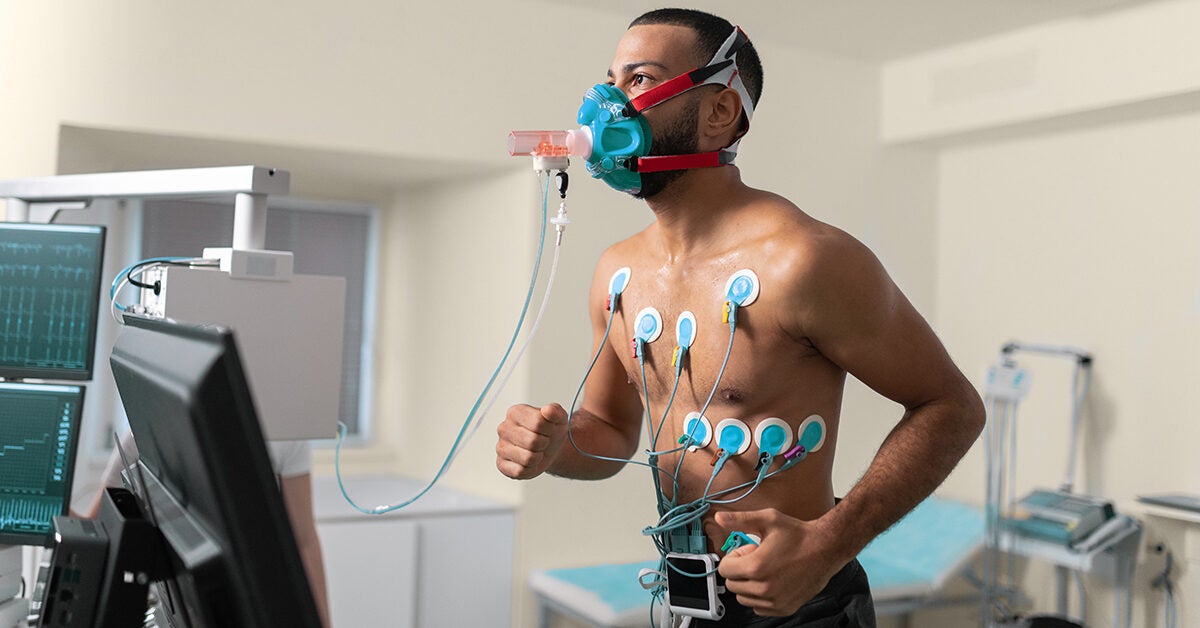
Traditional Methods for Measuring VO2 Max
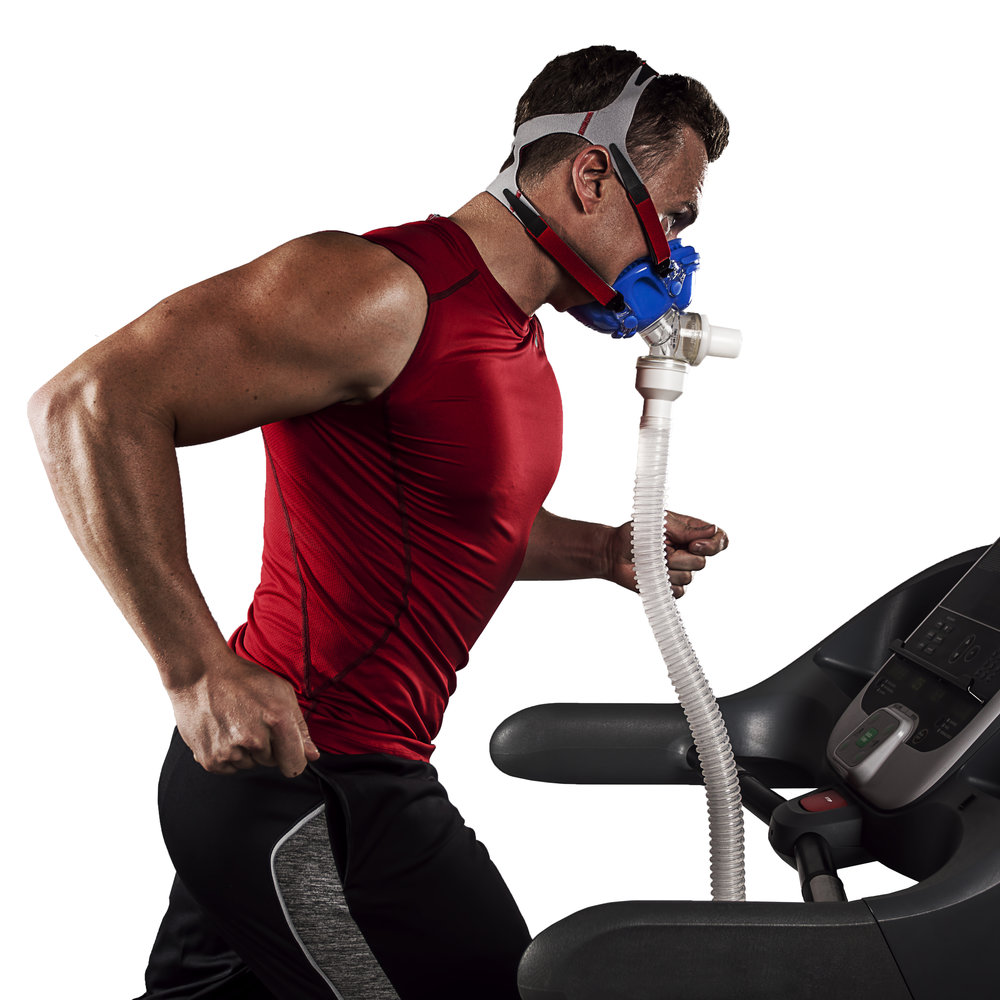
To accurately measure VO2 Max, laboratory-based methods are often employed. Direct calorimetry, which involves directly measuring the amount of heat produced by the body during exercise, is considered the gold standard for measuring VO2 Max. However, this method is expensive, complex, and not readily available for most individuals.
Indirect calorimetry, on the other hand, is a more accessible and practical approach. This method uses the relationship between oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production to estimate VO2 Max. Indirect calorimetry can be performed using a metabolic cart, which measures the volume and composition of exhaled gases during exercise.
While laboratory-based methods provide accurate and reliable results, they may not be feasible for everyone due to their cost and complexity. As a result, alternative methods for estimating VO2 Max have been developed, including field tests and calculations based on heart rate and running pace.
Estimating VO2 Max through Field Tests
Field tests offer a more accessible and practical alternative to laboratory-based methods for estimating VO2 Max. These tests typically involve performing a standardized exercise protocol, measuring exercise performance, and using a specific equation or conversion table to estimate VO2 Max.
One popular field test is the 1.5-mile run. This test requires participants to run as fast as possible over a distance of 1.5 miles. The time to complete the run is then used to estimate VO2 Max using a conversion table or equation. The 1.5-mile run is a simple and convenient test that can be performed almost anywhere, making it a popular choice for fitness enthusiasts and athletes.
Another commonly used field test is the 12-minute run. In this test, participants run as far as possible over a period of 12 minutes. The distance covered is then used to estimate VO2 Max using a specific equation. The 12-minute run is a versatile test that can be used to assess both aerobic endurance and anaerobic capacity.
Step tests are another option for estimating VO2 Max. These tests involve stepping up and down on a bench or platform at a specific rate for a set period of time. Heart rate is measured during and after the test, and the results are used to estimate VO2 Max. Step tests are a convenient and low-impact option for individuals who may have joint or mobility limitations.
While field tests are generally less accurate than laboratory-based methods, they can still provide valuable insights into cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. By regularly performing field tests and tracking changes in VO2 Max, individuals can monitor their progress, set realistic goals, and optimize their training programs.
