Understanding Calories and Their Role in Fitness
Calories are a fundamental aspect of fitness and overall health. In essence, calories represent the energy that our bodies obtain from food and beverages. This energy is essential for various bodily functions, such as breathing, digestion, and physical activity. When discussing calories burned running one mile, it is crucial to understand the role of calories in fitness and how running can contribute to a caloric deficit, which is necessary for weight loss.
How Running Affects Caloric Expenditure
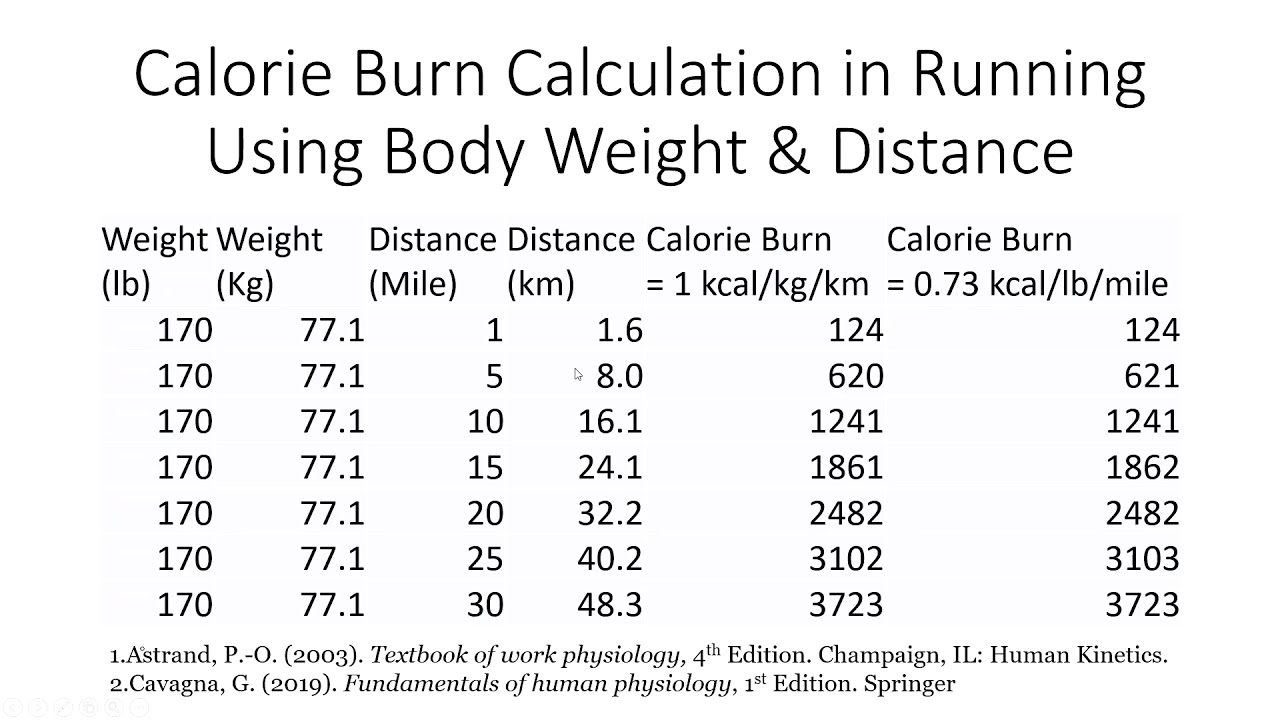
Running is an effective way to burn calories, and the number of calories burned running one mile can vary depending on several factors. First and foremost, an individual’s body weight significantly influences the number of calories burned during a run. Generally, the heavier a person is, the more calories they will burn while running. However, this relationship is not linear, as the body’s efficiency in converting weight into energy also plays a role.
Running speed is another critical factor in determining the calories burned running one mile. The faster a person runs, the more energy they must expend to maintain that speed, resulting in more calories burned. Lastly, the duration of the run is also an essential factor, as longer runs will inevitably lead to more calories burned over time.
The Impact of Terrain and Incline on Caloric Burn
Beyond body weight, running speed, and duration, the terrain and incline of a running route can significantly impact the calories burned running one mile. Running on softer surfaces, such as grass or trails, can result in more calories burned compared to running on harder surfaces, like concrete or asphalt. This is because softer surfaces require more effort to propel oneself forward, leading to increased energy expenditure.
Inclines, whether running uphill or on a treadmill with an incline setting, can also boost the number of calories burned during a mile run. This is because running uphill requires more effort from the leg muscles, which in turn increases the overall energy expenditure. Additionally, running at an incline can lead to a higher heart rate, further contributing to the calories burned during the run.
