Understanding the Resting Heart Rate: An Overview
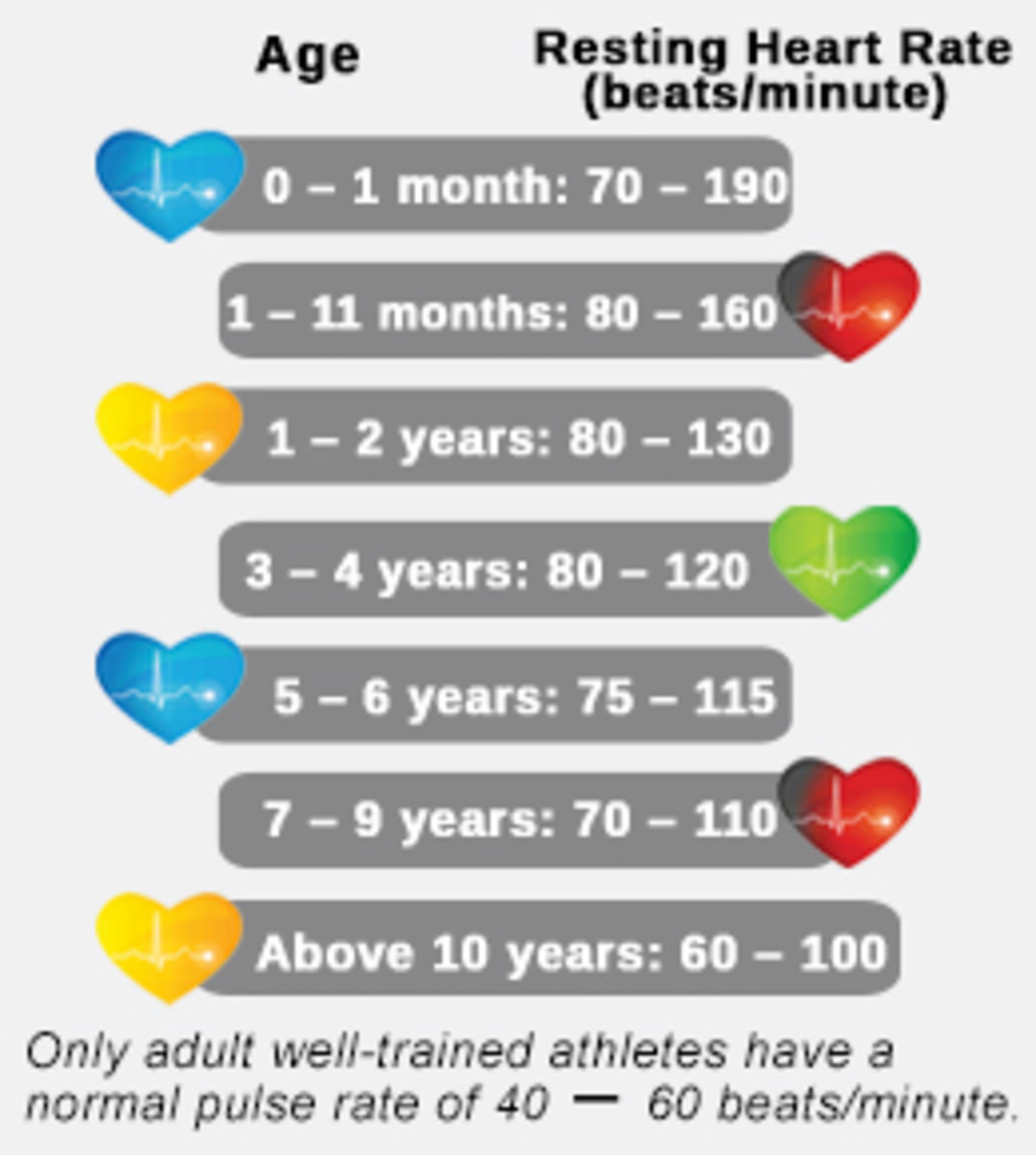
Resting heart rate (RHR) refers to the number of heartbeats per minute while at rest. Typically, a lower RHR indicates better cardiovascular fitness and overall health. How do you lower your resting heart rate? By adopting a healthy lifestyle and incorporating regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and quality sleep, you can effectively decrease your RHR and improve your overall well-being.
Identifying Factors Influencing Your Resting Heart Rate
Several factors can affect your resting heart rate (RHR), including age, fitness level, genetics, and lifestyle habits. Understanding these factors is crucial when learning how do you lower your resting heart rate. As you age, your RHR tends to increase due to natural physiological changes. However, maintaining a high level of fitness can help counteract this effect. Genetics also play a role in determining your RHR, but a healthy lifestyle can still make a significant impact. Lifestyle habits, such as smoking, excessive caffeine consumption, and stress, can elevate your RHR, making it essential to prioritize healthier choices for long-term RHR reduction.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle: Foundation for a Lower Resting Heart Rate
A healthy lifestyle forms the cornerstone of reducing your resting heart rate (RHR). By incorporating regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and quality sleep, you can effectively lower your RHR and improve your overall well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity, consuming a diet rich in whole foods, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep are all interconnected and contribute to a healthier heart.
