What are Triglycerides and Why Do They Matter?
Triglycerides are a type of fat, or lipid, found in the blood. They play a crucial role in providing energy to the body, particularly when at rest or between meals. However, maintaining appropriate levels of triglycerides is essential for overall health, especially in relation to heart health. High triglyceride levels, also known as hypertriglyceridemia, can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of death worldwide.
The term “triglycerides” might not be familiar to many, but the concept of “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) is increasingly relevant in the context of preventive healthcare. By understanding the significance of triglycerides and their ideal levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
How to Measure Triglyceride Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Measuring triglyceride levels is a crucial step in understanding your overall health, particularly in relation to heart health. The process typically involves a blood test, which can be performed in various settings, such as a healthcare provider’s office, laboratory, or even at home with specific testing kits.
When it comes to measuring triglycerides, fasting is essential. This is because triglyceride levels can fluctuate significantly based on recent food and drink consumption. Generally, healthcare professionals recommend fasting for 8 to 12 hours before the blood test. During this time, it’s best to avoid food, beverages (except water), and even chewing gum to ensure accurate results.
Several methods are available for measuring triglyceride levels. The most common approach is a standard blood test, which involves drawing a small sample of blood from a vein in the arm. This method is widely used due to its accuracy and reliability. Alternatively, at-home testing kits are available, allowing individuals to measure their triglyceride levels in the comfort of their own homes. These kits typically involve a finger-prick blood sample, with results provided within minutes.
Regardless of the method chosen, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals when measuring triglyceride levels. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual health profiles and help interpret the results. By understanding “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have), individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Ideal Triglyceride Levels: What Should You Aim For?
Understanding the optimal triglyceride levels is essential for maintaining heart health and overall well-being. For adults, the ideal triglyceride levels generally fall within specific ranges, which can vary based on factors such as age, sex, and overall health.
In general, desirable triglyceride levels are considered to be below 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood. Borderline-high triglycerides range from 150 to 199 mg/dL, while high triglycerides fall between 200 and 499 mg/dL. Very high triglycerides, which significantly increase the risk of health complications, exceed 500 mg/dL.
It’s important to note that these ranges serve as general guidelines and may not apply to every individual. Personalized targets for “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) can be determined in consultation with healthcare providers, who take into account an individual’s unique health profile and risk factors. For instance, individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or other health conditions may require more stringent triglyceride level targets.
Regular monitoring and management of triglyceride levels can contribute to improved health outcomes and reduced risk of complications. By working closely with healthcare providers and implementing evidence-based strategies, individuals can effectively maintain their triglyceride levels within the optimal range, promoting long-term well-being and heart health.
Factors Influencing Triglyceride Levels: A Closer Look
Various factors can impact triglyceride levels, making it essential to understand these influences to maintain healthy levels and reduce the risk of associated health complications. Some of the primary factors include diet, exercise, alcohol consumption, and medical conditions.
Diet plays a significant role in triglyceride levels. Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats, sugars, and refined carbohydrates can contribute to elevated triglycerides. Conversely, incorporating heart-healthy foods such as whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help lower triglyceride levels. It’s crucial to strike a balance between consuming these beneficial foods and avoiding those that negatively impact triglyceride levels.
Physical activity is another critical factor in managing triglyceride levels. Regular exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, can help lower triglycerides and improve overall heart health. Aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week is recommended for maintaining healthy triglyceride levels.
Alcohol consumption can also impact triglyceride levels. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to elevated triglycerides, increasing the risk of health complications. Limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men, can help maintain healthy triglyceride levels.
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and hypothyroidism, can contribute to high triglyceride levels. In these cases, addressing the underlying condition and working closely with healthcare providers to manage triglyceride levels is essential. By understanding the factors that influence triglyceride levels, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) and promote overall well-being.
Consequences of High Triglyceride Levels: What You Need to Know
Elevated triglyceride levels can have significant consequences on an individual’s health, increasing the risk of developing various medical conditions. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for early detection and intervention.
One of the most well-known health risks associated with high triglycerides is cardiovascular disease. Excess triglycerides in the bloodstream can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, a hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This process can restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. Therefore, managing “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) is essential for maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of these potentially life-threatening conditions.
