What is a High Heart Rate After Running?
A high heart rate after running, also known as post-exertional tachycardia, refers to an elevated pulse rate that persists after physical activity. Normal post-exercise heart rate ranges can vary depending on factors such as age, fitness level, and exertion level. However, a heart rate that remains above 100 beats per minute (bpm) for more than a few minutes after stopping exercise may be considered high.
Several factors can contribute to a high heart rate after running, including dehydration, poor fitness level, and underlying medical conditions. Dehydration can cause the heart to work harder to pump blood, leading to an elevated heart rate. Poor fitness level can also contribute to a high heart rate, as the heart may need to work harder to supply oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during exercise. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, anemia, or thyroid disorders, can cause an elevated heart rate after running.
It is important to note that a high heart rate after running is not always a cause for concern. However, if the elevated heart rate persists for an extended period or is accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, it may be a sign of a more serious medical issue. In such cases, it is recommended to seek professional medical attention.
Identifying the Causes of a High Heart Rate Post-Run
A high heart rate after running can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from dehydration to underlying medical conditions. Dehydration is a common cause of an elevated heart rate after running, as the body needs water to maintain normal blood volume and cardiovascular function. When the body is dehydrated, the heart needs to work harder to pump blood, leading to an increased heart rate.
Poor fitness level can also contribute to a high heart rate after running. When the body is not accustomed to regular exercise, the heart may need to work harder to supply oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during physical activity. Over time, regular exercise and progressive training can help improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running.
Certain medical conditions can also cause an elevated heart rate after running. These may include heart disease, anemia, or thyroid disorders. In some cases, a high heart rate after running may be a sign of a more serious medical issue, such as a heart arrhythmia or cardiomyopathy. If the elevated heart rate persists for an extended period or is accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, it is important to seek professional medical attention.
Other factors that can contribute to a high heart rate after running include stress, anxiety, and caffeine or stimulant intake. It is important to manage these factors and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of an elevated heart rate after running.
How to Measure Your Heart Rate Post-Run
Measuring your heart rate after running is a simple and effective way to monitor your cardiovascular health and fitness level. The proper technique for measuring your heart rate involves finding your pulse and counting the number of beats per minute. Here are the steps to follow:
- Wait for at least 10 minutes after finishing your run to allow your heart rate to return to a resting state.
- Place the tips of your index and middle fingers on the inside of your wrist, just below the base of your thumb. Alternatively, you can place your fingers on the side of your neck, just below your jawbone.
- Count the number of beats you feel for 15 seconds, then multiply by four to get your heart rate per minute.
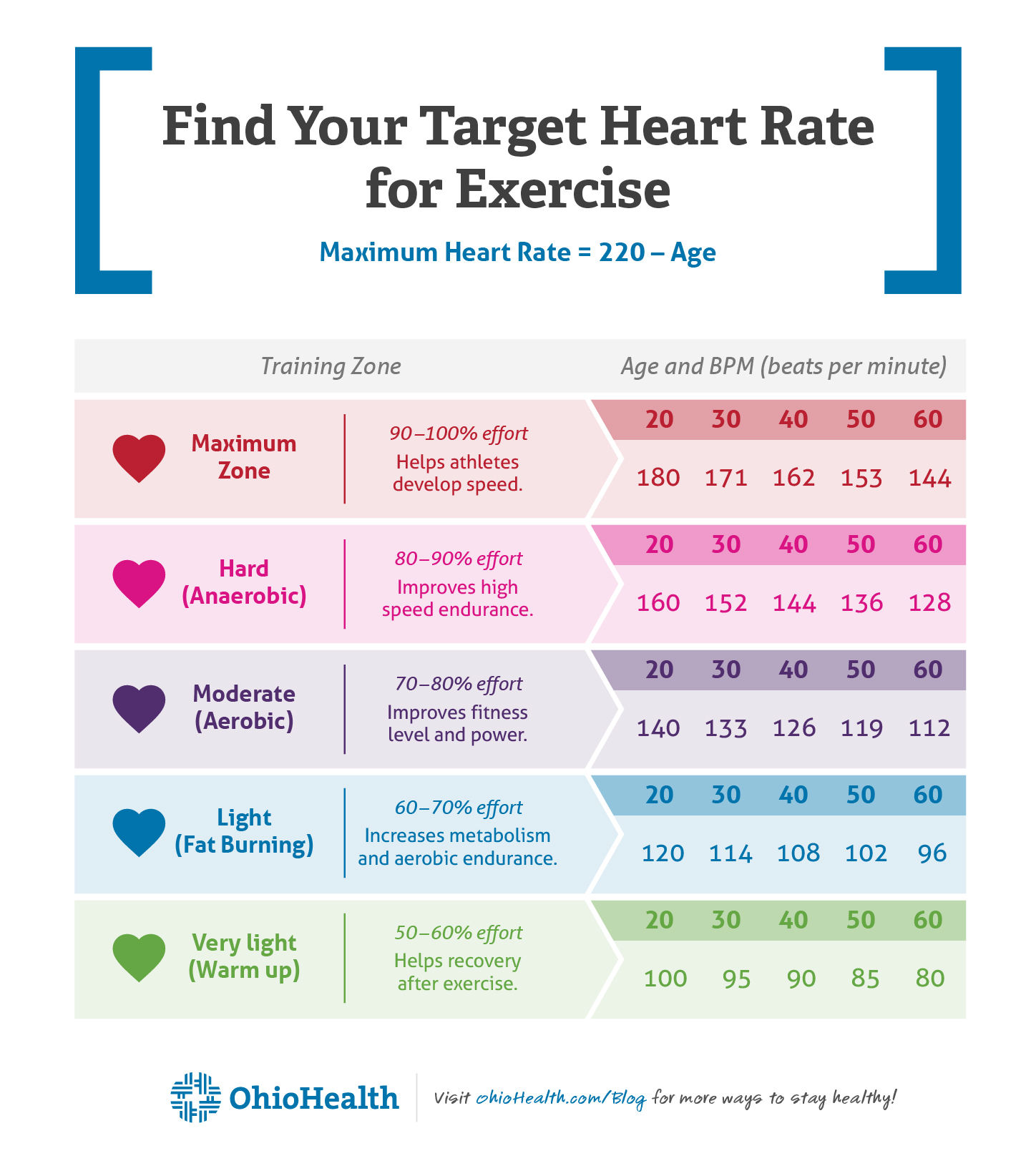
- Compare your heart rate to the recommended target zones for your age and fitness level.
For adults, a normal resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. However, athletes and highly trained individuals may have a lower resting heart rate, as their hearts are more efficient at pumping blood. After exercise, a normal heart rate should return to its resting state within a few minutes. If your heart rate remains elevated for an extended period, it may be a sign of a high heart rate after running.