How to Estimate Calories Burned Running a Mile
Accurately estimating the calories burned running one mile can be challenging, as individual factors such as body weight, running efficiency, and fitness level can all impact the final tally. However, several methods and tools can help provide a reasonably accurate estimate.
Online calculators, such as those found on fitness websites or apps, can help estimate the calories burned running a mile based on user-inputted data, including body weight, running speed, and duration. These calculators typically use standardized formulas, such as the METs (Metabolic Equivalent of Task) method, to estimate energy expenditure.
Fitness trackers, such as smartwatches or dedicated running watches, can also provide estimates of calories burned during a run. These devices often use a combination of built-in sensors, such as accelerometers and heart rate monitors, to track movement and physiological responses during exercise, providing more personalized and accurate estimates of calories burned.
Comparing Calories Burned Running a Mile to Other Activities
While running a mile is an effective way to burn calories, it is essential to understand how it stacks up against other popular physical activities. This broader perspective can help individuals make more informed decisions about their exercise routines and overall fitness goals.
For instance, swimming, cycling, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can all burn similar or even greater numbers of calories compared to running a mile. Swimming, for example, can burn up to 400 calories in just 30 minutes for a 155-pound individual, while a vigorous cycling session can burn around 600 calories in an hour. HIIT workouts, which typically involve short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods, can burn up to 800 calories per hour, depending on the specific exercises and the individual’s intensity.
However, it is essential to consider factors beyond just caloric expenditure when comparing different activities. For example, running outdoors can provide mental health benefits, such as stress relief and improved mood, that may not be as readily available with other forms of exercise. Additionally, individual preferences, accessibility, and the availability of equipment or facilities can all impact the choice of physical activity.
Maximizing Caloric Burn during a Mile Run
While running a mile is already an efficient way to burn calories, there are several strategies and techniques that can help increase the caloric expenditure during this activity. Implementing these methods can help individuals maximize their workout and achieve their fitness goals more effectively.
Interval training, which involves alternating between periods of high-intensity exercise and lower-intensity recovery, can significantly boost the number of calories burned during a mile run. By incorporating short bursts of sprinting or fast-paced running into a mile run, individuals can increase their heart rate and metabolic rate, leading to a higher caloric burn. For example, alternating between 30 seconds of all-out sprinting and 90 seconds of jogging or walking can create an effective interval training session.
Strength exercises, such as lunges, squats, and jumping jacks, can also be integrated into a mile run to enhance the overall caloric burn. By performing these exercises at various points throughout the run, individuals can engage different muscle groups and increase their energy expenditure. Additionally, strength exercises can help improve running efficiency and speed, further contributing to the number of calories burned during a mile run.
Maintaining a Balanced Approach to Fitness and Nutrition
While understanding the calories burned running one mile is essential for tracking fitness progress and setting goals, it is equally important to consider the role of nutrition in overall health and well-being. A balanced approach to fitness and nutrition involves not only focusing on caloric expenditure during exercise but also paying attention to the quality and composition of the diet.
To maintain a healthy balance, individuals should aim to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients to support exercise recovery, muscle growth, and overall health. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water before, during, and after exercise can help optimize performance and aid in recovery.
It is also crucial to find a balance between caloric intake and expenditure to support weight loss or maintenance goals. Consuming more calories than needed can lead to weight gain, while consistently consuming fewer calories than burned can result in weight loss. However, it is essential to approach weight loss in a sustainable and healthy manner, focusing on long-term lifestyle changes rather than short-term dietary restrictions.
Long-Term Strategies for Sustainable Weight Loss and Fitness
Achieving and maintaining long-term weight loss and fitness goals often involves more than just focusing on the calories burned running one mile. By incorporating consistent exercise, a balanced diet, and sustainable lifestyle changes, individuals can create a comprehensive approach to weight loss and fitness that promotes long-term success.
Consistency is key when it comes to exercise and weight loss. Regularly engaging in physical activity, such as running a mile a few times a week, can help individuals burn calories, build endurance, and improve overall fitness. Additionally, incorporating a variety of exercises, including strength training, stretching, and low-impact activities, can help prevent injury and keep workouts interesting and engaging.
A balanced diet, rich in nutrient-dense foods, plays a crucial role in weight loss and overall health. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and controlling portion sizes, individuals can create a sustainable eating pattern that supports their weight loss and fitness goals. Additionally, staying hydrated and practicing mindful eating can help optimize digestion, reduce cravings, and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Finally, it is essential to approach weight loss and fitness goals with a long-term mindset, focusing on sustainable lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes or fad diets. By setting realistic goals, tracking progress, and seeking support from friends, family, or a professional, individuals can create a comprehensive plan that promotes long-term success and overall well-being.