The Concept of ‘Bad’ Carbs: Separating Fact from Fiction
Carbohydrates, often abbreviated as ‘carbs,’ are one of the three primary macronutrients, alongside proteins and fats. They serve as the body’s primary energy source, but not all carbs are created equal. The term ‘bad’ carbs has become popular in the health and wellness sphere, but what does it truly mean? In this article, we will explore the concept of ‘bad’ carbs and clarify the difference between complex and simple carbohydrates. Understanding the impact of various carbs on health and weight management is crucial for those seeking to maintain a balanced diet and improve their overall well-being.
Simple Carbohydrates: A Closer Look at the ‘Bad’ Carbs
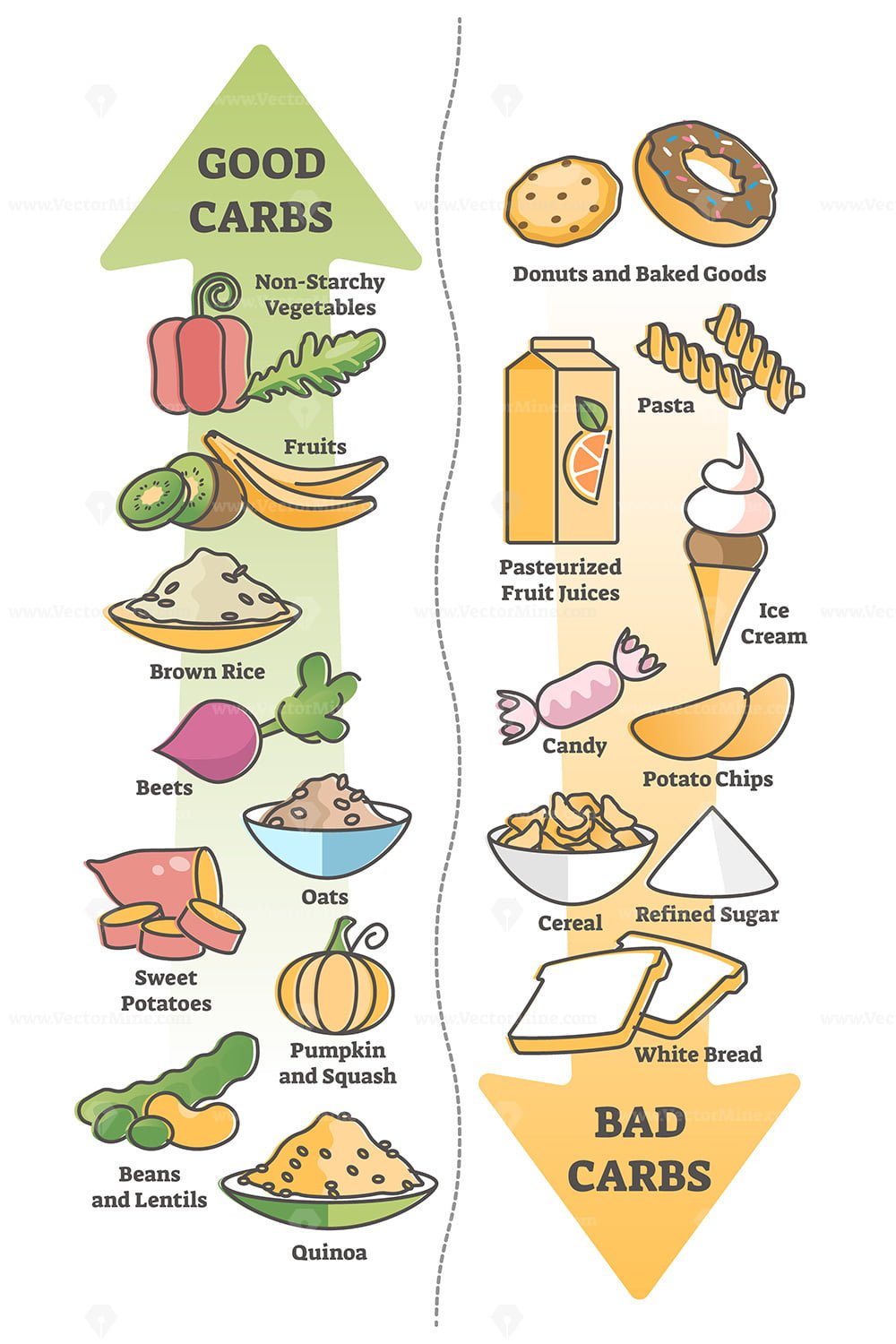
Simple carbohydrates, often referred to as ‘bad’ carbs, are a type of carbohydrate that is quickly absorbed by the body due to their simple chemical structure. These carbs can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to a surge in energy followed by a crash. Moreover, simple carbs often provide minimal nutritional value, making them an unideal choice for those seeking to maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
Common sources of simple carbohydrates include sweets, such as candies, cakes, and cookies, as well as sugary drinks like soda and fruit juice. White bread, rice, and pasta made from refined grains are also high in simple carbs. These foods, while often delicious, should be consumed in moderation, as they can contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and chronic diseases when consumed excessively.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MyfGFki5LxA
Complex Carbohydrates: Nutritious Alternatives to Simple Carbs
Complex carbohydrates, often considered ‘good’ carbs, are a type of carbohydrate that takes longer for the body to digest due to their more complex chemical structure. These carbs provide a steady supply of energy and are often packed with essential nutrients, making them a healthier choice compared to simple carbs.
Whole grains, such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and quinoa, are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates. Legumes, including beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are also high in complex carbs, as well as fiber and plant-based protein. Vegetables, particularly starchy ones like potatoes, sweet potatoes, and corn, are another important source of complex carbs. These foods contribute to a balanced and nutritious diet, promoting overall health and well-being.
