, support muscle recovery, and contribute to rehydration.
- Individual needs: Adjust post-exercise hydration strategies based on individual needs and circumstances. Factors such as sweat rate, environmental conditions, and exercise intensity can impact fluid and electrolyte losses, requiring personalized rehydration plans.
By following these strategies and tips, athletes can effectively enhance recovery and rehydration through proper post-exercise hydration. Proper hydration is a crucial aspect of an athlete’s routine and should be prioritized before, during, and after physical activity to support optimal performance, endurance, and overall health.