Shortness of Breath: A Common Experience
The sensation of not being able to breathe deeply or fully is a common experience that can occur in a variety of situations. For example, some people might feel this way after engaging in strenuous exercise, such as running or lifting weights. Others might experience breathlessness during times of stress or anxiety, or when they are exposed to allergens or irritants that affect their respiratory system. Regardless of the cause, it is important to understand why this sensation occurs and what can be done to alleviate it.
Anxiety and Panic Attacks: A Possible Culprit
Anxiety and panic attacks are common causes of breathlessness. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, anxiety disorders affect approximately 18% of the adult population in the United States, and panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder, affects about 2.7% of the population. People with anxiety disorders often experience physical symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and breathlessness, that can be triggered by stress, fear, or other emotional states.
Breathlessness caused by anxiety or panic attacks is often described as a feeling of tightness or constriction in the chest, along with rapid, shallow breathing. This can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and a feeling of detachment from reality. These symptoms can be frightening, but they are not life-threatening and can be managed with appropriate treatment and self-care strategies.
If you are experiencing breathlessness due to anxiety or panic attacks, there are several things you can do to manage your symptoms. These might include:
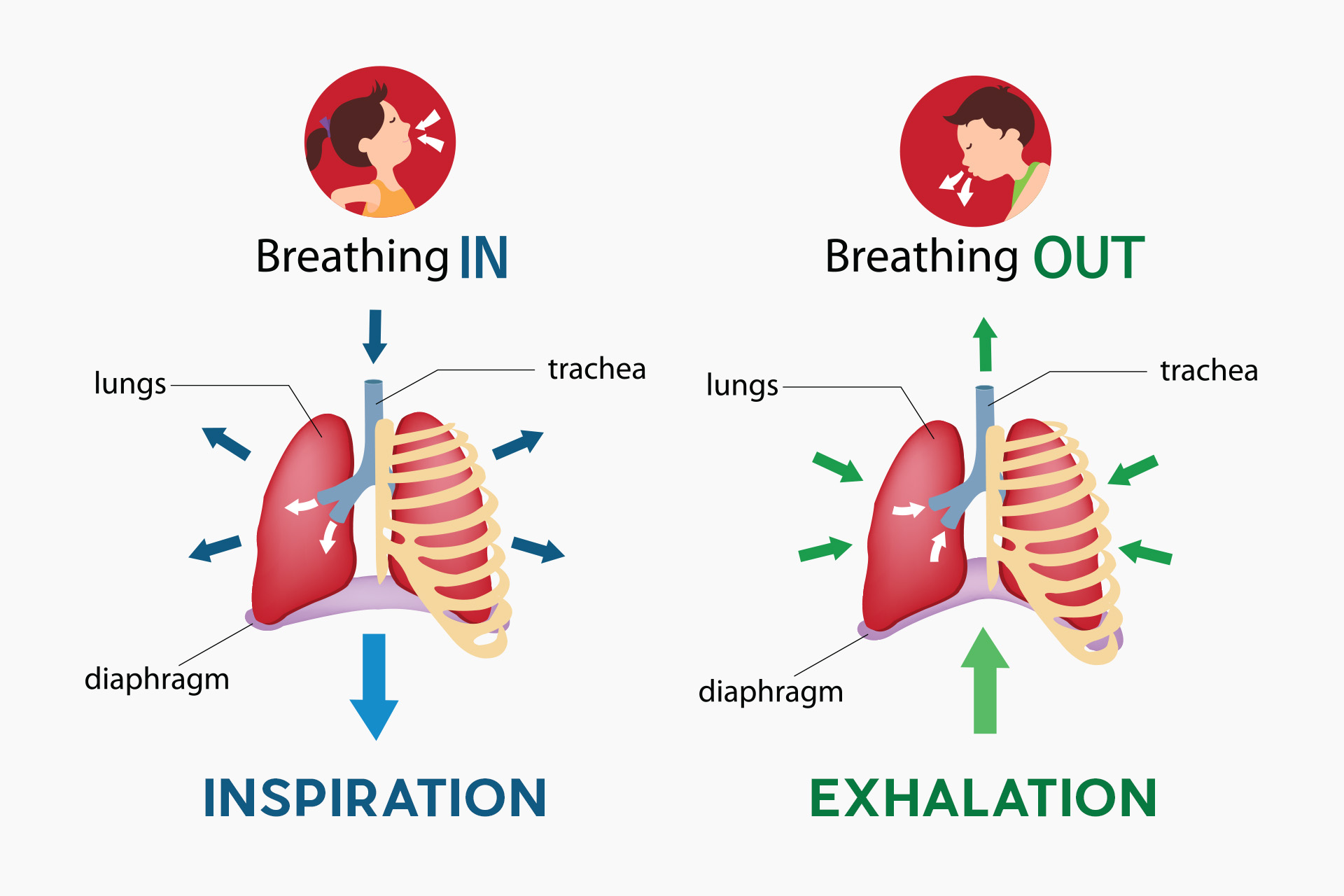
- Deep breathing exercises: Slow, deep breathing can help to calm the body and mind, and can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and panic. Try inhaling slowly through your nose, counting to four as you breathe in, and then exhaling slowly through your mouth, counting to four as you breathe out. Repeat this process several times until you feel your breathing become more relaxed and regular.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: This technique involves tensing and then releasing different muscle groups in the body, starting with the toes and working your way up to the head. This can help to release tension and promote relaxation, which can in turn help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and panic.
- Mindfulness techniques: Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment, without judgment or distraction. This can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and panic by bringing your attention away from worrying thoughts and back to the here and now. Try focusing on your breath, the sensations in your body, or the sounds around you, and allow any thoughts or distractions to pass by without engaging with them.