How to Effectively Limit ‘Bad’ Carbs in Your Diet
Reducing the intake of simple carbohydrates can have numerous health benefits, from improved weight management to a lower risk of chronic diseases. To effectively limit ‘bad’ carbs in your diet, consider implementing the following practical tips:
-
Meal Planning: Plan your meals in advance to ensure you have a variety of nutritious options on hand. Incorporate complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats into your meals to create a balanced diet.
-
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes when consuming simple carbohydrates. Opt for smaller servings and balance them with other nutrient-dense foods.
-
Mindful Eating: Pay attention to the flavors, textures, and sensations of your food as you eat. This practice can help you better understand your body’s hunger and fullness cues, making it easier to limit simple carbs.
-
Choose Complex Carbs: Swap simple carbs for complex ones by incorporating whole grains, legumes, and vegetables into your meals. These foods provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
-
Limit Added Sugars: Reduce your consumption of added sugars by avoiding sugary drinks, sweets, and processed foods. Opt for natural sources of sugar, such as fruits, instead.
Navigating Food Labels: Identifying ‘Bad’ Carbs
Understanding food labels is crucial when it comes to limiting simple carbohydrates and making healthier choices. Here’s how to decipher food labels and recognize the presence of ‘bad’ carbs:
-
Ingredients: Always check the list of ingredients first. Simple carbohydrates are often listed as sugar, high fructose corn syrup, dextrose, or any word ending in ‘-ose.’ If these ingredients appear near the top of the list, the product is likely high in simple carbs.
-
Sugar Content: Look for the ‘Total Sugars’ section on the Nutrition Facts label. This will indicate the amount of sugar in grams per serving. Aim for products with lower sugar content, ideally under 5 grams per serving. Be aware that ‘Added Sugars’ are a subset of ‘Total Sugars’ and can be highlighted separately on some food labels.
-
Serving Sizes: Pay attention to serving sizes, as they can be misleading. If a product contains multiple servings but you plan to consume the entire package, multiply the sugar content by the number of servings to get a more accurate picture of your carb intake.