Calculating VO2 Max from Heart Rate and Running Pace
In addition to laboratory-based and field tests, VO2 Max can also be estimated using formulas and equations based on heart rate and running pace. These calculations are often more accessible and convenient than laboratory or field tests, as they can be performed during regular training sessions.
One popular method for estimating VO2 Max is the Cooper test. This test involves running as far as possible in 12 minutes, and then using the distance covered to estimate VO2 Max using the following formula:
VO2 Max (ml/kg/min) = (distance in meters / 12) x 0.2 + 3.5
The Cooper test is a simple and convenient way to estimate VO2 Max, but it does have some limitations. For example, it may not be accurate for individuals with a wide range of fitness levels or running abilities.
Another commonly used method for estimating VO2 Max is the Heart Rate Ratio Method. This method involves measuring heart rate during and after exercise, and then using the following formula to estimate VO2 Max:
VO2 Max (ml/kg/min) = 15 x (HRmax / HRrest)
The Heart Rate Ratio Method is a convenient and non-invasive way to estimate VO2 Max, but it does require accurate measurement of maximum and resting heart rate.
It is important to note that these calculations are based on certain assumptions and may not be accurate for all individuals. Factors such as age, sex, fitness level, and exercise modality can all affect the accuracy of these calculations. However, they can still provide valuable insights into cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance, and can be used to monitor progress and set training goals.
Using Wearable Devices to Measure VO2 Max
In recent years, wearable technology has revolutionized the way we track and measure fitness. Smartwatches and fitness trackers can now estimate VO2 Max using heart rate data and motion sensors. These devices offer a convenient and accessible way to monitor cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance, and can be used to set training goals and track progress over time.
There are a variety of wearable devices available on the market, each with their own features, accuracy, and cost. Some popular options include the Garmin Forerunner series, the Polar Vantage series, and the Apple Watch. These devices typically use heart rate data and motion sensors to estimate VO2 Max during exercise, and provide real-time feedback and coaching to help users optimize their training.
When choosing a wearable device for measuring VO2 Max, it is important to consider factors such as accuracy, ease of use, and compatibility with other devices and apps. Some devices may be more accurate than others, and may provide more detailed insights into cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. However, these devices may also be more expensive and may require more frequent charging or maintenance.
It is also important to note that wearable devices are not a replacement for laboratory-based or field tests for measuring VO2 Max. While these devices can provide valuable insights into cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance, they may not be as accurate as laboratory-based or field tests. However, they can still be a useful tool for monitoring progress and setting training goals, and can be used in conjunction with other methods for measuring VO2 Max.
Interpreting and Utilizing Your VO2 Max Results
Once you have measured your VO2 Max using one of the methods discussed in this article, it is important to understand what your results mean and how to use them to improve your fitness. Here are some guidelines for interpreting and acting upon your VO2 Max results:
- Set Realistic Goals: Use your VO2 Max results to set realistic and achievable fitness goals. For example, if your VO2 Max is low, you may want to focus on improving your cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly reassess your VO2 Max to monitor your progress and adjust your training intensity. As your fitness level improves, your VO2 Max should also increase.
- Adjust Training Intensity: Use your VO2 Max results to adjust your training intensity and optimize your workout routine. For example, if your VO2 Max is high, you may benefit from high-intensity interval training or tempo runs.
- Individual Variation: Keep in mind that VO2 Max can vary widely between individuals, and may be influenced by factors such as age, sex, genetics, and fitness level. Therefore, it is important to focus on your own progress and improvement, rather than comparing yourself to others.
It is also important to note that VO2 Max is just one aspect of fitness, and should be considered in conjunction with other metrics such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body composition. By regularly assessing and tracking your VO2 Max, you can gain valuable insights into your cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance, and use this information to optimize your workout routine and achieve your fitness goals.
Practical Tips for Improving Your VO2 Max
Improving your VO2 Max can have numerous benefits for your cardiovascular health and overall fitness. Here are some evidence-based recommendations for enhancing your VO2 Max:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief periods of rest or active recovery. This type of training has been shown to be highly effective for improving VO2 Max, as well as other aspects of fitness such as cardiovascular health, insulin sensitivity, and body composition.