It is important to note that while these strategies can be helpful in managing symptoms of anxiety and panic, they are not a substitute for professional medical treatment. If you are experiencing breathlessness or other symptoms of anxiety or panic attacks, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Asthma and Allergies: Another Possible Cause
Asthma and allergies are common conditions that can cause breathlessness. According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, approximately 25 million people in the United States have asthma, and allergies are a common trigger for asthma symptoms. Allergies, which affect approximately 50 million people in the United States, can also cause breathlessness and other respiratory symptoms on their own.
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe. This can lead to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, as well as breathlessness. Allergies, on the other hand, occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to a substance that is normally harmless, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. This can cause symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose, as well as breathlessness and other respiratory symptoms.
If you have asthma or allergies, there are several things you can do to manage your symptoms and reduce your risk of breathlessness. These might include:
- Avoiding triggers: If you know what triggers your asthma or allergy symptoms, try to avoid these triggers as much as possible. This might involve staying indoors during peak pollen seasons, using air filters in your home, or avoiding certain foods or substances that you are allergic to.
- Using medication: There are several types of medication that can help to manage asthma and allergy symptoms, including quick-relief inhalers, long-acting inhalers, and oral medications. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for using these medications, and to report any side effects or changes in your symptoms.
- Practicing good self-care: Getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can all help to reduce your risk of asthma and allergy symptoms. It is also important to avoid smoking and to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, as this can worsen asthma and allergy symptoms.
If you are experiencing breathlessness due to asthma or allergies, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With appropriate management, it is possible to reduce your risk of breathlessness and improve your overall respiratory health.
