The Significance of Measuring Your Walking Speed
Understanding your 1 mile walking time can be a valuable metric for tracking your fitness progress and setting realistic goals for your walking routine. By measuring your walking speed, you gain insights into your overall health and physical condition, allowing you to tailor your exercise regimen to your unique needs and abilities.
One of the primary benefits of monitoring your 1 mile walking time is the ability to track improvements over time. As you consistently engage in walking exercises and incorporate healthy habits into your lifestyle, you will likely notice a gradual decrease in the time it takes to walk a mile. This progress serves as a powerful motivator, encouraging you to maintain your exercise routine and continue striving for improvement.
Additionally, measuring your 1 mile walking time can help you set achievable goals based on your current fitness level. For instance, if you can walk a mile in 20 minutes, you might aim to reduce that time to 18 minutes, then 15 minutes, and so on. These incremental goals provide a clear path for improvement, making it easier to stay focused and committed to your walking routine.
Furthermore, understanding your 1 mile walking time can contribute to improved overall health. Regular walking has been shown to offer numerous benefits, such as enhanced cardiovascular health, weight management, and stress reduction. By measuring your walking speed, you can ensure that you are maintaining a brisk pace, which is essential for reaping these health advantages.
In conclusion, measuring your 1 mile walking time is a simple yet powerful tool for tracking fitness progress, setting realistic goals, and improving overall health. By incorporating this metric into your walking routine, you can better understand your physical abilities and make informed decisions about your exercise regimen, ultimately leading to a healthier, happier lifestyle.
How to Calculate Your Current Walking Speed
To determine your 1 mile walking time, you can follow a simple process that involves measuring the distance and time it takes to walk a mile. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you calculate your current walking speed:
Choose a Measurement Method: Decide whether you will use a pedometer, smartphone app, or a marked walking route to measure your distance. Pedometers and apps can provide accurate estimates, while marked routes allow for precise measurements.
Measure Your Distance: If using a pedometer or app, ensure that the device or application is set up correctly and calibrated to your stride length. For a marked route, find a safe, flat, and accurately measured path, such as a running track or a clearly marked trail.
Time Your Walk: Using a stopwatch or the timer function on your smartphone, record the time it takes to walk the mile-long route or the equivalent distance using a pedometer or app.
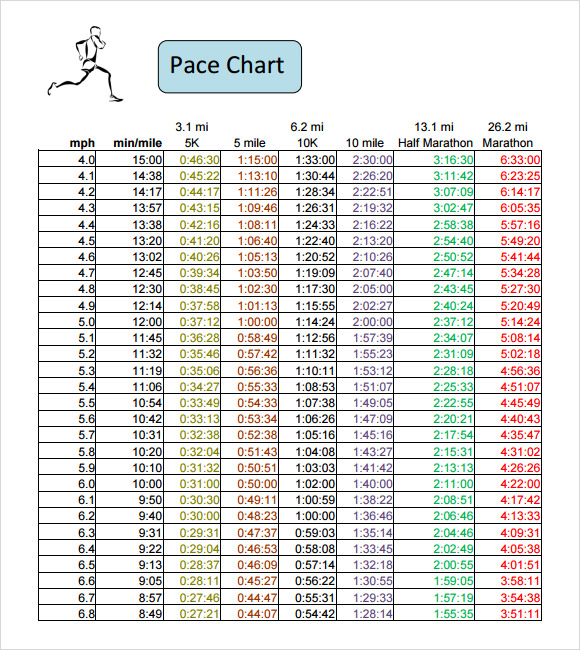
Calculate Your Speed: Divide the total distance (1 mile) by the time it took to walk that distance. The result will be your current walking speed in miles per hour (mph). For example, if it takes you 20 minutes to walk a mile, your walking speed would be 3 mph (60 minutes divided by 20 minutes equals 3 mph).
Factor in Rest Breaks: If you require rest breaks during your walk, include the time spent resting when calculating your 1 mile walking time. This will provide a more accurate representation of your actual walking speed.
By following these steps, you can easily calculate your current walking speed and establish a baseline for tracking your progress. Regularly measuring your 1 mile walking time can help you monitor improvements, set realistic goals, and optimize your walking routine for maximum health benefits.
