What Does It Mean When Your Knee Burns?
A burning sensation in the knee can be a cause for concern for many individuals. While it might be tempting to dismiss it as a minor issue, a burning knee can indicate an underlying condition that requires attention. The difference between a burning sensation and pain is that the former is often more of a persistent, dull discomfort, whereas pain can be sharp and acute. A burning knee might be a symptom of nerve damage, inflammation, or overuse injuries. These issues can lead to conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, chondromalacia patella, or osteoarthritis. Addressing the root cause of a burning knee is essential to prevent further damage and alleviate discomfort. By understanding the potential causes and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can maintain their knee health and overall mobility.
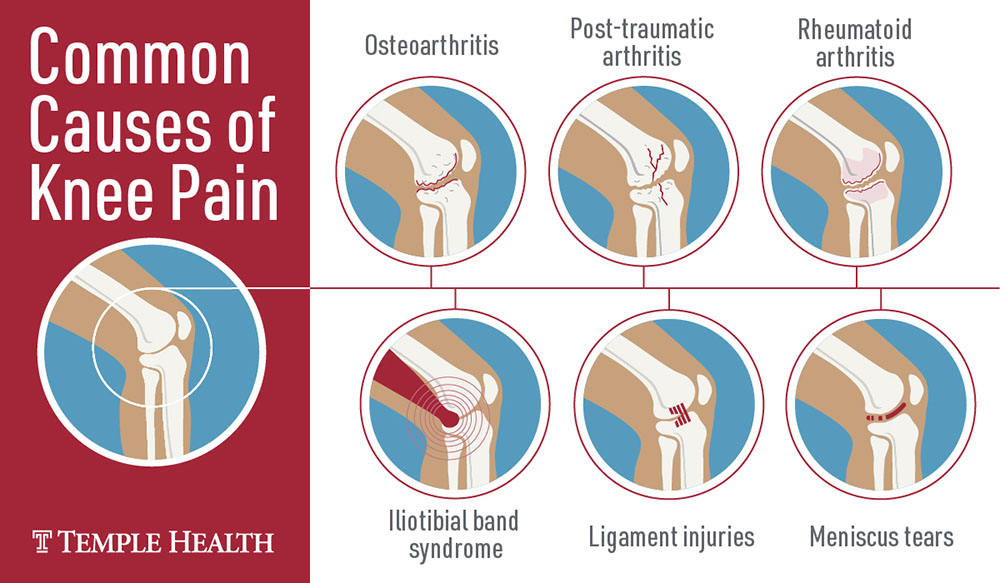
Common Causes of Burning Knee Sensations
A burning knee can be attributed to various factors, ranging from nerve damage to inflammation and overuse injuries. Nerve damage, such as that caused by diabetic neuropathy, can result in abnormal sensations, including burning. Inflammation, which can be triggered by conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or tendinitis, can also lead to a burning sensation in the knee. Overuse injuries, which occur due to repetitive stress on the knee joint, can cause irritation and inflammation, leading to a burning feeling. Several specific conditions are associated with a burning knee, including patellofemoral pain syndrome, chondromalacia patella, and osteoarthritis. Patellofemoral pain syndrome, also known as “runner’s knee,” is characterized by pain and inflammation in the front of the knee, often accompanied by a burning sensation. Chondromalacia patella, a condition that affects the cartilage under the kneecap, can cause a grating or burning sensation in the knee. Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is a degenerative joint disease that can cause knee pain, stiffness, and a burning sensation.
It is essential to address a burning knee, as it may indicate an underlying condition that requires treatment. By understanding the potential causes and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can take steps to alleviate their discomfort and maintain their knee health.
How to Assess Your Knee Health
Assessing your knee health is crucial for understanding the cause of a burning sensation and determining the best course of action. Self-assessment can help you monitor symptoms, track progress, and identify potential aggravating factors. Start by paying attention to the frequency, duration, and intensity of the burning sensation. Keep a journal to document your observations, which can help you identify patterns or triggers. While self-assessment is essential, it is equally important to consult a medical professional if you experience a burning knee. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, diagnose any underlying conditions, and recommend appropriate treatment options. During your appointment, be prepared to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any relevant family medical history. The doctor may perform a physical examination, order imaging tests, or recommend blood tests to help diagnose the issue.