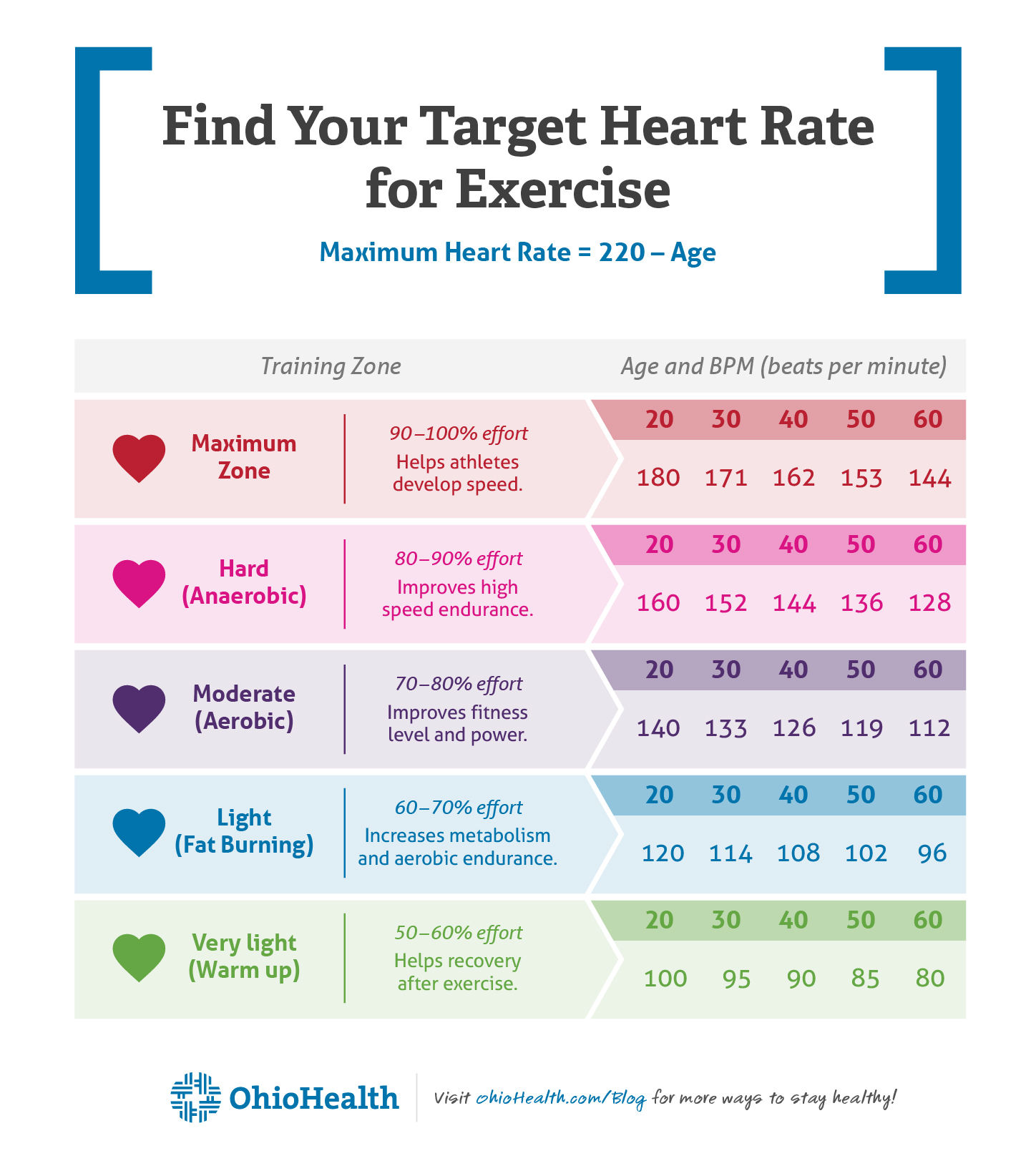
Regular Aerobic Exercise: A Key Component in Lowering Resting Heart Rate
Regular aerobic exercise is a crucial strategy for reducing your resting heart rate (RHR). Aerobic activities, such as running, swimming, and cycling, increase your heart’s efficiency and lower your RHR over time. To maximize the benefits of aerobic exercise, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by the American Heart Association. Additionally, incorporate interval training, which involves alternating between high-intensity and low-intensity exercise, to further challenge your cardiovascular system and promote a lower RHR.
Incorporating Strength Training: Enhancing the Effects of Aerobic Exercise
Strength training plays a vital role in supporting aerobic exercise and further reducing your resting heart rate (RHR). By incorporating resistance training into your weekly exercise routine, you can build lean muscle mass, improve your cardiovascular system’s efficiency, and enhance overall heart health. Aim for two strength training sessions per week, focusing on all major muscle groups. Consider incorporating bodyweight exercises, free weights, resistance bands, or machines to create a well-rounded routine that complements your aerobic activities.
Mindful Eating: Nutritional Strategies for a Lower Resting Heart Rate
A balanced diet rich in whole foods can significantly contribute to lowering your resting heart rate (RHR). Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats can help improve heart health and overall well-being. Some heart-healthy foods to consider incorporating into your diet include leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and avocados. Additionally, practicing portion control and moderating your consumption of processed foods can further support your efforts to reduce your RHR.
Managing Stress and Improving Sleep: Crucial Elements in Reducing Resting Heart Rate
Stress and sleep are two critical factors that can significantly impact your resting heart rate (RHR). High stress levels and poor sleep quality can elevate your RHR, while effective stress management and improved sleep can contribute to a lower RHR. To manage stress, consider incorporating techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into your daily routine. To enhance sleep quality, establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your sleep environment is cool, dark, and quiet.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Strategies: Ensuring Long-Term Success
Monitoring your resting heart rate (RHR) is essential for tracking your progress and ensuring the effectiveness of your reduction strategies. By consistently measuring your RHR, you can identify trends, assess the impact of lifestyle changes, and adjust your approach as needed. Utilize technology, such as fitness trackers or smartwatches, to simplify the tracking process and maintain motivation. Regularly review your RHR data to determine whether your current strategies are working or if adjustments are necessary to continue lowering your RHR.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/symptoms-of-heart-failure-getting-worse-5189593-FINAL-2611ff1280434a4c9daafd3f05f43461.jpg)