It is recommended to measure your heart rate regularly after running to monitor your cardiovascular health and fitness level. By tracking your heart rate over time, you can identify trends and patterns that may indicate the need for further evaluation or intervention.
When to Worry About a High Heart Rate Post-Exercise
A high heart rate after running is not always a cause for concern, as it can be a normal response to physical activity. However, there are certain circumstances under which a high heart rate after running may indicate a more serious medical issue. Here are some situations in which you should seek professional help:
- If your heart rate remains elevated for an extended period after exercise, even after rest and hydration.
- If you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness during or after exercise.
- If you have a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or other medical conditions that may affect your cardiovascular health.
- If you notice a sudden or significant increase in your resting heart rate, or if you experience palpitations or irregular heart rhythms.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A high heart rate after running may be a sign of a more serious medical issue, such as a heart arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, or other cardiovascular condition. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment or referral to a specialist.
It is important to note that a high heart rate after running is not always a cause for concern. However, if you are concerned about your heart rate or experience any symptoms during or after exercise, it is always better to be safe and seek medical attention. By taking care of your cardiovascular health and monitoring your heart rate, you can reduce the risk of serious medical issues and improve your overall fitness and well-being.
Management Strategies for a High Heart Rate Post-Run
If you experience a high heart rate after running, there are several practical strategies you can use to manage and reduce your heart rate. Here are some tips to help you manage a high heart rate after running:
- Proper hydration: Dehydration can contribute to a high heart rate after running. Make sure to drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to stay hydrated. You can also consume sports drinks or electrolyte-rich beverages to help replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
- Cool-down exercises: Gradually reducing your heart rate after exercise can help prevent a high heart rate. Incorporate cool-down exercises, such as walking or stretching, into your post-run routine to help your heart rate return to its resting state.
- Breathing techniques: Deep, controlled breathing can help reduce your heart rate and promote relaxation. Practice deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or pursed-lips breathing, to help manage a high heart rate after running.
- Progressive training: Regular exercise and progressive training can help improve your cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your runs over time to build endurance and improve your heart health.
- Cross-training activities: Incorporating cross-training activities, such as swimming or cycling, can help improve your overall fitness and reduce the risk of injury and overuse. Cross-training can also help vary your exercise routine and prevent boredom or burnout.
- Balanced diet: A balanced and nutritious diet can support heart health, exercise performance, and recovery. Make sure to consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to perform at its best.
By following these management strategies, you can help reduce your risk of a high heart rate after running and improve your overall fitness and well-being. Remember to listen to your body and seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or concerns during or after exercise.