Typical Walking Speeds for Different Age Groups and Fitness Levels
Understanding the average walking speed for various age groups and fitness levels can help you set personalized goals for improving your 1 mile walking time. Here is a general overview of typical walking speeds:
Average Adult Walking Speed: For most healthy adults, the average walking speed is approximately 3 to 4 miles per hour (mph). This range can vary depending on factors such as fitness level, age, and terrain.
Age-Related Considerations: As individuals age, their walking speed may naturally decrease due to factors such as muscle loss, decreased flexibility, and changes in balance. However, regular exercise and strength training can help maintain or even improve walking speed in older adults.
Fitness Level: Individuals with higher fitness levels typically have faster walking speeds than those with lower fitness levels. Regular exercise, such as walking, running, or cycling, can help improve overall fitness and increase walking speed.
Setting Personalized Goals: Based on your current age, fitness level, and walking speed, you can set realistic and achievable goals for improving your 1 mile walking time. For example, if your current walking speed is 4 mph, you might aim to increase it to 4.5 mph over several months through consistent exercise and training.
By understanding the typical walking speeds for different age groups and fitness levels, you can better assess your own walking pace and establish personalized goals for improvement. Remember that progress takes time, so be patient and consistent in your efforts to increase your walking speed.
Factors That Affect Walking Speed
Various factors can influence your walking speed, including terrain, footwear, and physical condition. Optimizing these factors can help you achieve a faster pace and improve your 1 mile walking time. Here are some factors to consider:
Terrain: Walking on flat, even surfaces typically allows for a faster walking speed than navigating hills, uneven terrain, or obstacles. However, incorporating hill walking into your routine can help improve leg strength and overall walking speed.
Footwear: Wearing appropriate footwear can significantly impact your walking speed and comfort. Choose shoes that provide adequate support, cushioning, and traction. Avoid shoes with worn-out soles or poor arch support, as these can lead to discomfort and decreased walking speed.
Physical Condition: Factors such as muscle strength, flexibility, and balance can affect your walking speed. Regular exercise, including strength training and stretching, can help improve these aspects of physical fitness and enhance your walking pace.
Weather Conditions: Inclement weather, such as rain, snow, or extreme temperatures, can impact your walking speed. Dress appropriately for the weather and exercise caution when walking on slippery or wet surfaces.
Mental State: Your mental state can also influence your walking speed. Maintaining a positive attitude, setting realistic goals, and staying motivated can help you achieve a faster walking pace.
By understanding and optimizing these factors, you can improve your walking speed and achieve a faster 1 mile walking time. Remember that consistent exercise and training are essential for long-term progress.
How to Increase Your Walking Speed Over Time
Incorporating specific exercises, techniques, and strategies into your walking routine can help you increase your walking speed and improve your 1 mile walking time. Here are some practical tips and exercises to consider:
Interval Training: Incorporate short bursts of faster walking into your routine, alternating between high-intensity and low-intensity intervals. This approach can help improve cardiovascular fitness and increase walking speed.
Hill Walking: Incorporate hills into your walking route to challenge your leg muscles and improve overall strength. Walking uphill can help increase your walking speed, while walking downhill can improve your stride length and cadence.
Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises, such as squats, lunges, and calf raises, into your routine to build leg strength and improve walking speed.
Proper Posture: Maintain proper posture while walking, keeping your head up, shoulders back, and core engaged. This alignment can help improve your walking efficiency and increase your speed.
Cadence: Focus on increasing your cadence, or the number of steps you take per minute. A higher cadence can help improve your walking speed and reduce the risk of injury.
Stride Length: While increasing stride length can help improve walking speed, it is essential to maintain a natural stride length and avoid overstriding, which can lead to injury.
Incorporate Walking into Daily Routine: Incorporate walking into your daily routine by taking stairs instead of elevators, walking during lunch breaks, or choosing to walk instead of drive for short distances.
Consistency and Progression: Consistently engage in walking exercises and progressively increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of your workouts over time. This approach can help you achieve long-term improvements in your walking speed and 1 mile walking time.
