Understanding Caloric Expenditure and Walking
Caloric expenditure is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. Engaging in physical activities, such as walking, plays a significant role in burning calories and improving overall health. This article focuses on the topic of how many calories burn in 20000 steps, providing a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence caloric burn during a walking routine.
The Role of Body Metrics in Calculating Caloric Burn
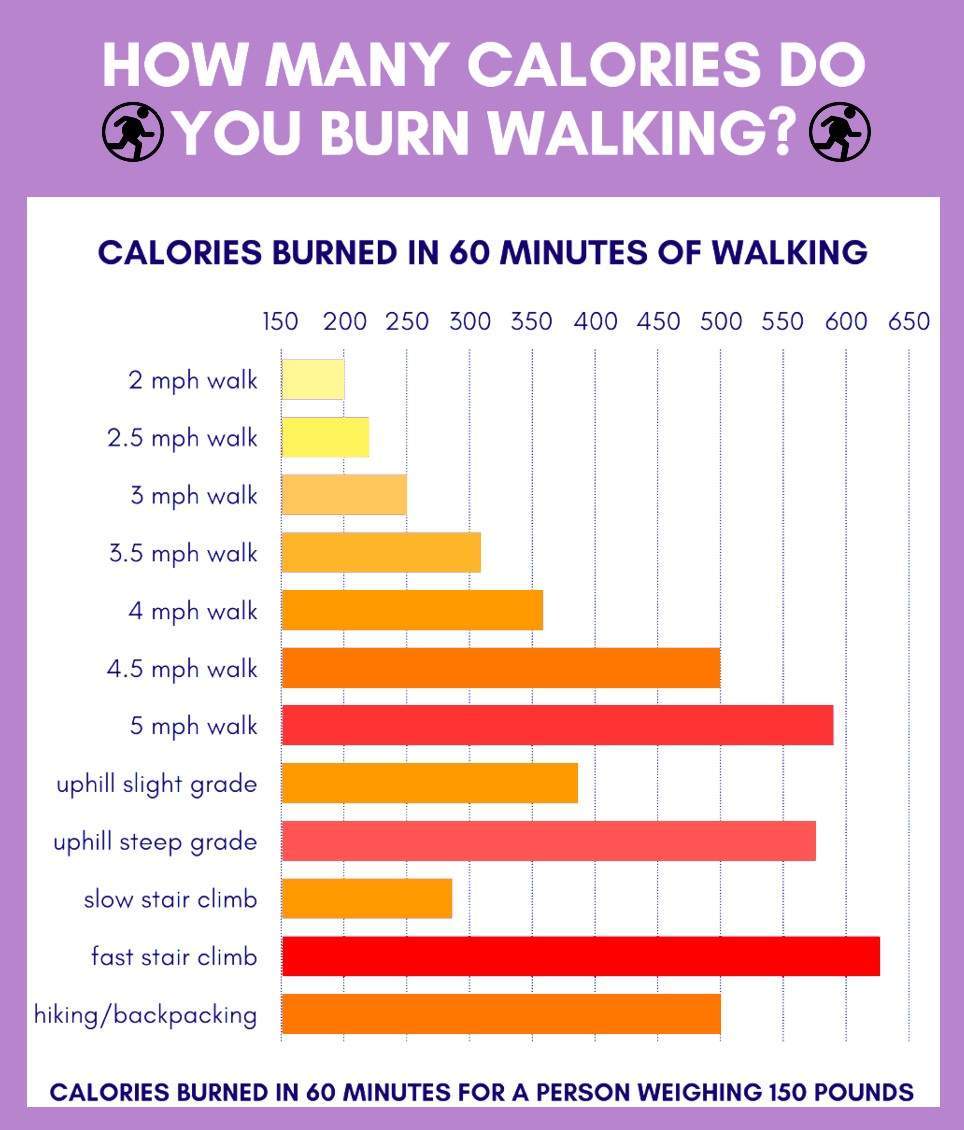
Caloric burn during a 20,000-step walk is influenced by various factors, including body weight, age, gender, and walking pace. For instance, an individual weighing 150 pounds (68 kg) will burn more calories than someone weighing 120 pounds (54 kg) when walking the same distance. Similarly, older individuals typically burn fewer calories than younger individuals due to age-related muscle loss and decreased metabolism.
Gender also plays a role in caloric burn, as men generally have more muscle mass and a higher metabolic rate than women. As a result, men tend to burn more calories during physical activities. Walking pace is another crucial factor, as a brisk walk can burn up to 50% more calories than a leisurely stroll. Therefore, understanding your body metrics and adjusting your walking pace can significantly impact the number of calories you burn during a 20,000-step walk.
Estimating Caloric Burn with Pedometer Applications
Pedometer applications and smartwatches have revolutionized the way individuals track their physical activities, including estimating the number of calories burned during a walk. These devices use complex algorithms that consider user data, such as body weight, age, gender, and walking pace, to calculate caloric expenditure. By accurately tracking steps, distance, and time, these applications can provide a relatively accurate estimation of how many calories burn in 20000 steps.