-
Fiber Content: Look for products with higher fiber content, as fiber can help slow down the absorption of simple carbohydrates. Aim for at least 3 grams of fiber per serving for optimal health benefits.
The Role of ‘Bad’ Carbs in Chronic Diseases
Simple carbohydrates, or ‘bad’ carbs, have been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. These carbs are quickly absorbed by the body, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and increased insulin production. Over time, this can result in insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, and may contribute to weight gain and obesity.
Obesity
Foods high in simple carbohydrates, such as sweets, sugary drinks, and white bread, often contain high amounts of calories and minimal nutritional value. Consuming these foods regularly can lead to excessive calorie intake, weight gain, and obesity. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health and can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Diabetes
Regular consumption of simple carbohydrates can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Over time, the body may become less sensitive to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This condition, known as insulin resistance, can lead to consistently high blood sugar levels and may result in a diabetes diagnosis. Limiting simple carbohydrates and incorporating complex carbs, fiber, and protein into your diet can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes.
Heart Disease
Simple carbohydrates have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, primarily due to their association with obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels. Consuming a diet high in simple carbs can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and the formation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. By limiting simple carbs and focusing on complex carbs, fiber, and healthy fats, you can help reduce the risk of heart disease and support overall heart health.
Success Stories: Real-Life Transformations Through Carb Restriction
Reducing the intake of simple carbohydrates can lead to significant health improvements, as evidenced by these inspiring success stories:
Sarah’s Journey: From Diabetes to Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Sarah was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at the age of 45. Her doctor recommended a low-carb diet to help manage her blood sugar levels. By eliminating sweets, sugary drinks, and white bread from her diet, Sarah was able to lower her A1C levels and reduce her dependence on medication. Today, she maintains normal blood sugar levels and enjoys improved energy and overall health.
John’s Transformation: Dropping 50 Pounds and Improving Cardiovascular Health
John, a father of two, struggled with obesity for years. After learning about the link between simple carbohydrates and weight gain, he decided to make a change. By reducing his carb intake and focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables, John lost 50 pounds and significantly improved his cardiovascular health. He now serves as a role model for his family and friends, inspiring them to make healthier choices.
Emily’s Victory: Overcoming Sugar Addiction and Boosting Self-Confidence
Emily, a busy marketing professional, found herself consuming sugary snacks and drinks throughout the day to cope with stress. After recognizing the impact of simple carbohydrates on her energy levels and self-confidence, she decided to make a change. By gradually reducing her carb intake and incorporating complex carbs, protein, and healthy fats into her diet, Emily overcame her sugar addiction and experienced a significant boost in self-confidence. She now enjoys cooking nutritious meals and sharing her knowledge with others.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet: Integrating ‘Good’ Carbs and Other Nutrients
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. While reducing simple carbohydrate intake is essential, it’s equally important to incorporate complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Here are some examples of well-rounded meals and snacks to help you make healthier choices:
Meal Ideas
-
Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables, grilled chicken, and a lemon-tahini dressing
-
Brown rice bowl with black beans, roasted sweet potatoes, avocado, and salsa
-
Spaghetti squash with turkey meatballs, marinara sauce, and a side of steamed broccoli
-
Stir-fry with tofu, mixed vegetables, and tamari sauce served over whole grain noodles
Snack Ideas
-
Apple slices with almond butter and chia seeds
-
Carrot and cucumber sticks with hummus and a sprinkle of hemp hearts
-
Edamame with sea salt and a squeeze of lemon
-
Rice cakes topped with avocado, cherry tomatoes, and a sprinkle of nutritional yeast
By combining complex carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats, you can create balanced meals and snacks that provide sustained energy and essential nutrients. Remember, it’s not just about limiting ‘bad’ carbs but also about incorporating ‘good’ carbs and other nutrients to support your overall health and well-being.