Understanding the Importance of Hydration in Endurance Sports
Proper hydration is a critical factor in endurance sports, playing a significant role in optimizing performance, maintaining health, and ensuring safety. Dehydration, a state of excessive fluid loss, can negatively impact various physiological functions, leading to decreased exercise capacity, impaired cognitive function, and increased risk of heat-related illnesses. This comprehensive guide delves into the science of hydration in endurance sports, providing valuable insights and practical tips for athletes to enhance their hydration strategies.

The Science Behind Hydration: How the Body Regulates Fluid Balance
The human body is a complex system that maintains fluid balance through intricate physiological mechanisms. The kidneys, hormones, and the cardiovascular system play crucial roles in regulating fluid balance, ensuring proper hydration levels for optimal physiological functioning. In endurance sports, understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing effective hydration strategies.
The Role of the Kidneys
The kidneys are primarily responsible for filtering waste products and maintaining the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. They can adjust the amount of urine produced based on the body’s hydration status. In a well-hydrated state, the kidneys produce larger volumes of dilute urine, while in a dehydrated state, they produce smaller volumes of concentrated urine to conserve water.
The Impact of Hormones
Various hormones, such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone, help regulate fluid balance. ADH, produced by the pituitary gland, promotes water reabsorption in the kidneys, reducing urine production and conserving water. Aldosterone, produced by the adrenal glands, increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, which in turn promotes water retention. During exercise, the body releases these hormones to help maintain fluid balance, but dehydration can disrupt this delicate hormonal balance.
The Cardiovascular System’s Response
The cardiovascular system plays a vital role in regulating fluid balance by adjusting blood volume and blood pressure. During exercise, the body increases cardiac output and blood flow to the skin to dissipate heat and maintain core temperature. Dehydration can impair this process, as reduced blood volume leads to decreased stroke volume and cardiac output, ultimately compromising thermoregulation and exercise performance.
Dehydration’s Effects on Fluid Balance Mechanisms
Dehydration can negatively impact the body’s fluid balance mechanisms, impairing the kidneys’ ability to regulate electrolyte and water levels. This can lead to decreased urine production, increased urine concentration, and electrolyte imbalances. Additionally, dehydration can disrupt hormonal regulation, leading to reduced ADH and aldosterone secretion, further exacerbating fluid balance issues. These consequences can have severe implications for endurance athletes, as impaired fluid balance mechanisms can compromise exercise performance, health, and safety.

How to Stay Hydrated During Endurance Sports: Practical Tips and Strategies
Proper hydration is crucial for optimal performance, health, and safety in endurance sports. Developing effective hydration strategies is essential for athletes participating in activities such as marathons, triathlons, and cycling events. By following practical tips and strategies, endurance athletes can maintain fluid balance and optimize their performance.
Drink Regularly
Endurance athletes should aim to drink regularly throughout their exercise sessions. Consuming fluids at regular intervals can help maintain hydration levels and prevent excessive fluid loss. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends consuming 16-20 ounces of water or sports drinks 4 hours before exercise and 8-12 ounces every 10-15 minutes during exercise.
Monitor Urine Color
Monitoring urine color can provide valuable insights into hydration status. A well-hydrated athlete’s urine should be light yellow or clear. Darker urine colors, such as amber or honey, may indicate dehydration. However, it is essential to note that certain supplements and medications can affect urine color, so athletes should consider these factors when assessing their hydration status.
Adjust Hydration Plans Based on Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can significantly impact fluid loss during exercise. In hot and humid environments, athletes may experience increased sweating, leading to more significant fluid and electrolyte losses. In these conditions, athletes should consider consuming sports drinks with electrolytes to help maintain fluid balance. Additionally, athletes should adjust their hydration plans based on the duration and intensity of their exercise sessions.
Pre-Exercise Hydration
Proper pre-exercise hydration is essential for optimal performance. Athletes should aim to consume 16-20 ounces of water or sports drinks 4 hours before exercise and 8-12 ounces 2 hours before exercise. This strategy allows the body sufficient time to process fluids and eliminate excess through urine.
During-Exercise Hydration
During-exercise hydration is critical for maintaining fluid balance and preventing dehydration. Athletes should aim to consume 8-12 ounces of water or sports drinks every 10-15 minutes during exercise. Sports drinks with electrolytes and carbohydrates can help replenish energy stores and maintain fluid balance.
Post-Exercise Rehydration
Post-exercise rehydration is essential for recovery and optimal performance in subsequent exercise sessions. Athletes should aim to consume 20-24 ounces of water or sports drinks for every pound of body weight lost during exercise. This strategy can help replace fluids and electrolytes lost through sweating and promote optimal recovery.
