Understanding the Meaning and Importance of “¿Qué hora es?”
The Spanish phrase “¿Qué hora es?” translates to “What time is it?” in English. This common expression is essential for daily activities and appointments, ensuring that you maintain a well-organized schedule. Knowing the current time is crucial for punctuality, whether you’re meeting a friend for “un café” or attending a business meeting. By mastering the art of telling time in Spanish, you’ll enhance your language skills and improve your overall experience in Spanish-speaking cultures.
How to Ask “What Time Is It?” in Spanish: A Comprehensive Guide
To ask “What time is it?” in Spanish, you can use the simple and direct phrase “¿Qué hora es?”. This formal inquiry is suitable for most situations, including speaking to strangers, professionals, or in formal settings. However, in informal conversations with friends or family, you can use the colloquial expression “¿Qué hora tienes?”.
To pronounce “¿Qué hora es?” correctly, break down the phrase into its individual components: “ké” (qué), “ór” (hora), and “es” (es). For “¿Qué hora tienes?”, the pronunciation is “ké” (qué), “ór” (hora), “tié” (tienes).
When addressing someone older or in a formal context, use “usted” instead of “tú”. For example, “¿A qué hora es la cita, señor?”.
In summary, to ask “What time is it?” in Spanish, use “¿Qué hora es?” for formal situations and “¿Qué hora tienes?” for informal conversations. Remember to consider the context and adjust your language accordingly.
Alternative Ways to Express “What Time Is It?” in Spanish
While “¿Qué hora es?” is the most common way to ask “What time is it?” in Spanish, there are alternative expressions that you can use in specific situations. These phrases showcase your language skills and add variety to your conversations.
One alternative is “¿Tienes hora?”. This question translates to “Do you have the time?”. It is more casual and can be used with friends or when addressing someone younger. However, be cautious when using this phrase with strangers, as it may come across as too informal.
Another option is “¿Qué tal las horas?”. This expression, which means “How are the hours?”, is a colloquial way to ask about the time. It is best used in informal settings or among friends, as it creates a friendly and conversational atmosphere.
Choose the appropriate phrase based on the context and the relationship you have with the person you are speaking to. By doing so, you will demonstrate your understanding of Spanish culture and language nuances.
Responding to “What Time Is It?” in Spanish: Essential Phrases
Once you’ve mastered asking “What time is it?” in Spanish, it’s crucial to learn how to respond appropriately. Here are some essential phrases and vocabulary to help you communicate the current time in both digital and analog clock formats.
Digital Clock Format
To express the time in a digital format, use the structure “son las” followed by the hour and minutes. For example:
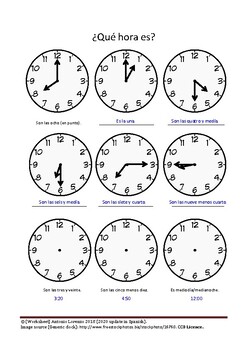
- “Son las tres y veinte” (It’s 3:20).
- “Son las once y cuarenta y cinco” (It’s 11:45).
Analog Clock Format
To describe the time using an analog clock, use the structure “son las” followed by the hour and the phrase “y” (and) before the minutes. For instance:
- “Son las dos y diez” (It’s 2:10).
- “Son las cinco y media” (It’s 5:30).
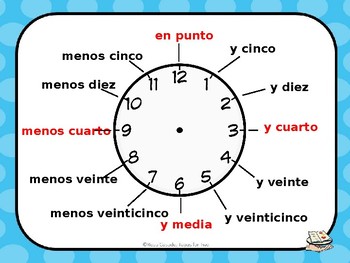
Note that “media” means “half” in Spanish, so “y media” is equivalent to “half past” in English. To express quarter past or quarter to, use “y cuarto” and “menos cuarto”, respectively. For example:
- “Son las siete y cuarto” (It’s 7:15).
- “Son las diez menos cuarto” (It’s 9:45).
By learning these essential phrases and vocabulary, you will be able to communicate the current time confidently in Spanish, whether you’re using digital or analog clock formats.
Digital vs. Analog Clocks: Recognizing Time Formats in Spanish
When learning how to tell time in Spanish, it’s essential to understand the differences between digital and analog clocks. Both formats are widely used, and recognizing each one will help you communicate more effectively.
Digital Clocks in Spanish
Digital clocks display the time using numbers, and Spanish speakers use the phrase “son las” followed by the hour and minutes. For example:
- “Son las dieciséis y treinta” (It’s 16:30).
- “Son las veintidós y cuarenta y cinco” (It’s 22:45).
Analog Clocks in Spanish
Analog clocks have hands that point to the hours and minutes. Spanish speakers use the same structure as with digital clocks, “son las” followed by the hour, and the word “y” (and) before the minutes. For instance:
- “Son las ocho y veinte” (It’s 8:20).
- “Son las once y media” (It’s 11:30).
In Spanish, “media” means “half”, so “y media” is equivalent to “half past” in English. To express quarter past or quarter to, use “y cuarto” and “menos cuarto”, respectively. For example:
- “Son las diez y cuarto” (It’s 10:15).
