What Causes Bleeding After a Workout?
Bleeding after a workout can be caused by several factors, including capillary rupture, dehydration, and intense physical exertion. Capillary rupture, or the breaking of tiny blood vessels, is a common cause of bleeding after a workout, especially during high-impact activities such as running or jumping. Dehydration can also contribute to bleeding after a workout, as it can cause the blood to thicken, making it more likely to clot and rupture.
Intense physical exertion can also lead to bleeding after a workout, particularly in individuals who are new to exercise or who have recently increased the intensity or duration of their workouts. This is because strenuous exercise can increase the pressure in the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to rupture. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or high blood pressure, can increase the likelihood of bleeding after a workout.
Certain medications, such as blood thinners or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also increase the risk of bleeding after a workout. These medications can thin the blood, making it more likely to clot and rupture. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any new medications or supplements, especially if you are an athlete or plan to engage in regular exercise.
Recognizing Normal vs. Abnormal Bleeding
While some minor bleeding after a workout can be common, excessive or prolonged bleeding may indicate an underlying issue. Normal bleeding after a workout can include nosebleeds, bruising, or minor cuts. However, if bleeding is severe, lasts for an extended period, or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention.
Excessive bleeding after a workout can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a bleeding disorder or a blood vessel abnormality. Prolonged bleeding can also be a sign of an infection or other medical issue. It is important to monitor bleeding after a workout and seek medical attention if necessary.
Other symptoms that may accompany bleeding after a workout and indicate a more serious issue include dizziness, lightheadedness, or shortness of breath. These symptoms can be a sign of low blood pressure or other medical conditions and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Ignoring signs of excessive or prolonged bleeding after a workout can lead to serious complications, such as anemia or shock. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if bleeding is severe or accompanied by other symptoms.
Preventing Bleeding After a Workout
There are several steps you can take to prevent bleeding after a workout. Proper hydration is essential, as dehydration can increase the risk of capillary rupture. Adequate warm-up and cool-down periods can also help prevent bleeding by gradually increasing and decreasing blood flow to the muscles.
Gradual progression is also important when starting a new exercise routine or increasing the intensity of an existing one. Rapid increases in exercise intensity or duration can increase the risk of bleeding, so it is important to gradually increase the difficulty of your workouts over time.
Using appropriate protective gear during high-impact activities can also help prevent bleeding. This may include wearing helmets, knee pads, or elbow pads during activities such as cycling, skating, or rollerblading. Protective gear can help absorb impact and reduce the risk of capillary rupture.
If you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking specific medications that may increase the risk of bleeding, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise routine. They can provide guidance on how to safely engage in physical activity while minimizing the risk of bleeding.
First Aid Measures for Bleeding After a Workout
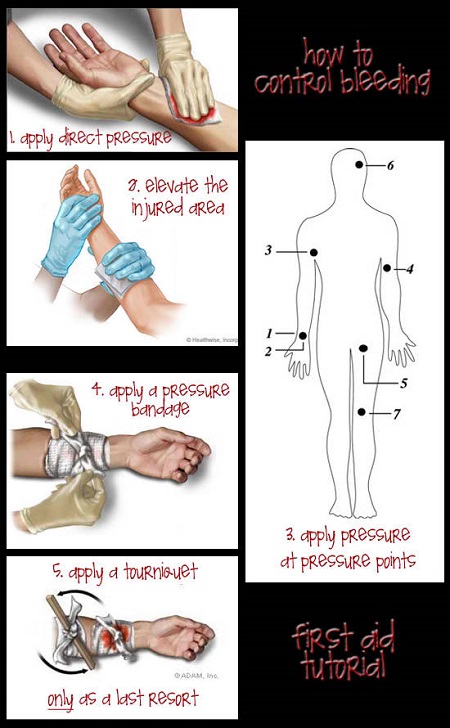
If you experience bleeding after a workout, there are several basic first aid measures you can take to manage the bleeding and prevent infection. First, apply pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage to help stop the bleeding. Elevate the affected area if possible, as this can help reduce blood flow to the area and promote clotting.
It is important to maintain cleanliness and hygiene when managing bleeding after a workout. Wash your hands thoroughly before touching the wound, and use clean bandages or cloths to apply pressure. Change the bandage frequently to prevent infection, and monitor the wound for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or pus.
If bleeding is severe or does not stop after 15 minutes of applied pressure, seek medical attention immediately. Prolonged or excessive bleeding can be a sign of a more serious issue and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention
In some cases, bleeding after a workout may indicate a more serious underlying issue and require medical attention. It is important to seek medical attention if bleeding is excessive, prolonged, or accompanied by other symptoms. Excessive bleeding may be a sign of a bleeding disorder or other medical condition, while prolonged bleeding can increase the risk of infection or other complications.