- Tempo Runs: Tempo runs involve sustained, moderate-intensity exercise for a continuous period of time. This type of training can help improve your lactate threshold, which is the point at which lactic acid begins to accumulate in the muscles, leading to fatigue. By improving your lactate threshold, you can sustain higher exercise intensities for longer periods of time, which can help improve your VO2 Max.
- Strength Training: Strength training can help improve your muscular endurance, which is an important component of VO2 Max. By increasing your muscle mass and strength, you can sustain higher exercise intensities for longer periods of time, which can help improve your VO2 Max.
- Proper Nutrition: Adequate nutrition is essential for fueling your workouts and supporting recovery. Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help optimize your fitness potential and support improvements in VO2 Max.
- Adequate Sleep: Sleep is essential for recovery and adaptation to exercise. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support optimal recovery and adaptation to training.
- Consistency and Progression: Consistency and progression are key factors in improving VO2 Max. Aim to gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of your workouts over time, while allowing adequate recovery between sessions.
It is important to note that improvements in VO2 Max may take time and consistent effort. By incorporating these practical tips into your fitness program, you can help optimize your workout routine and achieve your fitness goals.
Potential Limitations and Precautions when Measuring VO2 Max
While measuring VO2 Max can be a valuable tool for assessing cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance, there are several potential limitations and challenges to consider. Here are some factors to keep in mind when measuring and interpreting your VO2 Max results:
- Variability in Technique: Different methods for measuring VO2 Max may yield slightly different results due to variations in technique and protocol. For example, direct calorimetry may be more accurate than indirect calorimetry, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming. Similarly, field tests may be less accurate than laboratory-based tests, but they are more accessible and convenient for many individuals.
- Motivation: Measuring VO2 Max can be physically demanding and may require maximum effort. Individuals who are not adequately motivated or prepared may not be able to achieve their true VO2 Max, leading to underestimation of their fitness level.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as altitude, temperature, and humidity can affect VO2 Max measurements. For example, exercising at high altitudes may result in lower VO2 Max values due to reduced oxygen availability.
- Health Concerns and Medical Conditions: Individuals with certain health conditions or medical concerns may need to take additional precautions when measuring VO2 Max. For example, individuals with heart conditions, respiratory issues, or other medical concerns may need to consult with a healthcare provider before engaging in strenuous exercise or undergoing VO2 Max testing.
To ensure accurate and safe measurement of VO2 Max, it is important to follow proper protocols and guidelines, and to consult with a healthcare provider or fitness professional if necessary. By understanding the potential limitations and challenges of measuring VO2 Max, you can help ensure that your results are accurate and meaningful, and use this information to optimize your fitness program and achieve your goals.
Summary: The Value of Knowing Your VO2 Max
Understanding and tracking your VO2 Max can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. By measuring and interpreting your VO2 Max results, you can set realistic training goals, monitor progress, and optimize your workout routine.
There are several methods for measuring VO2 Max, each with its own advantages and limitations. Laboratory-based methods such as direct and indirect calorimetry can provide accurate and reliable results, but may be expensive and time-consuming. Field tests such as the 1.5-mile run, 12-minute run, and step tests can be more accessible and convenient, but may be less accurate. Wearable technology such as smartwatches and fitness trackers can also estimate VO2 Max, but may vary in accuracy and cost.
When interpreting your VO2 Max results, it is important to consider individual variation and regular reassessment. Setting realistic goals, monitoring progress, and adjusting your training intensity can help you optimize your fitness potential and improve your cardiovascular health.
It is also important to keep in mind potential limitations and challenges when measuring VO2 Max, such as variability in technique, motivation, and environmental factors. Safety tips and recommendations should be taken into account, especially for individuals with health concerns or medical conditions.
In summary, understanding and tracking your VO2 Max can be a valuable tool for assessing and improving your cardiovascular fitness. By exploring various methods and tools for measuring and improving your VO2 Max, you can optimize your workout routine and achieve your fitness goals.