In conclusion, proper hydration is crucial for optimal performance, health, and safety in endurance sports. By following practical tips and strategies, such as drinking regularly, monitoring urine color, and adjusting hydration plans based on weather conditions, endurance athletes can maintain fluid balance and optimize their performance. Pre-exercise, during-exercise, and post-exercise hydration strategies are essential components of effective hydration plans for endurance athletes.
The Role of Sports Drinks and Hydration Aids in Endurance Sports
The science of hydration in endurance sports involves understanding the benefits and limitations of sports drinks and hydration aids. These products can help endurance athletes maintain fluid balance and replenish energy stores, but overconsumption can also pose risks. Therefore, it is essential to develop individualized hydration plans based on each athlete’s unique needs.
Sports Drinks
Sports drinks are beverages designed to help athletes maintain fluid balance and replenish energy stores during exercise. They typically contain carbohydrates, electrolytes, and water. The carbohydrates in sports drinks provide energy to working muscles, while the electrolytes help maintain fluid balance by regulating the body’s water content. Sodium, in particular, is an essential electrolyte that helps the body retain water and prevent hyponatremia, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by low blood sodium levels.
However, it is essential to note that not all sports drinks are created equal. Some products may contain high levels of sugar, artificial flavors, and colors, which can lead to gastrointestinal distress and other adverse effects. Therefore, athletes should choose sports drinks carefully and look for products with a balanced carbohydrate-to-electrolyte ratio, low sugar content, and minimal additives.
Hydration Aids
Hydration aids, such as electrolyte tablets, gels, and bars, can also help endurance athletes maintain fluid balance and replenish energy stores. Electrolyte tablets, for example, can be added to water to provide a quick and convenient source of sodium and other essential electrolytes. Gels and bars, on the other hand, can provide a concentrated source of carbohydrates and electrolytes that can be consumed during exercise.
However, it is essential to note that hydration aids should be used judiciously and in conjunction with a well-designed hydration plan. Overconsumption of these products can lead to excessive fluid intake, which can dilute the body’s sodium levels and lead to hyponatremia. Therefore, athletes should follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and adjust their hydration plans based on their unique needs and the duration and intensity of their exercise sessions.
Individualized Hydration Plans
The science of hydration in endurance sports involves developing individualized hydration plans based on each athlete’s unique needs. Factors such as body weight, sweat rate, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions can all impact hydration needs. Therefore, athletes should regularly monitor their hydration status and adjust their hydration plans accordingly.
In some cases, athletes may benefit from using hydration aids or sports drinks to help maintain fluid balance and replenish energy stores. However, it is essential to note that these products should be used judiciously and in conjunction with a well-designed hydration plan. By developing individualized hydration plans based on their unique needs, endurance athletes can optimize their hydration strategies and improve their performance, health, and safety.
In conclusion, the science of hydration in endurance sports involves understanding the benefits and limitations of sports drinks and hydration aids. These products can help endurance athletes maintain fluid balance and replenish energy stores, but overconsumption can also pose risks. Therefore, it is essential to develop individualized hydration plans based on each athlete’s unique needs. By following practical tips and strategies, endurance athletes can optimize their hydration strategies and improve their performance, health, and safety.
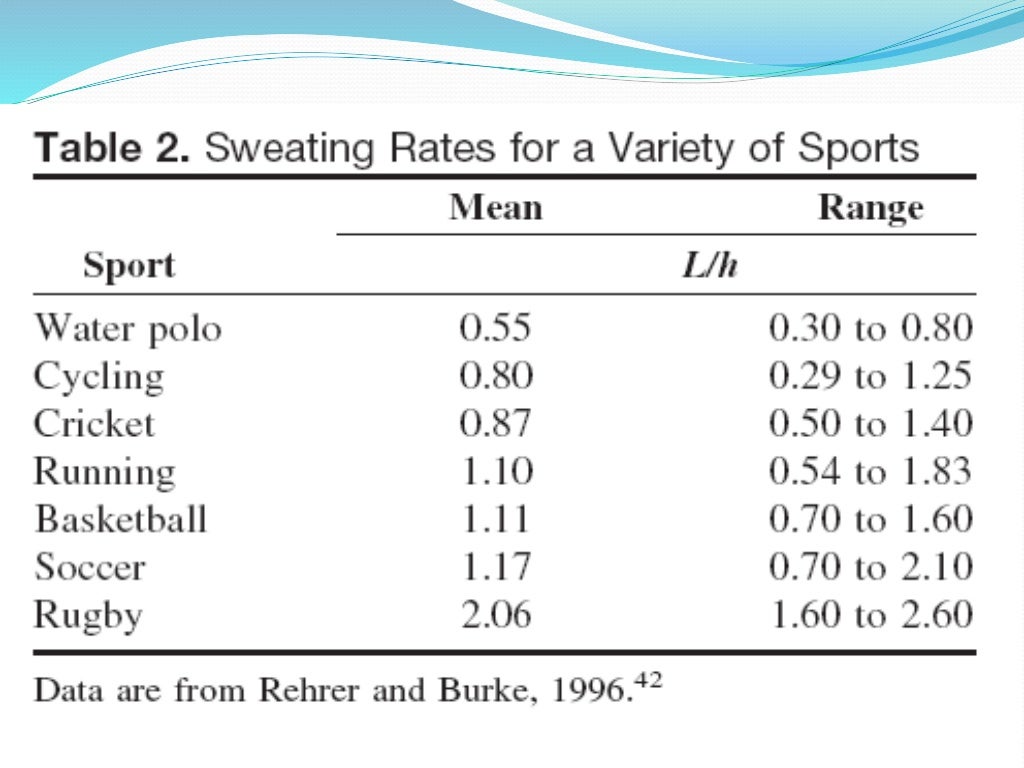
Hydration and Performance: The Latest Research and Findings
The science of hydration in endurance sports is an ever-evolving field, with new research and findings emerging regularly. Recent studies have shed light on the critical role of hydration in preventing fatigue, improving cognitive function, and enhancing exercise capacity.
