What Does ‘Calories Per Mile’ Mean?
Calories per mile is a term used to describe the amount of energy expended during physical activities while covering a mile. This metric is essential for fitness enthusiasts, joggers, and athletes as it helps them understand their energy requirements, track progress, and make informed decisions about their exercise routines. By comprehending the number of calories burned per mile, individuals can maintain a healthy balance between their energy intake and output, ensuring optimal fitness and well-being.
How to Calculate Calories Burned Per Mile: A Step-by-Step Approach
Calculating calories burned per mile involves considering several factors, including body weight, age, gender, and exercise intensity. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine your calories burned per mile:
- Determine your body weight in pounds or kilograms.
- Identify the specific physical activity you will be performing, such as running, walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Establish your exercise intensity, which can be categorized as low, moderate, or high.
- Utilize the appropriate formula or consult a reliable online calculator to compute the calories burned per mile based on your body weight, activity, and intensity.
- Consider using fitness trackers or smartwatches, which can automatically calculate calories burned per mile based on your personal data and activity.
The Role of Body Weight in Calculating Calories Per Mile
Body weight significantly influences the number of calories burned per mile during physical activities. Generally, the heavier an individual is, the more calories they will burn per mile due to the increased energy required to move a larger body mass. For example, a 200-pound person running a mile will burn more calories than a 150-pound person running the same distance, even if they maintain the same pace.
To further illustrate the impact of body weight on calories burned per mile, consider the following examples:
- Walking: A 150-pound person burns approximately 80-100 calories per mile walking, while a 200-pound person burns around 120-160 calories per mile.
- Running: A 150-pound person burns approximately 100-130 calories per mile running, while a 200-pound person burns around 150-200 calories per mile.
While body weight plays a crucial role in determining calories burned per mile, it is essential to remember that other factors, such as age, gender, and exercise intensity, also impact caloric expenditure. By taking all these factors into account, individuals can gain a more accurate understanding of their caloric needs and adjust their exercise routines and diets accordingly.
Influence of Age and Gender on Calories Burned Per Mile
Age and gender play essential roles in determining the number of calories burned per mile during physical activities. These factors affect metabolism, muscle mass, and hormonal differences, which can influence caloric expenditure.
Age
As individuals age, their metabolism tends to slow down, resulting in a decrease in the number of calories burned per mile. This is primarily due to a loss of muscle mass and a decrease in physical activity levels. However, maintaining an active lifestyle and engaging in regular strength training can help offset these age-related changes and optimize caloric expenditure.
Gender
Gender differences also impact the number of calories burned per mile. Generally, men burn more calories per mile than women due to their higher muscle mass and lower body fat percentages. However, this gap narrows when adjusting for body weight, as heavier individuals tend to burn more calories than lighter individuals, regardless of gender.
It is essential to consider age and gender when calculating calories burned per mile, as these factors can significantly influence caloric expenditure. By understanding how these variables affect caloric needs, individuals can make more informed decisions about their exercise routines and diets, ultimately promoting overall fitness and well-being.
Exercise Intensity: A Crucial Factor in Calculating Calories Burned Per Mile
Exercise intensity significantly influences the number of calories burned per mile during physical activities. By understanding the differences in caloric expenditure between low, moderate, and high-intensity workouts, individuals can optimize their exercise routines and achieve their fitness goals more effectively.
Low-Intensity Workouts
Low-intensity workouts, such as slow walking or easy cycling, typically burn fewer calories per mile than moderate or high-intensity activities. These exercises are an excellent option for beginners, individuals recovering from injuries, or those looking to maintain a steady pace while conserving energy.
Moderate-Intensity Workouts
Moderate-intensity workouts, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming laps, offer a balance between caloric expenditure and endurance. These exercises are suitable for individuals seeking to improve their fitness levels without overexerting themselves. Moderate-intensity workouts burn more calories per mile than low-intensity activities but less than high-intensity workouts.
High-Intensity Workouts
High-intensity workouts, such as sprinting, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), or cycling at high speeds, burn the most calories per mile. These exercises are ideal for experienced athletes or individuals looking to challenge themselves and significantly increase their caloric expenditure. However, high-intensity workouts should be approached with caution, as they can increase the risk of injury or burnout if not properly managed.
By incorporating a variety of exercise intensities into their fitness routines, individuals can maximize their caloric expenditure and promote overall well-being. Remember that exercise intensity is just one factor to consider when calculating calories burned per mile, and it is essential to account for body weight, age, gender, and other variables to gain a comprehensive understanding of caloric needs.
Popular Activities and Their Associated Calories Burned Per Mile
Understanding the number of calories burned per mile for popular physical activities can help fitness enthusiasts, joggers, and athletes make informed decisions about their exercise routines. Here are some common activities and their corresponding caloric expenditures:
Running
The exact number of calories burned per mile while running depends on factors such as body weight, running pace, and terrain. On average, a 150-pound individual burns around 100-130 calories per mile running at a moderate pace on flat terrain. To maximize caloric expenditure during runs, consider incorporating interval training, hills, or varying terrains.