Another potential consequence of elevated triglyceride levels is pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas. High triglycerides can lead to the accumulation of fat in the pancreas, causing irritation and inflammation. Severe cases of pancreatitis can result in hospitalization, and in rare instances, may even be life-threatening. By maintaining healthy triglyceride levels, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing pancreatitis and other associated complications.
In addition to these health risks, high triglycerides can also contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels. Managing triglyceride levels is a critical component of addressing metabolic syndrome and promoting overall well-being.
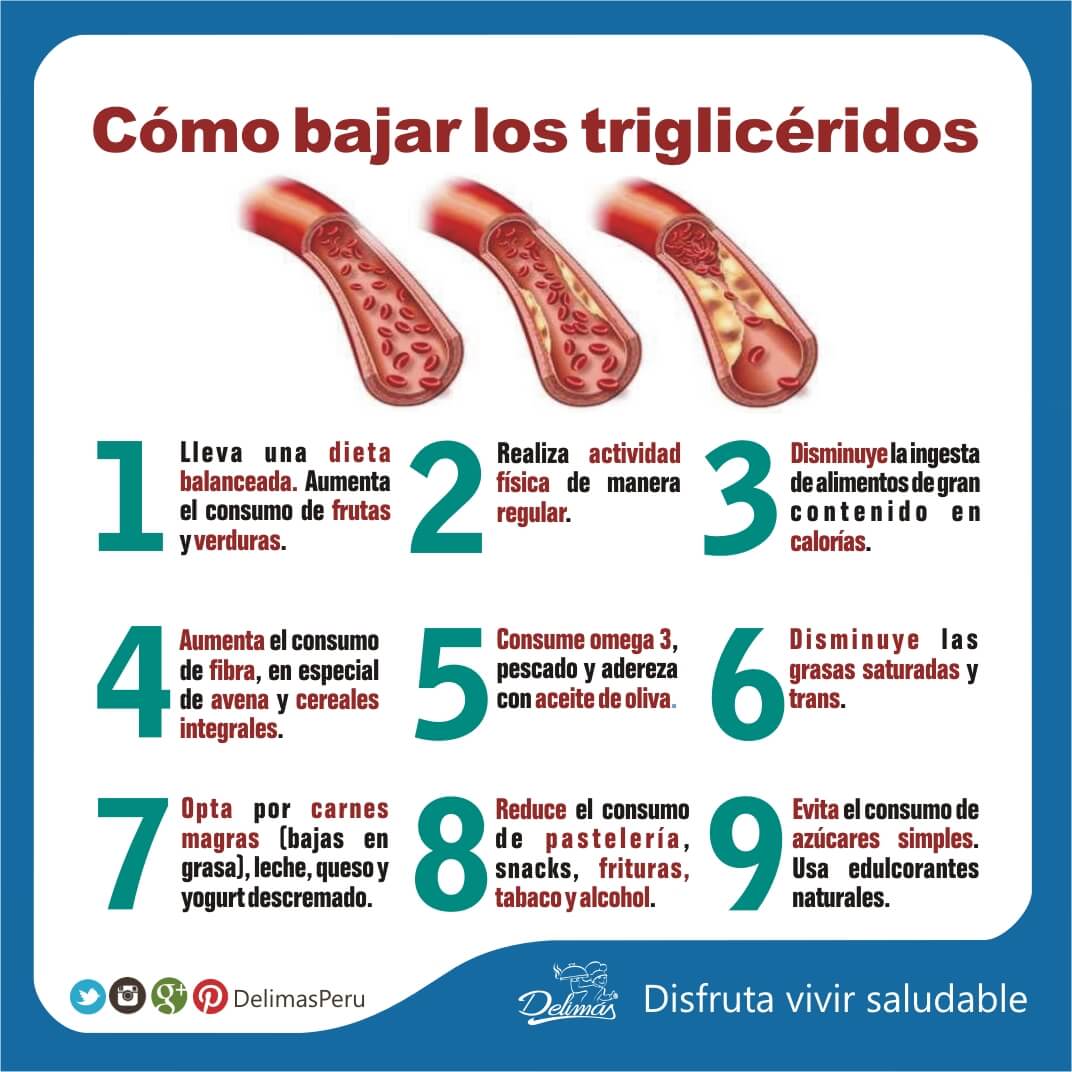
Strategies for Lowering Triglyceride Levels: A Holistic Approach
Maintaining healthy triglyceride levels is essential for overall well-being and heart health. Adopting a holistic approach that combines evidence-based strategies can help individuals effectively lower their triglyceride levels and reduce the risk of associated health complications. Here are some practical tips for managing triglycerides:
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet: Aim to consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of saturated and trans fats, sugars, and refined carbohydrates. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, can also help lower triglyceride levels.