Bleeding accompanied by other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or shortness of breath, may indicate a more serious issue and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. These symptoms can be a sign of low blood pressure or other medical conditions and should not be ignored.
Ignoring signs of excessive or prolonged bleeding after a workout can lead to serious complications, such as anemia or shock. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if bleeding is severe or accompanied by other symptoms.
In some cases, bleeding after a workout may require medical procedures or over-the-counter medications. Medical procedures, such as stitches or cauterization, may be necessary for severe wounds, while over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be recommended for minor bleeding or discomfort.
Treatment Options for Bleeding After a Workout
The treatment options for bleeding after a workout will depend on the severity and underlying cause of the bleeding. For minor bleeding, such as nosebleeds or bruising, over-the-counter medications and wound care may be sufficient. Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage discomfort and reduce swelling, while wound care can help prevent infection and promote healing.
For more severe bleeding, medical procedures may be necessary. Stitches or cauterization may be required for deep wounds, while blood transfusions may be necessary for severe blood loss. In some cases, hospitalization may be required to monitor the bleeding and ensure proper healing.
If bleeding is caused by a pre-existing medical condition, such as a bleeding disorder, managing the underlying condition may be necessary to prevent future bleeding. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures. Regular medical check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can help manage pre-existing medical conditions and prevent bleeding after a workout.
Regardless of the severity of the bleeding, it is important to seek prompt medical attention if bleeding is excessive, prolonged, or accompanied by other symptoms. Ignoring signs of bleeding after a workout can lead to serious complications, such as anemia or shock. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment can help prevent these complications and ensure proper healing.
Long-Term Management of Bleeding After a Workout
Managing bleeding after a workout requires a long-term approach that includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing pre-existing medical conditions, and adjusting exercise routines as needed. Regular medical check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can help prevent and manage bleeding after a workout.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing bleeding after a workout. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress. A healthy lifestyle can help prevent dehydration, which is a common cause of bleeding after a workout. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water before, during, and after exercise can help prevent capillary rupture and other bleeding-related issues.
Managing pre-existing medical conditions is also important for preventing bleeding after a workout. Athletes with bleeding disorders or other medical conditions that increase the risk of bleeding should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a management plan. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures. Regular medical check-ups can help monitor the condition and adjust the management plan as needed.
Adjusting exercise routines can also help prevent bleeding after a workout. Athletes should gradually increase the intensity and duration of their workouts to prevent excessive physical exertion, which can increase the risk of bleeding. Adequate warm-up and cool-down periods can also help prevent bleeding by gradually increasing and decreasing blood flow to the muscles. Using appropriate protective gear during high-impact activities can also help prevent bleeding.
Regular medical check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can help prevent and manage bleeding after a workout. Healthcare providers can provide guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing pre-existing medical conditions, and adjusting exercise routines as needed. By working closely with healthcare providers, athletes can prevent bleeding and ensure safe and effective workouts.
Case Studies of Athletes Who Have Experienced Bleeding After a Workout
Bleeding after a workout can be a common issue for athletes, but in some cases, it can indicate an underlying medical condition. Here are some real-life examples of athletes who have experienced bleeding after a workout and how they managed their condition:
Case Study 1: The Marathon Runner with Excessive Nosebleeds
John, a 35-year-old marathon runner, experienced excessive nosebleeds after his long-distance runs. He sought medical attention and was diagnosed with a bleeding disorder. With proper management, including medications and lifestyle changes, John was able to continue his marathon training while minimizing the risk of bleeding.
Case Study 2: The Cyclist with Prolonged Bruising
Sarah, a 28-year-old cyclist, noticed prolonged bruising after her rides. She consulted with her healthcare provider and was diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency. By adjusting her diet and taking supplements, Sarah was able to improve her nutrient intake and reduce the likelihood of bruising.
Case Study 3: The Weightlifter with Muscle Bleeding
Mike, a 45-year-old weightlifter, experienced muscle bleeding after intense workouts. He worked with his healthcare provider to adjust his exercise routine, incorporating gradual progression and adequate warm-up and cool-down periods. By making these changes, Mike was able to continue his weightlifting routine while minimizing the risk of bleeding.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of seeking medical attention for bleeding after a workout, especially if it is excessive, prolonged, or accompanied by other symptoms. By working closely with healthcare providers, athletes can manage their condition and prevent future bleeding. It is also essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, manage pre-existing medical conditions, and adjust exercise routines as needed to prevent bleeding after a workout.