The Importance of Proper Training and Conditioning
Proper training and conditioning play a crucial role in improving cardiovascular fitness and reducing the risk of a high heart rate after running. By following a regular exercise routine and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your runs, you can build endurance, improve your heart health, and reduce your risk of injury and overuse.
Progressive training involves starting with lower-intensity workouts and gradually increasing the difficulty over time. This approach allows your body to adapt to the increased demands of exercise and reduces the risk of injury or burnout. By following a progressive training plan, you can improve your cardiovascular fitness, build endurance, and reduce your risk of a high heart rate after running.
Regular exercise can also help improve your heart health and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. By strengthening the heart muscle and improving circulation, regular exercise can help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular function. These benefits can help reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running and improve your overall health and well-being.
In addition to regular exercise, proper conditioning is also important for reducing the risk of a high heart rate after running. This includes proper warm-up and cool-down exercises, stretching, and strength training. By incorporating these elements into your exercise routine, you can improve your flexibility, build strength, and reduce your risk of injury and overuse.
In summary, proper training and conditioning are essential for improving cardiovascular fitness and reducing the risk of a high heart rate after running. By following a progressive training plan, incorporating cross-training activities, and practicing proper conditioning techniques, you can improve your heart health, build endurance, and enjoy a safe and effective running routine.
The Benefits of Incorporating Cross-Training Activities
Cross-training activities, such as swimming, cycling, or strength training, can help improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of injury and overuse. By incorporating cross-training activities into your exercise routine, you can build strength, improve flexibility, and reduce the impact on your joints.
Cross-training activities can also help improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running. By varying your exercise routine and incorporating different activities, you can challenge your heart and lungs in new ways and improve your overall fitness level. This can help reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running and improve your exercise performance.
Swimming, for example, is a low-impact activity that can help improve cardiovascular fitness and build endurance. The water provides natural resistance, which can help build strength and improve muscle tone. Swimming can also help improve flexibility and range of motion, which can reduce the risk of injury and overuse.
Cycling is another excellent cross-training activity that can help improve cardiovascular fitness and build endurance. Cycling is a low-impact activity that is easy on the joints, making it an excellent option for individuals with joint pain or injuries. Cycling can also help improve balance, coordination, and leg strength.
Strength training is another important cross-training activity that can help improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of injury and overuse. Strength training exercises, such as squats, lunges, or push-ups, can help build muscle strength and endurance. This can help improve exercise performance, reduce the risk of injury, and improve overall health and well-being.
In summary, incorporating cross-training activities, such as swimming, cycling, or strength training, can help improve overall fitness and reduce the risk of a high heart rate after running. By varying your exercise routine and incorporating different activities, you can challenge your heart and lungs in new ways, build strength, improve flexibility, and reduce the risk of injury and overuse.
The Role of Nutrition in Heart Health and Exercise Performance
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in supporting heart health, exercise performance, and recovery. Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help provide the energy and nutrients needed to support a healthy heart and optimal exercise performance.
When it comes to managing a high heart rate after running, nutrition can play a key role. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help support heart health and exercise performance. Here are some recommendations for pre- and post-run meals and snacks:
- Pre-run meals: Aim to eat a balanced meal that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats 2-3 hours before your run. This can help provide sustained energy and prevent a spike in blood sugar levels. Examples of pre-run meals include whole grain toast with avocado and eggs, or a bowl of oatmeal with fruit and nuts.
- Pre-run snacks: If you’re running within an hour of eating, opt for a lighter snack that is easy to digest. Examples of pre-run snacks include a banana, a small handful of nuts, or a piece of whole grain toast with nut butter.
- Post-run meals: After a run, aim to eat a balanced meal that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats within an hour of finishing your workout. This can help replenish energy stores, support muscle recovery, and reduce inflammation. Examples of post-run meals include grilled chicken with roasted vegetables and quinoa, or a smoothie made with fruit, spinach, protein powder, and almond milk.
- Post-run snacks: If you’re not hungry for a full meal right away, opt for a snack that combines carbohydrates and protein. Examples of post-run snacks include Greek yogurt with berries, or a handful of trail mix with dried fruit and nuts.
In addition to eating a balanced diet, it’s also important to stay properly hydrated before, during, and after exercise. Dehydration can contribute to a high heart rate after running, so aim to drink plenty of water or other fluids throughout the day. You can also consume sports drinks or electrolyte-rich beverages during or after exercise to help replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
In summary, a balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in supporting heart health, exercise performance, and recovery. By eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods and staying properly hydrated, you can help manage a high heart rate after running and improve your overall health and well-being.