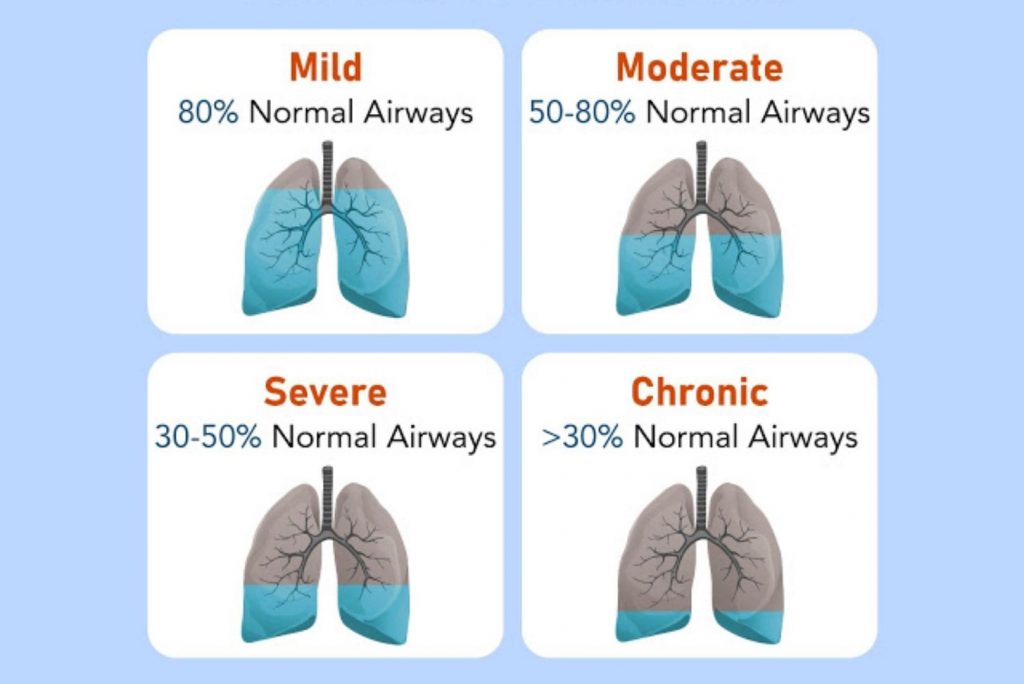
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A More Serious Concern
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease that can cause feelings of breathlessness and other respiratory symptoms. According to the American Lung Association, COPD affects approximately 16 million adults in the United States, and is the third leading cause of death in the country. COPD is a progressive disease, which means that it gets worse over time, and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
COPD is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can make it difficult to breathe. This can lead to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, as well as breathlessness. COPD is often caused by long-term exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or chemical fumes, and is most commonly diagnosed in people over the age of 40. There is no cure for COPD, but there are several treatments and strategies that can help to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
If you have COPD, there are several things you can do to manage your symptoms and improve your respiratory health. These might include:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, and quitting smoking is the most effective way to slow the progression of the disease. There are many resources available to help you quit smoking, including counseling, medication, and support groups.
- Using medication: There are several types of medication that can help to manage COPD symptoms, including bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, and combination inhalers. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for using these medications, and to report any side effects or changes in your symptoms.
- Practicing good self-care: Getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can all help to improve your respiratory health and reduce your risk of COPD symptoms. It is also important to avoid exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and chemical fumes, as these can worsen COPD symptoms.
If you are experiencing breathlessness due to COPD, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With appropriate management, it is possible to reduce your risk of breathlessness and improve your overall respiratory health.
Other Possible Causes of Breathlessness
There are several other possible causes of breathlessness, including heart disease, obesity, and lung infections. It is important to be aware of these potential causes and to consult a healthcare professional if you are concerned about your breathing.
Heart disease is a common cause of breathlessness, as it can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, and affects approximately 659,000 Americans each year. Symptoms of heart disease-related breathlessness might include chest pain, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Obesity is another possible cause of breathlessness, as it can put extra strain on the respiratory system. According to the CDC, approximately 42.4% of adults in the United States are obese, and this can increase the risk of several health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems. If you are concerned about your weight and its impact on your breathing, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional about strategies for managing your weight and improving your overall health.
Lung infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, can also cause breathlessness. These infections can cause inflammation and congestion in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Symptoms of lung infections might include cough, chest pain, and fever, as well as breathlessness. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention, as lung infections can be serious and require treatment.
In general, it is important to be aware of your breathing and to consult a healthcare professional if you are concerned about your breathing or experiencing any symptoms of respiratory problems. With appropriate diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to manage breathlessness and improve your overall respiratory health.
How to Manage Breathlessness: Tips and Strategies
Breathlessness can be a distressing and uncomfortable sensation, but there are several strategies that can help to manage this symptom, regardless of the underlying cause. Here are some tips and techniques that you might find helpful:
- Deep breathing exercises: Deep breathing can help to slow down your breathing and reduce feelings of breathlessness. To practice deep breathing, try inhaling slowly and deeply through your nose, counting to four as you breathe in. Then, exhale slowly through your mouth, counting to four as you breathe out. Repeat this process several times, focusing on the sensation of your breath moving in and out of your body.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and then releasing different muscle groups in your body. This can help to reduce tension and anxiety, and can also help to slow down your breathing. To practice progressive muscle relaxation, start by tensing the muscles in your toes and feet, holding the tension for a few seconds, and then releasing it. Then, move on to the muscles in your legs, hips, stomach, chest, back, shoulders, neck, and face, repeating the process of tensing and releasing.