Preventing Fatigue
Dehydration can lead to fatigue, which can negatively impact endurance performance. A study published in the Journal of Athletic Training found that even mild dehydration (1-2% loss of body weight) can impair exercise performance and increase perceived exertion. Therefore, maintaining proper hydration during endurance sports is essential to prevent fatigue and improve performance.
Improving Cognitive Function
Hydration is also crucial for cognitive function during endurance sports. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that dehydration can impair cognitive function, including attention, working memory, and long-term memory. Therefore, maintaining proper hydration during endurance sports can help athletes stay focused and perform at their best.
Enhancing Exercise Capacity
Proper hydration can also enhance exercise capacity during endurance sports. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that athletes who drank enough fluid to maintain their body weight during exercise had a higher exercise capacity than those who became dehydrated. Therefore, staying hydrated during endurance sports can help athletes push themselves harder and longer.
Practical Recommendations
Based on the latest scientific evidence, endurance athletes should aim to maintain proper hydration before, during, and after exercise. Pre-exercise hydration involves drinking enough fluid to ensure that the urine is light yellow or clear. During-exercise hydration involves drinking regularly, ideally every 15-20 minutes, to replace fluids lost through sweat. Post-exercise rehydration involves drinking enough fluid to replace 125-150% of the fluid lost during exercise, as well as consuming electrolytes and carbohydrates to replenish energy stores.
It is essential to note that individual hydration needs may vary based on factors such as body weight, sweat rate, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions. Therefore, endurance athletes should regularly monitor their hydration status and adjust their hydration plans accordingly. By following practical tips and strategies based on the latest scientific evidence, endurance athletes can optimize their hydration strategies and improve their performance, health, and safety.

Common Hydration-Related Issues in Endurance Sports: Prevention and Treatment
Endurance athletes face a range of hydration-related issues that can impact their performance, health, and safety. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these issues, athletes can take steps to prevent and manage them effectively.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than it takes in, leading to a decrease in total body water content. In endurance sports, dehydration can result from sweating, breathing, and urine production. Symptoms of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, and dizziness. Severe dehydration can lead to heat injury, hypovolemic shock, and even death.
To prevent dehydration, endurance athletes should drink regularly, ideally every 15-20 minutes, during exercise. They should also monitor their urine color, aiming for a pale yellow or clear color. Pre-exercise hydration involves drinking enough fluid to ensure that the urine is light yellow or clear. Post-exercise rehydration involves drinking enough fluid to replace 125-150% of the fluid lost during exercise, as well as consuming electrolytes and carbohydrates to replenish energy stores.
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia occurs when the body has too much water and not enough sodium, leading to a decrease in sodium concentration in the blood. In endurance sports, hyponatremia can result from overhydration, or drinking too much water without replacing sodium losses. Symptoms of hyponatremia include nausea, vomiting, headache, and seizures.
To prevent hyponatremia, endurance athletes should consume sports drinks or electrolyte tablets that contain sodium and other electrolytes. They should also avoid drinking too much water without replacing sodium losses. Treatment for hyponatremia involves restoring sodium levels through intravenous fluids or oral supplements.
Exercise-Associated Muscle Cramps
Exercise-associated muscle cramps (EAMC) occur when muscles involuntarily contract and cannot relax, leading to pain and discomfort. In endurance sports, EAMC can result from fatigue, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances. Symptoms of EAMC include muscle pain, stiffness, and spasms.
