Understanding the Average Height: A Closer Look
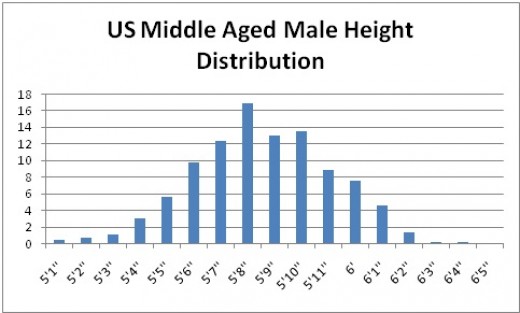
The “average height of a U.S. male” is a statistical measure that represents the central tendency of the male population’s height in the United States. Calculating this value involves determining the arithmetic mean of heights, which is the sum of all male heights divided by the total number of males. This metric offers valuable insights into the growth patterns, health, and well-being of the U.S. male population.
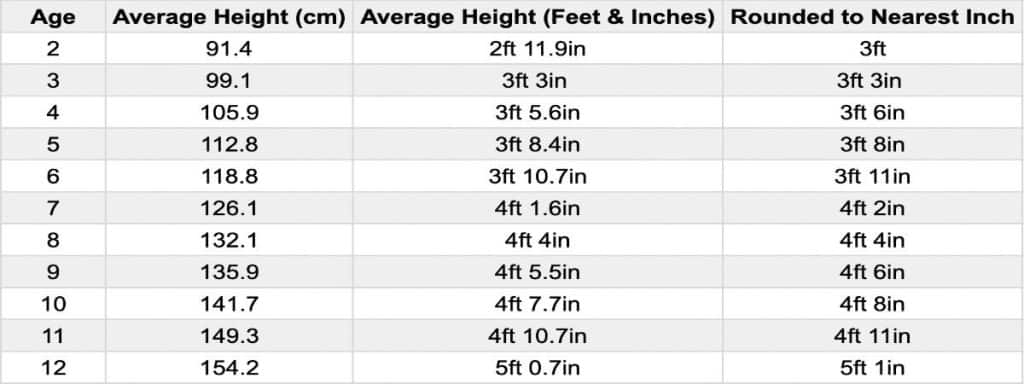
When examining the “average height of a U.S. male,” it is crucial to consider factors that may influence height, such as age, genetics, and ethnicity. Age plays a significant role in determining height, as males typically reach their maximum height during their late teens or early twenties. Genetics also contribute to height, with research suggesting that up to 80% of height is heritable. Ethnicity can also influence height, as genetic variations and ancestral origins may result in differences in average height among various population groups.
Historical Trends: How Male Height in the U.S. Has Changed Over Time
Throughout history, the “average height of a U.S. male” has experienced fluctuations due to various factors. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the average height of American males increased, partly due to improvements in nutrition and living conditions. The Industrial Revolution, for instance, led to advancements in agriculture, food preservation, and distribution, providing the population with a more diverse and nutrient-rich diet.
During the mid-20th century, the average height of U.S. males remained relatively stable. However, since the late 20th century, there has been a slight decline in the average height of American males. This decrease may be attributed to changes in dietary habits, reduced physical activity, and increased obesity rates, all of which can negatively impact growth and development.
Moreover, the average height of U.S. males has historically varied across different immigrant groups. For example, immigrants from Northern and Western Europe often had a taller average height than those from Southern and Eastern Europe. As these groups assimilated and intermarried, the average height of the U.S. male population shifted, reflecting the diverse genetic backgrounds of the American people.