For example, some popular pedometer applications, such as MyFitnessPal, MapMyWalk, and Pacer, allow users to input their personal information and monitor their progress throughout the day. These applications also offer additional features, such as GPS tracking, social sharing, and workout history, making it easier for users to stay motivated and engaged in their fitness journey. By incorporating these tools into a daily routine, individuals can better understand their caloric burn and make informed decisions about their diet and exercise habits.
Comparing Caloric Burn Across Different Walking Distances
Caloric burn can vary significantly when walking different distances. For example, walking 5 miles (8 km) typically burns around 350 to 550 calories, depending on factors such as body weight, age, gender, and walking pace. In contrast, walking 10 miles (16 km) can burn between 700 and 1,100 calories, while walking 20,000 steps can burn approximately 800 to 1,400 calories, depending on the individual’s stride length and walking pace.
It is essential to note that caloric burn can differ between individuals, even when walking the same distance. For instance, a person weighing 150 pounds (68 kg) may burn 1,000 calories walking 20,000 steps, while a person weighing 120 pounds (54 kg) may burn only 800 calories during the same walk. Therefore, it is crucial to consider personal factors when estimating caloric burn and setting fitness goals.
Maximizing Caloric Burn: Tips and Techniques
To maximize caloric burn during a 20,000-step walk, consider incorporating hills, varying your pace, and engaging your upper body. Walking uphill can significantly increase the number of calories burned, as it requires more effort from your muscles. In addition, alternating between brisk walking and slower paces can help keep your metabolism elevated and burn more calories throughout your walk.
Engaging your upper body by pumping your arms while walking can also contribute to a higher caloric burn. This full-body approach not only increases overall energy expenditure but also helps improve posture and balance. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine is crucial for maximizing caloric burn and overall weight management.
The Science Behind Caloric Burn: A Look at the Research
Numerous scientific studies have investigated the relationship between walking and caloric burn. Researchers have found that walking is an effective and accessible form of exercise that can contribute to weight management and overall health. A study published in the Journal of Exercise Nutrition & Biochemistry found that walking 20,000 steps per day resulted in a significant increase in caloric burn compared to a sedentary lifestyle.
Another study in the Journal of Obesity reported that individuals who walked 10,000 to 11,000 steps per day weighed less and had a lower body mass index (BMI) than those who walked fewer than 5,000 steps daily. These findings suggest that increasing daily step count can lead to increased caloric burn and improved weight management.
It is essential to address common misconceptions about caloric expenditure during exercise. For example, some individuals believe that they can out-exercise a poor diet, but research shows that maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for overall weight management and long-term success. Additionally, it is essential to understand that caloric burn varies between individuals, and factors such as body weight, age, gender, and walking pace can significantly impact the number of calories burned during a 20,000-step walk.
Real-World Applications: Success Stories and Case Studies
Many individuals have successfully incorporated a 20,000-step walking routine into their daily lives, experiencing significant improvements in caloric burn and overall health. For example, Sarah, a 35-year-old woman weighing 150 pounds (68 kg), decided to challenge herself by walking 20,000 steps daily. After six months, she reported losing 15 pounds (6.8 kg) and improving her overall fitness level.
John, a 45-year-old man weighing 200 pounds (90.7 kg), also adopted a 20,000-step walking routine. Over the course of a year, he lost 50 pounds (22.7 kg) and reduced his body fat percentage by 10%. John’s success story demonstrates the long-term benefits of incorporating a regular walking routine into one’s lifestyle.
These success stories highlight the potential benefits of walking 20,000 steps daily. By consistently tracking their progress with pedometer applications and adjusting their pace and walking patterns, individuals can maximize their caloric burn and improve their overall health.
Maintaining a Balanced Approach: Long-Term Strategies for Caloric Burn and Weight Management
Incorporating a 20,000-step walking routine into your daily life can significantly contribute to your overall caloric burn and weight management goals. However, it is crucial to maintain a balanced approach to ensure long-term success. Set realistic goals based on your current fitness level and gradually increase your step count over time.
To maximize the benefits of your walking routine, combine it with a healthy, balanced diet. Consuming nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help fuel your body for your walks and support your weight management efforts. Additionally, maintaining a consistent exercise routine, including both cardiovascular activities like walking and strength training, can further enhance your caloric burn and overall fitness.
Tracking your progress is essential for maintaining motivation and ensuring you are on track to meet your goals. Utilize pedometer applications or smartwatches to monitor your daily step count and caloric burn. Regularly review your progress and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Finally, remember that support is vital for long-term success. Share your goals with friends, family, or healthcare professionals and seek their encouragement and guidance along the way. By maintaining a balanced approach and seeking support, you can successfully incorporate a 20,000-step walking routine into your daily life and achieve your caloric burn and weight management goals.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-many-calories-do-i-burn-every-day-3495464-final-dc03506ae07344f5a7ebeb4d3da0d90d.jpg)