To prevent EAMC, endurance athletes should maintain proper hydration and electrolyte balance. They should also perform regular stretching and strengthening exercises to improve muscle function and endurance. Treatment for EAMC involves stretching and massaging the affected muscles, as well as consuming fluids and electrolytes to replenish losses.
In conclusion, endurance athletes should be aware of common hydration-related issues, such as dehydration, hyponatremia, and EAMC. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these issues, athletes can take steps to prevent and manage them effectively. Practical recommendations for prevention and treatment include maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance, consuming sports drinks or electrolyte tablets, and performing regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
Individualizing Hydration Plans: Factors to Consider and How to Adjust
The significance of proper hydration in endurance sports cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts performance, health, and safety. However, there is no one-size-fits-all hydration plan, as individual factors such as body weight, sweat rate, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions play a crucial role in determining an athlete’s hydration needs. Therefore, it is essential to individualize hydration plans to optimize performance, health, and safety.
Body weight is a critical factor in determining an athlete’s hydration needs. Athletes who weigh more generally require more fluids than those who weigh less. Sweat rate, which is the amount of sweat lost during exercise, is another essential factor to consider. Athletes with a high sweat rate need to consume more fluids than those with a low sweat rate to maintain fluid balance. Exercise intensity also affects hydration needs, as more intense exercise leads to increased sweating and fluid loss. Environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and altitude, can also impact hydration needs. For example, athletes exercising in hot and humid conditions or at high altitudes may require more fluids than those exercising in cooler and drier conditions.
To individualize hydration plans, athletes can follow these practical recommendations. First, athletes should determine their sweat rate by weighing themselves before and after exercise, taking into account any fluids consumed during exercise. This will help athletes determine how much fluid they need to consume during exercise to maintain fluid balance. Second, athletes should adjust their hydration plans based on environmental conditions. For example, athletes exercising in hot and humid conditions may need to consume more fluids than those exercising in cooler and drier conditions. Third, athletes should monitor their hydration status by checking their urine color. A light yellow color indicates proper hydration, while a dark yellow color indicates dehydration. Finally, athletes should regularly evaluate and adjust their hydration plans based on their individual needs and performance goals.
In conclusion, individualizing hydration plans is crucial for optimizing performance, health, and safety in endurance sports. Factors such as body weight, sweat rate, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions can impact an athlete’s hydration needs. By following practical recommendations, such as determining sweat rate, adjusting hydration plans based on environmental conditions, monitoring hydration status, and regularly evaluating and adjusting hydration plans, athletes can optimize their hydration strategies and improve their performance, health, and safety.

The Future of Hydration Research and Technology in Endurance Sports
As the science of hydration in endurance sports continues to evolve, so too does the technology and research aimed at optimizing hydration strategies for athletes. By staying informed about the latest trends and innovations, endurance athletes can make more informed decisions about their hydration practices and improve their performance, health, and safety.
One area of particular interest is the development of wearable sensors that can monitor hydration levels in real-time. These sensors, which can be worn as wristbands, patches, or even embedded in clothing, use a variety of technologies to measure hydration status, including sweat analysis, skin temperature, and heart rate variability. By providing athletes with real-time feedback on their hydration levels, these sensors can help them adjust their hydration strategies on the fly and avoid the negative consequences of dehydration or overhydration.
Another area of focus is the development of personalized hydration algorithms that take into account an athlete’s individual characteristics, such as body weight, sweat rate, and exercise intensity. By analyzing data from wearable sensors, as well as other factors such as weather conditions and altitude, these algorithms can generate customized hydration plans that are tailored to an athlete’s unique needs. This approach not only helps athletes optimize their hydration strategies, but also reduces the risk of overhydration or underhydration, which can have serious health consequences.
In addition to these technologies, there are also a number of novel hydration products that are being developed to help endurance athletes stay hydrated and perform at their best. For example, some companies are exploring the use of hydrogen-infused water, which has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as the potential to improve exercise performance. Other products, such as freeze-dried fruit snacks and edible hydration films, offer convenient and portable sources of hydration that can be consumed on the go.
As the science of hydration in endurance sports continues to advance, it is clear that technology and innovation will play an increasingly important role in helping athletes optimize their hydration strategies and improve their performance. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and developments, endurance athletes can make more informed decisions about their hydration practices and achieve their goals with confidence.
The science of hydration in endurance sports is a critical factor in an athlete’s success, and staying informed about the latest research and technologies can help endurance athletes optimize their hydration strategies and perform at their best. From wearable sensors and personalized hydration algorithms to novel hydration products and innovative hydration practices, there are many exciting developments on the horizon that have the potential to transform the way athletes approach hydration and improve their performance, health, and safety.


