Understanding the Basics: Calories and Weight
Calories are a fundamental unit of energy, and they play a critical role in our daily lives. In the context of weight management, calories are essential to understanding how our bodies gain, lose, and maintain weight. The question “how many calories are in one pound?” is a common one, and it highlights the importance of understanding the relationship between calories and weight.
Foods contain varying amounts of calories, and these calories come from three primary macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Protein and carbohydrates each contain approximately 4 calories per gram, while fats contain approximately 9 calories per gram. These macronutrients are essential to our bodies, and they provide the energy we need to function. However, consuming too many calories can lead to weight gain, while consuming too few can lead to weight loss.
It’s important to note that not all calories are created equal. For example, 100 calories from a piece of fruit will have a different impact on the body than 100 calories from a candy bar. This is because the fruit contains essential nutrients and fiber, while the candy bar is primarily made up of sugar and unhealthy fats. Therefore, it’s essential to focus on nutrient-dense foods rather than just counting calories.
The Connection Between Calories and Pounds
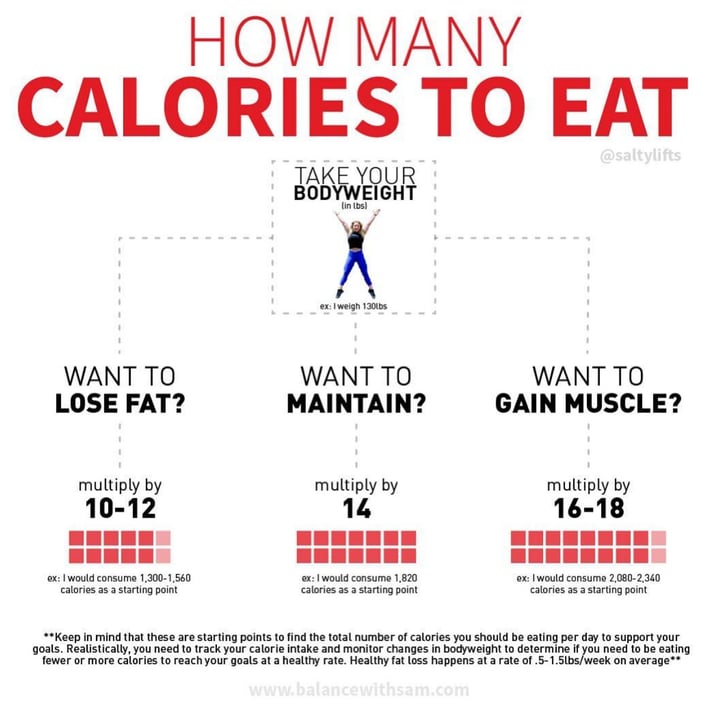
The question “how many calories are in one pound?” is a common one, and the answer is that there are approximately 3,500 calories in a pound of fat. This means that if you consume 3,500 more calories than you burn, you will gain one pound of fat. Conversely, if you burn 3,500 more calories than you consume, you will lose one pound of fat.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified explanation of the relationship between calories and weight. In reality, weight gain and loss are influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, metabolism, and activity level. However, maintaining a caloric balance is still a crucial component of weight management.
To put the caloric content of a pound of fat into perspective, consider that a pound of fat is roughly the equivalent of 16 sticks of butter or 56 slices of bacon. This highlights the importance of maintaining a caloric balance and emphasizes the value of choosing nutrient-dense foods over calorie-dense foods.
When it comes to weight loss, it’s important to focus on creating a caloric deficit in a healthy and sustainable way. This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise. For example, reducing caloric intake by 500 calories per day and burning an additional 500 calories through exercise would result in a caloric deficit of 1,000 calories per day, leading to a weight loss of approximately two pounds per week.
Calculating Caloric Intake and Expenditure
Calculating caloric intake and expenditure is an essential component of weight management and overall health. Caloric intake refers to the number of calories consumed through food and drink, while caloric expenditure refers to the number of calories burned through physical activity and metabolic processes.
To maintain a healthy weight, it’s important to maintain a caloric balance, meaning that caloric intake and expenditure are roughly equal. This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise.