- Mindfulness techniques: Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment, without judgment or distraction. This can help to reduce anxiety and stress, and can also help to slow down your breathing. To practice mindfulness, try focusing on your breath, the sensations in your body, or the sounds around you. If your mind starts to wander, gently bring your attention back to the present moment.
- Physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity can help to improve your respiratory health and reduce your risk of breathlessness. If you are experiencing breathlessness, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. It is also important to listen to your body and to stop and rest if you start to feel breathless or dizzy.
- Medication: There are several types of medication that can help to manage breathlessness, including bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, and combination inhalers. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for using these medications, and to report any side effects or changes in your symptoms.
Different strategies work for different people, so it is important to experiment and find what works best for you. With practice and patience, it is possible to manage breathlessness and improve your overall respiratory health.
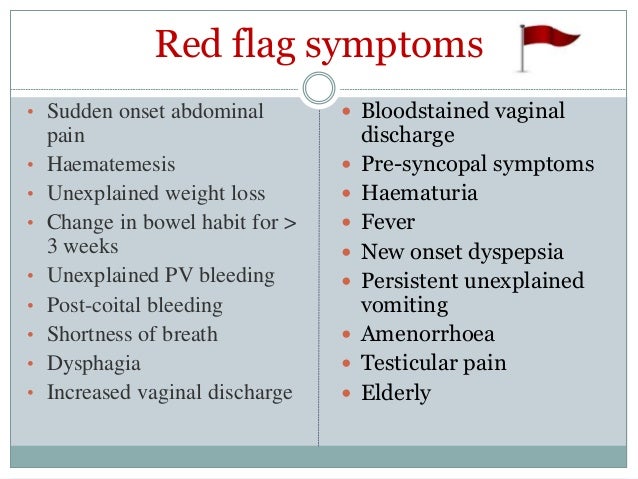
When to Seek Medical Attention: Red Flags and Warning Signs
Breathlessness can be a sign of a serious medical condition, and it is important to seek medical attention if you are concerned about your breathing. Here are some guidelines for when to seek medical attention:
- If you are experiencing chest pain: Chest pain can be a sign of a heart attack or other serious medical condition, and it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing chest pain or discomfort.
- If you are experiencing shortness of breath with other symptoms: Shortness of breath can be a symptom of several different medical conditions, and it is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing shortness of breath along with other symptoms, such as chest pain, cough, fever, or swelling in the legs and ankles.
- If you have a history of heart or lung disease: If you have a history of heart or lung disease, it is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing shortness of breath or other respiratory symptoms. These conditions can worsen over time, and it is important to manage them effectively to prevent serious complications.
- If you are concerned about your breathing: If you are concerned about your breathing or experiencing any symptoms of respiratory problems, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, and can help you to manage your breathing and improve your overall respiratory health.
It is always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to your health, so don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you are concerned about your breathing. There are many resources available for finding a qualified healthcare provider, including your primary care physician, local hospitals and clinics, and online directories.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Breathing
Breathlessness is a common experience, and it can be caused by a variety of factors, including anxiety, asthma, allergies, and chronic lung diseases like COPD. While breathlessness can be distressing and uncomfortable, there are many strategies that you can use to manage this symptom and improve your overall respiratory health. These might include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness techniques, as well as medication and other treatments prescribed by a healthcare professional.
It is important to remember that breathlessness is not something to be feared or ignored. By taking an active role in managing your breathing and your overall health, you can reduce your risk of breathlessness and improve your quality of life. If you are concerned about your breathing or experiencing any symptoms of respiratory problems, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, and can help you to manage your breathing and improve your respiratory health.
Don’t let breathlessness hold you back. With the right strategies and support, you can take control of your breathing and enjoy a happier, healthier life.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/anxiety-attack-5088600-Final-b3ff4ac50a6d4c13833a0097896c2d95.jpg)