- “Son las dos menos cuarto” (It’s 1:45).
Understanding the differences between digital and analog clocks in Spanish will enable you to read time accurately and communicate more efficiently in Spanish-speaking environments.
Time Zones in Spain: Adapting to Local and Regional Time Differences
When dealing with time in Spanish-speaking countries, it’s essential to understand the time zones and how they might affect the current time. Spain, for example, observes Central European Time (CET, UTC +1) during standard time and Central European Summer Time (CEST, UTC +2) during daylight saving time.
Time Differences in Spain
Spain’s mainland and the Balearic Islands are in the CET time zone, while the Canary Islands are in the Western European Time (WET, UTC) zone, one hour behind the mainland. During daylight saving time, the difference remains the same, with the Canary Islands observing Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC +1).
Time Differences in Other Spanish-Speaking Countries
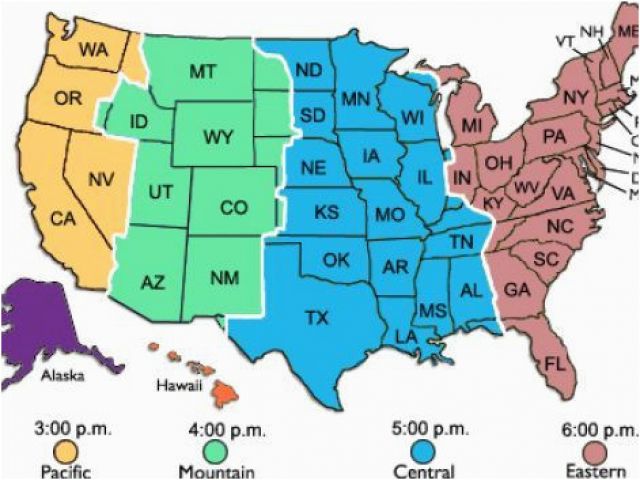
Spanish-speaking countries in the Americas, such as Mexico, Colombia, and Argentina, observe different time zones due to their geographical locations. For instance, Mexico has four time zones, ranging from the Pacific Time Zone (UTC -8) to the Eastern Standard Time Zone (UTC -5).
Being aware of these time differences will help you communicate more effectively and manage appointments or events in Spanish-speaking countries. Always double-check the time zone when scheduling calls or meetings to avoid confusion and ensure punctuality.
Using Technology to Check the Time in Spanish: Smartphones and Smartwatches
In today’s digital age, technology offers a convenient way to check the time in Spanish using smartphones and smartwatches. Here’s how to enable Spanish time display on these devices.
Smartphones
To set your smartphone to display time in Spanish, follow these steps:
- Access your phone’s settings menu.
- Find the “Language & Input” or “System Language” option.
- Choose “Spanish” as your preferred language.
- Your phone may restart to apply the changes.
Keep in mind that the exact steps may vary depending on your smartphone’s operating system and model.
Smartwatches
To set your smartwatch to display time in Spanish, follow these general steps:
- Connect your smartwatch to your smartphone.
- Access your smartwatch’s settings menu through your phone’s companion app.
- Find the “Language” or “Language & Input” option.
- Choose “Spanish” as your preferred language.
- Your smartwatch may require a restart to apply the changes.
Popular Spanish language apps, such as “Hola Spanish” or “Duolingo”, can also help you practice time-telling in Spanish. These apps offer interactive lessons and quizzes to improve your language skills.
By utilizing technology and Spanish language apps, you can easily practice telling time in Spanish and stay punctual for your daily activities and appointments.
Teaching Spanish Time: Tips and Resources for Language Learners
Mastering the art of telling time in Spanish can be a rewarding experience for language learners. Here are some tips and resources to help you improve your skills.
Tip 1: Learn Time-Telling Vocabulary
Familiarize yourself with time-telling vocabulary, such as “hora” (hour), “minuto” (minute), “y” (and), “media” (half), “cuarto” (quarter), and “menos” (less/minus). Practice using these words in sentences to reinforce your understanding.
Tip 2: Practice with Real-Life Scenarios
Incorporate time-telling practice into your daily routine. For example, ask for the time when ordering food or shopping, and respond using both digital and analog clock formats. This hands-on experience will help you become more comfortable with the language.
Tip 3: Utilize Language Learning Apps
Download language learning apps, such as “Duolingo”, “Babbel”, or “Rosetta Stone”, which offer lessons on time-telling in Spanish. These apps provide interactive activities and quizzes to help you learn and retain information.
Tip 4: Watch Spanish-Language Media
Expose yourself to Spanish-language media, such as TV shows, movies, or podcasts. Pay attention to how time is discussed and practice repeating the phrases to improve your pronunciation and comprehension.
Recommended Resources
- Online Courses: Telling Time in Spanish on Udemy
- Apps: Duolingo, Babbel, Rosetta Stone
- Books: “Easy Spanish Step-by-Step” by Barbara Bregstein
By following these tips and utilizing the recommended resources, you’ll be well on your way to mastering time-telling in Spanish and confidently answering “¿Qué hora es?” in various contexts.