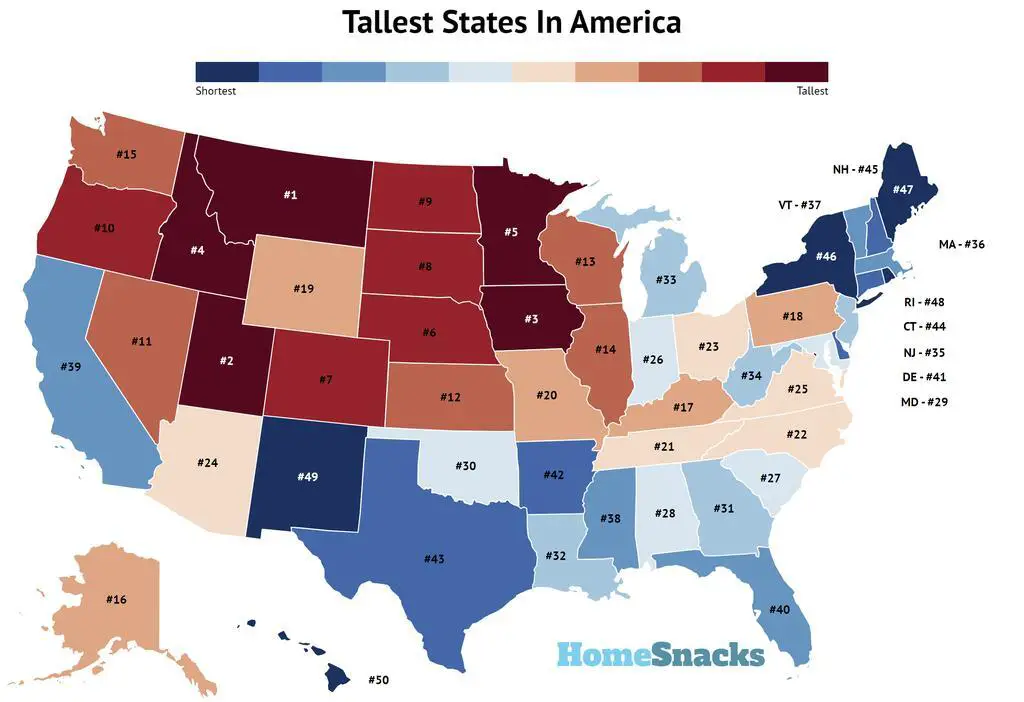
Geographical Variations: Regional Differences in Male Height Across the U.S.
The average height of a U.S. male can vary significantly across different regions, with several factors contributing to these disparities. Socioeconomic factors, cultural practices, and environmental influences all play a role in shaping the geographical distribution of male height within the United States.
For instance, states with higher average incomes and better access to healthcare and nutrition tend to have taller males, reflecting the positive impact of these resources on growth and development. Conversely, regions with lower socioeconomic status may have males with shorter average heights due to limited access to nutritious food, quality medical care, and safe living conditions.
Cultural practices can also influence male height. For example, certain communities may place a higher emphasis on nutrition, physical activity, and healthcare, leading to taller males in those areas. Additionally, environmental factors, such as altitude and climate, can affect male height, as research suggests that individuals living at higher altitudes tend to be slightly taller than their lowland counterparts.
Regional patterns in male height can provide valuable insights into the health and well-being of different populations across the U.S. By understanding these variations and the factors that contribute to them, policymakers, healthcare providers, and community leaders can develop targeted strategies to improve nutrition, healthcare, and overall living conditions, ultimately promoting optimal growth and development for all U.S. males, regardless of their geographical location.
Genetics and Ethnicity: The Impact on Male Height in the U.S.
Genetics and ethnicity play a significant role in determining the average height of a U.S. male. The genetic diversity of the U.S. population contributes to variations in male height, as different ancestral origins can result in distinct growth patterns and physical characteristics.
For example, individuals with Northern European ancestry often have a taller average height than those with Southern European or Asian ancestry. This difference can be attributed to the genetic variations that influence height, such as the number of gene copies associated with tall stature.
Moreover, the relationship between ancestry and height can be complex, as genetic factors interact with environmental influences, such as nutrition and healthcare, to shape an individual’s growth and development. As a result, the average height of a U.S. male with a specific ethnic background may vary depending on their access to resources and overall living conditions.
Exploring the relationship between genetics, ethnicity, and height can provide valuable insights into the health and well-being of different population groups in the U.S. By understanding these connections, healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers can develop targeted strategies to address health disparities, promote optimal growth and development, and ultimately, contribute to a healthier and more equitable society.
The Role of Nutrition and Health: How They Contribute to Male Height in the U.S.
Proper nutrition and overall health significantly impact the average height of a U.S. male. During growth and development, a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals, supports optimal growth and development. Moreover, maintaining a healthy lifestyle throughout adulthood can help preserve height and overall well-being.
Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, dairy products, legumes, and nuts, provide the necessary building blocks for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. Vitamins and minerals, including calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus, contribute to bone health and density, further supporting optimal height development.
In addition to nutrition, overall health and well-being play a crucial role in determining the average height of a U.S. male. Factors such as physical activity, sleep quality, stress management, and access to healthcare all influence growth and development. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and effective stress management strategies can promote optimal growth, while chronic stress, sleep deprivation, and sedentary lifestyles may hinder height development and overall well-being.
Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight is essential for optimal height development, as obesity can negatively impact growth and development during childhood and adolescence. Excess body weight can place additional stress on the skeletal system, potentially leading to complications such as bone deformities and reduced growth rates. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can maintain a healthy weight, support optimal growth, and contribute to overall well-being.
How to Measure Height: Best Practices and Common Misconceptions
Accurately measuring height is essential for tracking growth, monitoring health, and understanding the average height of a U.S. male. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure height correctly, addressing common misconceptions and ensuring the reliability of height measurements:
Stand against a flat, vertical surface: Choose a wall or a door frame that is smooth and plumb. This will ensure that the measuring surface is perpendicular to the ground, providing an accurate height measurement.
Remove shoes and headwear: Measure height without shoes or any headwear, such as hats or caps, to ensure the most accurate measurement possible.
Keep feet together and flat on the ground: Position the feet together, with heels touching the wall, and ensure that both feet are flat on the ground. This will help maintain a natural posture and prevent any distortions in the height measurement.
Keep arms at the sides: Let the arms hang naturally at the sides, with palms facing the thighs. This will help maintain a relaxed and upright posture.
Align the head, shoulders, and hips: Make sure the head, shoulders, and hips are touching the wall. Use a level or a spirit level to ensure that the head is in a neutral position, with the chin parallel to the floor.
Mark the height: Use a pencil or a piece of removable tape to mark the height at the top of the head. Record the measurement in inches or centimeters.
Regularly repeat the process: Periodically remeasure height to track growth and development, ensuring that the same method is used each time for consistency.
It is important to note that professional medical assessments, such as those conducted by healthcare providers, may offer a more accurate and standardized method for measuring height. These assessments can help identify any potential health concerns related to growth and development.
The Importance of Healthy Living: Maintaining Optimal Height and Well-being
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for optimizing height and overall well-being in males. By adopting healthy habits, individuals can support continued height development and maintenance throughout their lives. Here are some tips on proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management to promote optimal growth and well-being:
Proper Nutrition
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for growth and development. Consuming adequate amounts of protein, vitamins, and minerals can support optimal height development and overall health. Focus on incorporating the following foods into your diet:
- Lean proteins: poultry, fish, lean beef, eggs, tofu, and legumes
- Dairy products: milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Fruits and vegetables: aim for a variety of colors to ensure a broad range of vitamins and minerals
- Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and pasta
- Healthy fats: avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil
Exercise
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, promoting bone health, and supporting overall growth and development. Engage in a combination of weight-bearing and resistance exercises, such as:
- Running, walking, or jogging
- Jumping rope or jumping jacks
- Climbing stairs or using a stair-climbing machine
- Weightlifting or resistance band training
- Yoga or Pilates for flexibility and core strength
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact growth and development, as well as overall health and well-being. Implement stress management strategies, such as:
- Meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Yoga or tai chi
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep
- Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation
By prioritizing proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management, individuals can maintain optimal height and overall well-being, contributing to a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Global Comparisons: How the Average Height of a U.S. Male Compares to Other Countries
Understanding how the average height of a U.S. male compares to that of other countries can provide valuable insights into the factors influencing height development and overall well-being. Here, we highlight some notable differences and similarities, considering the potential cultural, environmental, and genetic influences that contribute to these variations:
Europe
In general, many European countries have taller average male heights compared to the U.S. For instance, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Denmark all boast average male heights above 5 feet 10 inches (178 cm). This can be attributed to a combination of factors, including genetics, nutrition, and healthcare standards.
Asia
In contrast, several Asian countries have lower average male heights than the U.S. For example, the average male height in China, Japan, and South Korea is below 5 feet 8 inches (173 cm). This discrepancy may be due to genetic factors, as well as differences in nutrition, healthcare, and socioeconomic conditions.
South America
Countries in South America exhibit a wide range of average male heights. Argentina and Uruguay have average male heights similar to or slightly higher than that of the U.S., while other countries, such as Peru and Bolivia, have lower average heights. These variations may be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic factors.
Australia and New Zealand
Males in Australia and New Zealand tend to have similar or slightly taller average heights compared to the U.S. This can be linked to genetic, nutritional, and healthcare factors, as well as overall living standards in these countries.
In conclusion, the average height of a U.S. male can vary significantly when compared to other countries. By examining these differences and similarities, researchers, policymakers, and healthcare providers can gain a better understanding of the factors influencing height development and overall well-being, ultimately working towards promoting optimal growth and health for all populations.