To calculate caloric intake, start by tracking the number of calories consumed each day. This can be done through a food diary or a calorie tracking app. Be sure to include all food and drink, including snacks and beverages. Once you have a clear picture of your daily caloric intake, you can make adjustments as needed to maintain a caloric balance.
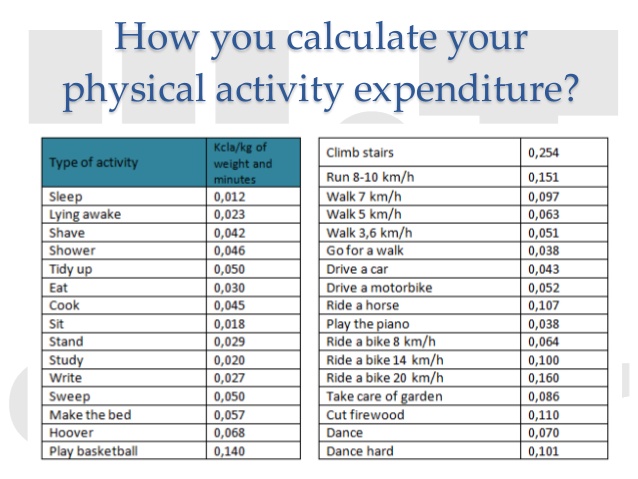
Caloric expenditure can be calculated through a variety of methods, including fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and metabolic testing. Regular physical activity is essential for caloric expenditure, as it helps to burn calories and boost metabolism. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises on two or more days per week.
It’s important to note that caloric needs vary from person to person, based on factors such as age, sex, weight, and activity level. To determine your individual caloric needs, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
Practical Applications: Using Caloric Information for Weight Management
Understanding the relationship between calories and weight is essential for effective weight management. Once you have a clear picture of your caloric needs and expenditure, you can use this information to make informed decisions about diet and exercise.
One practical application of caloric information is portion control. By understanding the caloric content of different foods, you can make informed decisions about portion sizes and ensure that you are not consuming more calories than you need. This can be especially helpful when eating out or attending social events where food is served.
Meal planning is another practical application of caloric information. By planning meals in advance, you can ensure that you are getting a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients while staying within your caloric needs. Meal planning can also help to reduce food waste and save time and money.
Exercise is an essential component of caloric expenditure and weight management. Regular physical activity can help to burn calories, boost metabolism, and improve overall health. Aim for a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to get the most benefits.
When it comes to weight loss, it’s important to focus on creating a caloric deficit in a healthy and sustainable way. This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise. For example, reducing caloric intake by 500 calories per day and burning an additional 500 calories through exercise would result in a caloric deficit of 1,000 calories per day, leading to a weight loss of approximately two pounds per week. However, it’s important to make sure that you are getting enough calories to support your body’s needs and avoid creating an unhealthy deficit.
Remember, when it comes to weight management and health, it’s not just about calories. It’s also important to focus on nutrient density, incorporating a variety of macronutrients and micronutrients into your diet, and practicing self-care. By taking a holistic approach to weight management and health, you can create long-term, sustainable changes that will benefit your body and mind.
Common Misconceptions About Calories and Weight Loss
When it comes to weight loss, there are many misconceptions about calories and their role in weight management. Here are some common misconceptions and the truth behind them:
Misconception 1: All calories are created equal
While it’s true that all calories contain the same amount of energy, not all calories are created equal when it comes to weight management and overall health. Nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that are important for overall health. Calorie-dense foods, on the other hand, may be high in calories but low in nutrients.
Misconception 2: Cutting calories is the only way to lose weight
While reducing caloric intake is an important component of weight loss, it’s not the only factor to consider. Focusing solely on calorie restriction can lead to nutrient deficiencies and a lack of satisfaction, which can make it difficult to stick to a weight loss plan long-term. Incorporating regular physical activity, practicing portion control, and focusing on nutrient-dense foods can help to support weight loss and overall health.
Misconception 3: Low-fat or diet foods are always a better choice
While low-fat or diet foods may be lower in calories, they are often highly processed and may contain added sugars, sodium, and other additives. It’s important to read labels carefully and focus on nutrient-dense, whole foods whenever possible.
Misconception 4: Snacking is always bad for weight loss
Snacking can be a helpful tool for weight loss, as long as you choose nutrient-dense, portion-controlled snacks. Snacking can help to prevent overeating at meals, provide essential nutrients, and support overall health.