The Benefits of Improving Your Walking Speed
Improving your walking speed can offer numerous benefits for your overall health, fitness, and daily life. Here are some advantages of focusing on reducing your 1 mile walking time:
Enhanced Cardiovascular Health: Walking at a faster pace can help improve cardiovascular fitness by increasing heart rate and promoting blood flow. This can lead to a healthier heart and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Weight Loss: Faster walking can help burn more calories, contributing to weight loss and management. Incorporating interval training, hill walking, and strength training into your routine can further enhance calorie burn and promote weight loss.
Stress Reduction: Walking is a proven stress-reduction activity, and walking at a faster pace can amplify these benefits. The increased physical exertion can help release endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, leading to reduced stress and improved mental well-being.
Improved Bone Health: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Faster walking can further enhance these benefits by increasing the intensity of the exercise.
Increased Endurance: Consistently working to improve your walking speed can help increase your overall endurance, allowing you to walk longer distances and participate in other physical activities for extended periods.
Boosted Confidence: Achieving a faster walking pace can provide a sense of accomplishment and boost self-confidence. This can translate to other areas of life, such as improved productivity and motivation in personal and professional settings.
Practical Applications: A faster walking pace can have practical applications in daily life, such as reducing commute time, completing errands more efficiently, and navigating busy streets or airports with ease.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Trying to Increase Your Walking Speed
When attempting to improve your 1 mile walking time, it is essential to avoid common pitfalls and misconceptions that can hinder progress. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
Overstriding: Overstriding occurs when you take excessively long steps, which can lead to inefficiency and increased risk of injury. Instead, focus on maintaining a natural stride length and increasing your cadence, or the number of steps you take per minute.
Poor Posture: Maintaining proper posture is crucial for efficient walking. Slouching or hunching over can restrict breathing and reduce power output, making it more challenging to walk faster. Ensure that you keep your head up, shoulders back, and core engaged while walking.
Inadequate Recovery Time: Increasing your walking speed places additional stress on your muscles and cardiovascular system. It is essential to allow for adequate recovery time between intense walking sessions to prevent injury and promote overall progress.
Neglecting Strength Training: Strength training exercises, such as squats, lunges, and calf raises, can help build the leg strength necessary for faster walking. Neglecting strength training may limit your ability to improve your walking speed.
Ignoring Terrain and Footwear: Walking on uneven terrain or wearing inappropriate footwear can negatively impact your walking speed and increase the risk of injury. Ensure that you wear supportive, comfortable shoes and choose walking routes with even surfaces when possible.
Focusing Solely on Speed: While improving your walking speed is a worthy goal, it is essential to consider other aspects of your fitness journey, such as overall health, endurance, and strength. Focusing solely on speed may lead to frustration or burnout, so be sure to maintain a balanced approach to your walking routine.
Real-World Applications of a Faster Walking Pace
A faster walking pace can have numerous practical applications in daily life, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and overall well-being. Here are some ways a reduced 1 mile walking time can positively impact your daily experiences:
Reduced Commute Time: If you walk to work, school, or run errands, a faster walking pace can help you save time and get to your destination more quickly. This can be particularly beneficial in congested urban areas where public transportation or driving may be time-consuming.
Improved Productivity: By reducing the time spent on daily tasks, you can free up valuable time for other activities, such as hobbies, socializing, or pursuing personal or professional goals. This increased productivity can lead to a more fulfilling and balanced lifestyle.
Boosted Confidence: Achieving a faster walking pace can provide a sense of accomplishment and boost self-confidence. This newfound confidence can translate to other areas of life, such as improved performance at work or in social situations.
Enhanced Exploration: When traveling or exploring new places, a faster walking pace can help you cover more ground and see more sights in a shorter amount of time. This can lead to a richer, more immersive travel experience.
Increased Fitness: A faster walking pace can contribute to overall fitness improvements, as it requires increased cardiovascular effort and muscle engagement. This can lead to enhanced endurance, strength, and overall health.
Time with Loved Ones: By reducing the time spent on daily tasks, you can create more opportunities to spend quality time with friends, family, or pets. This can lead to stronger relationships and a more connected, supportive social network.
Mental Clarity: Walking is a proven stress-reduction activity, and walking faster can amplify these benefits. The increased physical exertion can help release endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, leading to improved mental clarity and focus.
Financial Savings: By walking more often and at a faster pace, you may be able to save money on transportation costs, such as gas, public transportation fees, or parking. These savings can be invested in other areas of your life, such as personal development, travel, or leisure activities.