- Increase physical activity: Engage in regular exercise, particularly aerobic activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week to help maintain healthy triglyceride levels.
- Manage weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health and triglyceride management. If overweight, even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly impact triglyceride levels and overall well-being.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to elevated triglyceride levels. Limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men, can help maintain healthy triglyceride levels.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can impact triglyceride levels and overall health. Engage in stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to help manage stress and promote well-being.
It’s essential to consult with healthcare providers when implementing strategies to lower triglyceride levels. They can provide personalized recommendations based on individual health profiles and help individuals establish realistic goals for “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) to promote overall health and well-being.
Monitoring Triglyceride Levels Over Time: The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular monitoring of triglyceride levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By tracking progress and making necessary adjustments to lifestyle habits, individuals can effectively manage their triglyceride levels and reduce the risk of associated health complications. Here’s why consistent monitoring matters:
- Track progress: Regular monitoring allows individuals to assess the effectiveness of their triglyceride management strategies and make adjustments as needed. By tracking changes in triglyceride levels over time, individuals can determine whether their current approach is working or if alternative strategies should be considered.
- Identify patterns: Consistent monitoring can help identify patterns and trends in triglyceride levels. For instance, some individuals may notice that their triglyceride levels spike after consuming certain foods or engaging in specific activities. Recognizing these patterns can inform lifestyle choices and support long-term triglyceride management.
- Promote accountability: Regular check-ups can serve as a form of accountability, encouraging individuals to adhere to their triglyceride management plans and maintain healthy habits. By committing to regular monitoring, individuals demonstrate their dedication to managing “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) and promoting overall well-being.
To establish a monitoring schedule, individuals should consult with their healthcare providers. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized recommendations based on individual health profiles and help individuals determine the appropriate frequency and methods for monitoring triglyceride levels. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can ensure that their monitoring efforts are effective, efficient, and aligned with their overall health goals.
Living with High Triglycerides: Navigating Daily Life and Supporting Your Health
Managing high triglyceride levels can present unique challenges, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can effectively navigate daily life and promote overall well-being. Here are some tips for living with high triglycerides:
- Maintain a positive outlook: While managing high triglycerides can be challenging, focusing on the benefits of maintaining healthy levels and implementing effective strategies can help individuals stay motivated and optimistic. By adopting a proactive approach, individuals can take control of their health and make meaningful changes to their daily lives.
- Seek support: Sharing experiences and learning from others who are managing high triglycerides can provide valuable insights and encouragement. Consider joining support groups, either in-person or online, to connect with others who are navigating similar challenges.
- Establish a routine: Consistency is key when managing high triglycerides. Establishing a routine that incorporates heart-healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress-reduction techniques, can help individuals maintain healthy triglyceride levels and promote overall well-being.
- Communicate openly with healthcare providers: Regularly communicating with healthcare providers can help individuals stay informed about their triglyceride levels and any necessary adjustments to their management strategies. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can ensure that they are receiving the best possible care and support for managing their high triglycerides.
Remember, managing high triglycerides is an ongoing process, and it’s essential to be patient, persistent, and proactive. By adopting a holistic approach that combines evidence-based strategies, regular monitoring, and a strong support system, individuals can effectively navigate daily life with high triglycerides and promote overall health and well-being. Always consult with healthcare providers for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding “cuanto de triglicéridos debe tener una persona” (how much triglycerides should a person have) and other aspects of triglyceride management.