Misconception 5: You need to eliminate entire food groups to lose weight
Eliminating entire food groups can lead to nutrient deficiencies and an unbalanced diet. Instead, focus on incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods from all food groups in appropriate portion sizes.
By understanding the truth behind these common misconceptions, you can make informed decisions about your diet and weight loss plan and create long-term, sustainable changes for overall health and well-being.
The Role of Nutrient Density in Caloric Intake
When it comes to weight management and overall health, not all calories are created equal. Nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that are important for overall health, while calorie-dense foods may be high in calories but low in nutrients.
Nutrient density refers to the amount of nutrients a food provides per calorie. Foods that are high in nutrient density provide a high amount of nutrients per calorie, while foods that are low in nutrient density provide a low amount of nutrients per calorie. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, you can ensure that you are getting the nutrients your body needs while managing your caloric intake.
Here are some tips for incorporating nutrient-dense foods into your diet:
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible. Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are often higher in nutrients and lower in calories than processed foods.
- Focus on foods that are high in fiber. Fiber helps to promote feelings of fullness and can help to manage caloric intake. Foods that are high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Choose foods that are rich in protein. Protein is important for overall health and can help to promote feelings of fullness. Foods that are high in protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and tofu.
- Incorporate healthy fats. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and seeds, can help to promote feelings of fullness and support overall health.
- Limit added sugars and unhealthy fats. Foods that are high in added sugars and unhealthy fats are often low in nutrients and high in calories.
By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, you can ensure that you are getting the nutrients your body needs while managing your caloric intake. This can help to support weight management and overall health in the long term.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet: Incorporating Macronutrients and Micronutrients
When it comes to weight management and overall health, it’s important to incorporate a variety of macronutrients and micronutrients into your diet. Macronutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, and fats, provide energy and support various bodily functions. Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for overall health and well-being.
Protein
Protein is important for overall health and can help to promote feelings of fullness. Foods that are high in protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and tofu. Aim to include a source of protein in each meal and snack to help manage hunger and support muscle growth and repair.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over simple carbohydrates, such as sugar and white flour. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and are often higher in fiber and other nutrients.
Fats
Fats are important for overall health and can help to promote feelings of fullness. However, not all fats are created equal. Choose healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and seeds, over unhealthy fats, such as those found in fried foods and processed snacks. Healthy fats can help to support heart health, brain function, and overall well-being.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for overall health and well-being. Aim to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-dense foods in your diet to ensure that you are getting the micronutrients your body needs. Some key micronutrients to focus on include calcium, vitamin D, and iron.
By incorporating a variety of macronutrients and micronutrients into your diet, you can support overall health and well-being while managing your caloric intake. Aim to include a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fats in each meal and snack, and choose nutrient-dense foods whenever possible.
Long-Term Strategies for Weight Management and Health
When it comes to weight management and overall health, it’s important to focus on long-term strategies rather than quick fixes. Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy weight and promoting overall well-being in the long term:
Focus on a balanced diet
Aim to incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. By focusing on a balanced diet, you can ensure that you are getting the nutrients your body needs while managing your caloric intake.
Practice portion control
Pay attention to portion sizes and aim to eat until you are satisfied, rather than stuffed. This can help to prevent overeating and support weight management.
Incorporate regular exercise
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Regular exercise can help to support weight management, improve mood, and promote overall health and well-being.
Prioritize self-care
Get enough sleep, manage stress, and find time for activities that bring you joy. By prioritizing self-care, you can support overall health and well-being, which can in turn support weight management.
Avoid fad diets and quick fixes
Fad diets and quick fixes may promise quick results, but they are often unsustainable and can lead to negative consequences for overall health. Instead, focus on long-term strategies for weight management and overall health.
By incorporating these long-term strategies into your lifestyle, you can support weight management and overall health in the long term. Remember, it’s not about quick fixes or short-term gains, but about making sustainable changes that support your overall well-being.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between calories and weight is an important aspect of weight management and overall health. By calculating caloric intake and expenditure, using caloric information to make informed choices, focusing on nutrient density and a balanced diet, and incorporating long-term strategies for weight management and health, you can support your overall well-being and reach your weight management goals.