In addition to medical assessments, consider tracking your progress with specific exercises or lifestyle changes. This can help you determine whether these interventions are effective in alleviating your symptoms. Remember that addressing a burning knee requires patience and persistence, as it may take time to identify the root cause and find an effective treatment.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies for Burning Knees
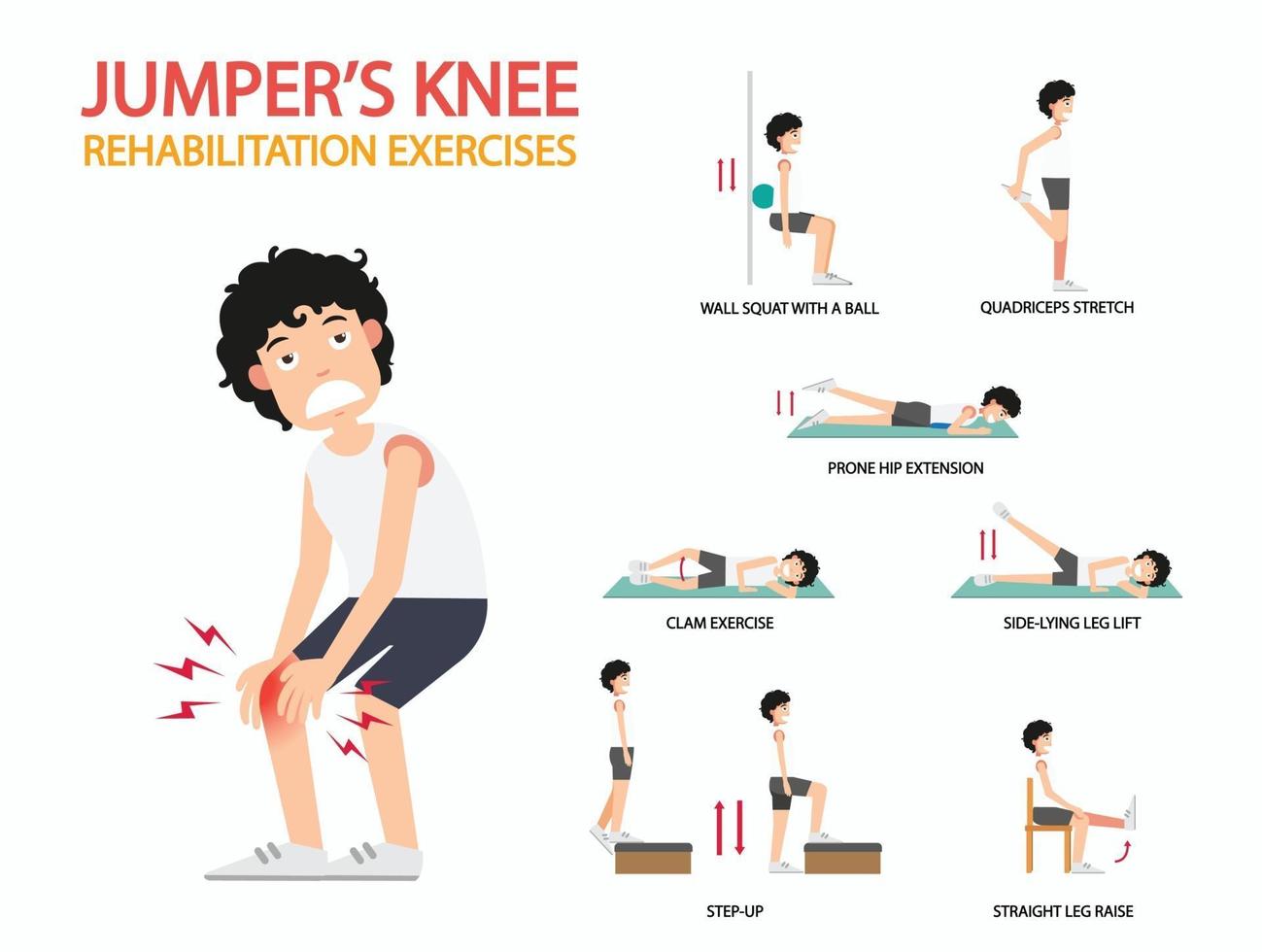
Preventing and treating a burning knee involves several practical strategies. The RICE method—rest, ice, compression, and elevation—can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Rest allows the knee to recover, while ice reduces inflammation and numbs the area. Compression with a knee brace or bandage can help minimize swelling, and elevation can further reduce inflammation and discomfort. Physical therapy and strengthening exercises can also play a crucial role in preventing and treating knee burning. A physical therapist can provide a customized exercise program to improve knee stability, flexibility, and strength. Building the muscles around the knee can help absorb shock and reduce stress on the joint, thereby alleviating burning sensations.