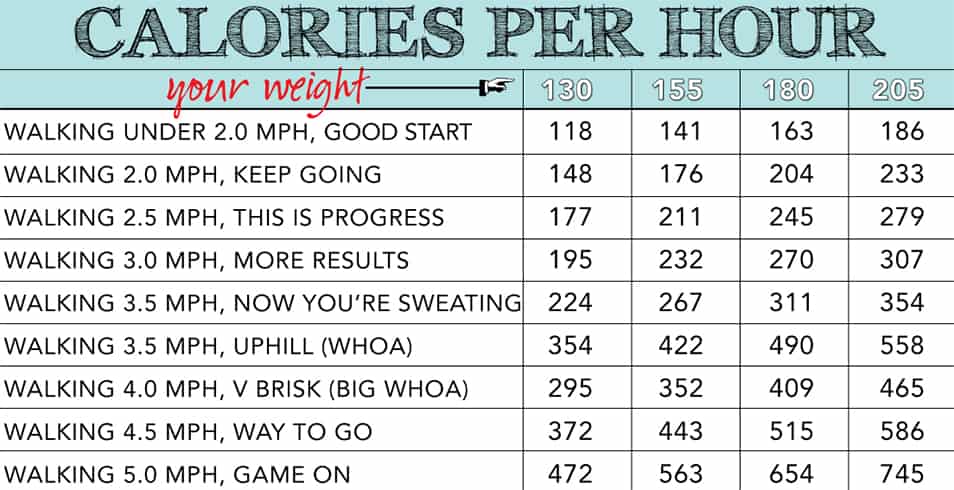
Walking
Walking is a low-impact activity that still offers significant caloric benefits. A 150-pound person burns approximately 80-100 calories per mile walking at a brisk pace. To increase caloric expenditure during walks, try power walking, walking uphill, or incorporating strength training exercises throughout the walk.
Cycling
The number of calories burned per mile while cycling depends on factors such as resistance, speed, and body position. On average, a 150-pound individual burns around 50-70 calories per mile cycling at a moderate pace. To maximize caloric expenditure during cycling sessions, consider incorporating hills, resistance training, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Swimming
Swimming is a full-body workout that offers excellent caloric benefits. A 150-pound person burns approximately 350-500 calories per hour swimming laps at a moderate pace. To increase caloric expenditure during swimming sessions, try incorporating different strokes, high-intensity intervals, or water resistance exercises.
By understanding the caloric expenditure associated with popular physical activities, individuals can make informed decisions about their exercise routines and optimize their fitness journeys. Remember that factors such as body weight, age, gender, and exercise intensity can impact the number of calories burned per mile, so it is essential to consider these variables when calculating caloric needs.
Maximizing Caloric Expenditure: Tips and Tricks for Burning More Calories Per Mile
For fitness enthusiasts, joggers, and athletes looking to optimize their caloric expenditure during physical activities, incorporating specific strategies can significantly increase the number of calories burned per mile. Here are some practical tips and tricks to help maximize caloric expenditure:
Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating between high-intensity and low-intensity exercise intervals. This approach can help increase caloric expenditure, improve cardiovascular fitness, and boost metabolism. For example, during a run, alternate between one minute at a high-intensity pace and two minutes at a slower, recovery pace.
Strength Training
Incorporating strength training exercises into your workout routine can help build lean muscle mass, which in turn increases caloric expenditure during physical activities. Consider adding bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or free weights to your workouts to target major muscle groups.
Varying Terrain and Incline
Changing the terrain and incline during physical activities can significantly impact the number of calories burned per mile. Running or walking on hilly terrain, for instance, can burn up to 50% more calories than exercising on flat surfaces. Similarly, cycling on inclines or using a stationary bike with adjustable resistance can help maximize caloric expenditure.
Cross-Training
Engaging in various physical activities can help keep workouts interesting and challenging while ensuring that different muscle groups are targeted. Cross-training also allows individuals to maintain a high level of caloric expenditure without overtaxing specific muscle groups or joints.
By incorporating these strategies into their fitness routines, individuals can effectively maximize their caloric expenditure and promote overall well-being. Remember that factors such as body weight, age, gender, and exercise intensity can impact the number of calories burned per mile, so it is essential to consider these variables when calculating caloric needs and setting fitness goals.
Maintaining a Balanced Lifestyle: Integrating Calories Burned Per Mile into Your Fitness Journey
While tracking calories burned per mile is essential for fitness enthusiasts, joggers, and athletes, it is crucial to remember that overall fitness and well-being should be the ultimate goals. Balancing caloric expenditure with a healthy, sustainable diet is vital for achieving and maintaining optimal health.
To ensure a balanced lifestyle, consider the following recommendations:
- Consume a well-rounded diet: Focus on incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, into your daily meals. Aim to consume the recommended daily servings for each food group based on your age, gender, and activity level.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall health and exercise performance. Ensure you consume enough water before, during, and after physical activities to maintain optimal hydration levels.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Eat when you’re hungry and stop when you’re satisfied. Avoid overeating or undereating, as both can negatively impact your health and fitness goals.
- Rest and recover: Allow your body adequate time to rest and recover between intense workout sessions. This will help prevent injuries, reduce the risk of burnout, and promote overall well-being.
By focusing on overall fitness and well-being, rather than solely on caloric expenditure, individuals can lead healthier, more balanced lifestyles. Remember that understanding the number of calories burned per mile is just one aspect of achieving and maintaining optimal health. By incorporating a well-rounded diet, proper hydration, mindful eating, and adequate rest, you can ensure a sustainable, long-term approach to fitness and well-being.