Proper footwear and orthotics can also contribute to knee health. Shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning can help distribute weight evenly across the foot, reducing pressure on the knee. Orthotics, such as shoe inserts or custom-made shoe supports, can further help align the foot and ankle, improving knee biomechanics and reducing the risk of injury.
In some cases, modifying activities or reducing exercise intensity may be necessary to allow the knee to heal. Gradually increasing activity levels as symptoms improve can help prevent re-injury and further damage. Consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist for guidance on appropriate activity modifications and return-to-activity plans.
Alternative Therapies and Modalities
In some cases, alternative therapies and modalities can provide additional relief for individuals experiencing a burning knee. These complementary approaches should be pursued under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, this process can help balance the body’s energy, or Qi, promoting healing and pain relief. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help alleviate knee pain and improve joint function, making it a potential option for managing knee burning.
Massage therapy can also offer benefits for individuals with knee burning. By manipulating soft tissues, massage can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain. A qualified massage therapist can provide targeted techniques to address knee issues, promoting relaxation and overall well-being.
Yoga, a mind-body practice that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, has been shown to improve joint health and reduce pain. Gentle yoga sequences can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, enhance flexibility, and promote relaxation. As with any exercise program, individuals with knee burning should consult a healthcare professional before starting a yoga practice to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Knee Health
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in knee health, and making adjustments can contribute to long-term well-being and reduced burning sensations. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess pounds put additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of injury and pain. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help manage weight and provide essential nutrients for joint health. Staying active is another essential component of knee health. Regular, low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and maintain a healthy weight. It is essential to avoid high-impact activities that may exacerbate knee burning, and to consult a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program.
Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation, can also benefit knee health. Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and inflammation, potentially leading to a burning sensation in the knee. By incorporating stress-reduction practices into their daily routine, individuals can help alleviate tension and promote overall well-being.
When to Consult a Medical Professional
In some cases, a burning knee may indicate a more serious underlying condition, necessitating professional medical attention. It is essential to be aware of warning signs and red flags that signal the need for an evaluation by a healthcare professional. If your knee burning is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, or redness, consult a medical professional immediately. These symptoms could indicate an infection, fracture, or other significant injury requiring prompt treatment. Additionally, if you experience a burning sensation combined with weakness, numbness, or tingling in the knee or leg, this may suggest nerve damage or a neurological issue, which requires further investigation.
Persistent or worsening symptoms, even without other red flags, should also prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider. Early intervention can help prevent further damage and alleviate discomfort. A medical professional can perform a thorough evaluation, diagnose any underlying conditions, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Working with healthcare professionals, such as primary care physicians, orthopedic specialists, or physical therapists, can provide valuable insights and guidance for managing knee burning. These professionals can help create personalized treatment plans, monitor progress, and adjust interventions as needed to ensure the best possible outcomes for long-term knee health.
Living with a Burning Knee: Real-Life Experiences and Coping Strategies
Experiencing a burning knee can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. Sharing personal stories and testimonials can offer valuable insights, encouragement, and coping strategies for those dealing with knee burning. One individual shares their experience with knee burning caused by patellofemoral pain syndrome. They describe the sensation as a “persistent, deep ache accompanied by a burning feeling that would sometimes radiate down my shin.” Through physical therapy, strengthening exercises, and lifestyle adjustments, they were able to manage their symptoms and return to their favorite activities.
Another person recounts their struggle with knee burning due to osteoarthritis. They emphasize the importance of maintaining a positive attitude and seeking support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals. By adopting a balanced, active lifestyle, managing their weight, and utilizing assistive devices when needed, they have been able to minimize the impact of knee burning on their daily life.
Coping strategies for living with a burning knee may include:
Pacing yourself: Break tasks into smaller segments and take regular breaks to avoid overexertion.
Prioritizing self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as meditation, warm baths, or reading.
Seeking support: Connect with friends, family, or support groups to share experiences, advice, and encouragement.
Practicing patience: Understand that managing knee burning is a process that requires time, persistence, and self-compassion.
By learning from the experiences of others and implementing effective coping strategies, individuals with a burning knee can better navigate their daily lives and maintain a positive, resilient outlook.